This document defines and discusses key concepts in chemistry, including:
- Chemistry is the study of matter and its composition, as well as changes in matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
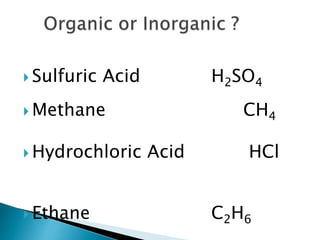
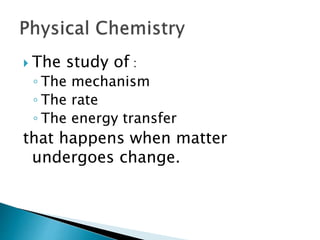
- There are different branches and fields within chemistry, including inorganic, organic, analytical, physical, and biochemistry.
- Important figures who contributed to the development of chemistry include the philosophers Empedocles and Democritus, as well as scientists such as Antoine Lavoisier, John Dalton, Amedeo Avogadro, Dmitri Mendeleev, and others. Their work established concepts like atoms, chemical reactions, conservation of mass, atomic theory, and the periodic table.