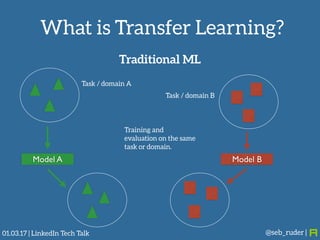
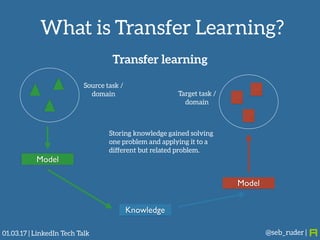
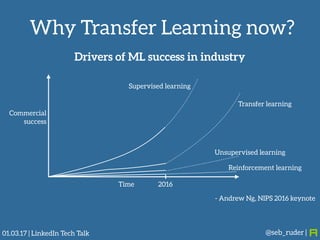
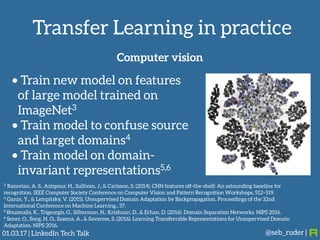
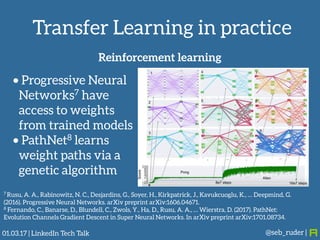
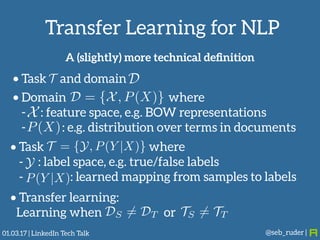
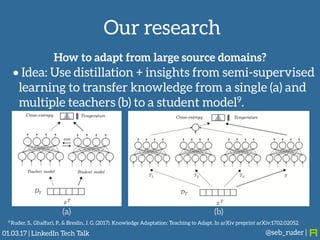
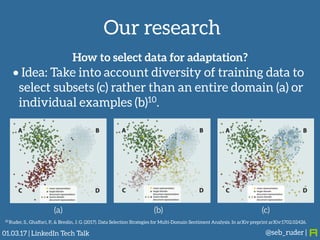
Sebastian Ruder gave a presentation on transfer learning in machine learning. He began by defining transfer learning as applying knowledge gained from solving one problem to a different but related problem. Transfer learning is now important because machine learning models have matured and are being widely deployed, but often lack labeled data for new tasks or domains. Ruder discussed examples of transfer learning in computer vision and natural language processing. He described his research focus on finding better ways to transfer knowledge between domains, tasks, and languages in large-scale, real-world applications.