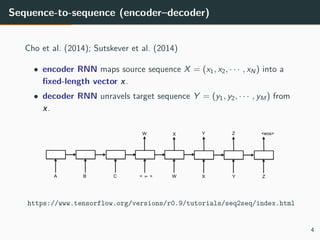
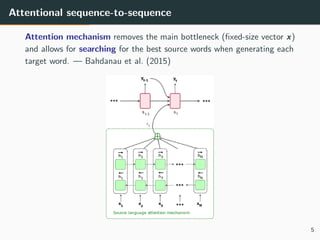
The document discusses multi-modal neural machine translation (NMT), defining machine translation and its related tasks, and providing insights into neural NMT architectures. It explores integration methods for image features within translation tasks and presents potential use cases, including news articles and e-commerce descriptions. The conclusion highlights the broad possibilities of multi-modal NMT and suggests further applications such as video subtitle translation and visual question answering.








![• Computer Vision: how to make machines understand images.
[Krizhevsky,Sutskever,Hinton2012] 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-december-multi-modal-nmt-slides-161214095820/85/Multi-modal-Neural-Machine-Translation-Iacer-Calixto-13-320.jpg)


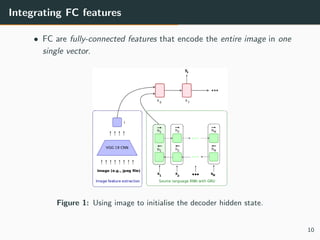
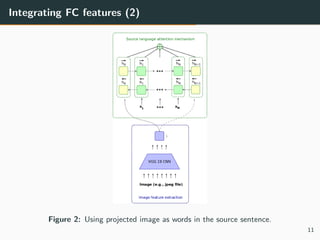
![Integrating FC features (3)
Figure 3: Attention-based Multimodal NMT [Huang et al. (2016)]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-december-multi-modal-nmt-slides-161214095820/85/Multi-modal-Neural-Machine-Translation-Iacer-Calixto-23-320.jpg)
![Integrating FC features (4)
Figure 4: Attention-based Multimodal NMT [Huang et al. (2016)]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-december-multi-modal-nmt-slides-161214095820/85/Multi-modal-Neural-Machine-Translation-Iacer-Calixto-24-320.jpg)
![Integrating CONV features
• CONV are convolutional features that encode different areas (i.e.,
patches) of the image separately.
Figure 5: Doubly-attentive decoder with two independent attention
mechanisms. [Calixto et al. (2016)]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-december-multi-modal-nmt-slides-161214095820/85/Multi-modal-Neural-Machine-Translation-Iacer-Calixto-25-320.jpg)
![Some numbers, why not?
Figure 6: BLEU and METEOR scores. [Huang et al. (2016)]
Model BLEU METEOR
Doubly-attentive decoder 36.2 53.1
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-december-multi-modal-nmt-slides-161214095820/85/Multi-modal-Neural-Machine-Translation-Iacer-Calixto-26-320.jpg)