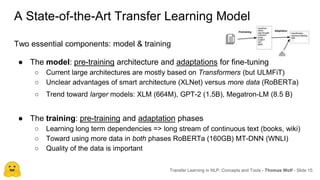
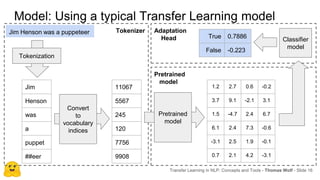
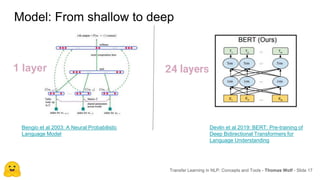
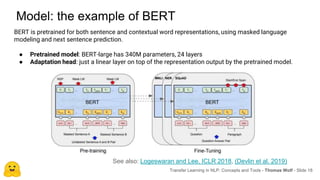
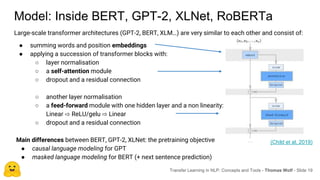
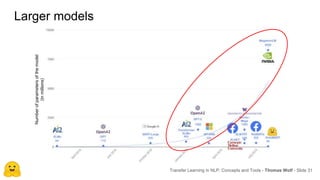
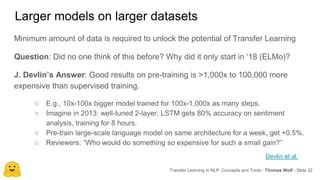
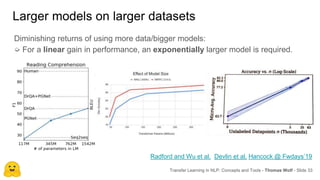
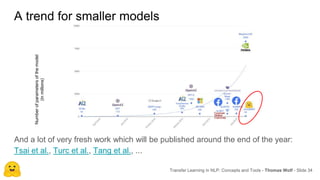
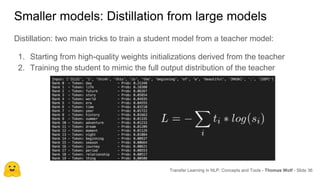
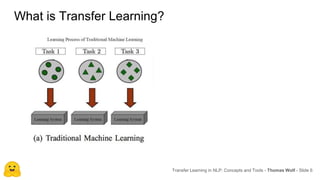
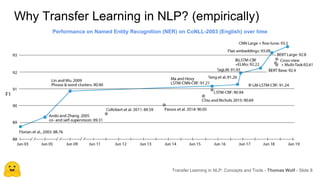
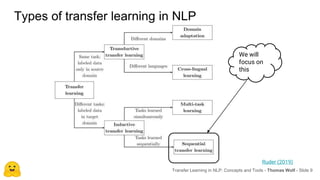
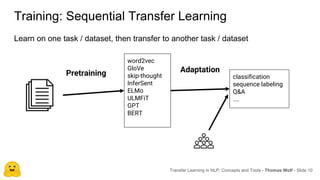
Transfer learning in NLP involves pre-training large language models on unlabeled text and then fine-tuning them on downstream tasks. Current state-of-the-art models such as BERT, GPT-2, and XLNet use bidirectional transformers pretrained using techniques like masked language modeling. These models have billions of parameters and require huge amounts of compute but have achieved SOTA results on many NLP tasks. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce model sizes through techniques like distillation while maintaining high performance. Open questions remain around model interpretability and generalization.




![[-0.4, 0.9, …]
History
Word vectors
cats = [0.2, -0.3, …]
dogs = [0.4, -0.5, …]
Sentence/doc vectors
It’s raining
cats and dogs.
We have two
cats.
[0.8, 0.9, …]
[-1.2, 0.0, …]
}
}
Word-in-context
vectors
We have two cats.
}
[1.2, -0.3, …]
It’s raining cats and dogs.
}
Transfer Learning in NLP: Concepts and Tools - Thomas Wolf - Slide 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transferlearninginnlp-190909115130/85/Thomas-Wolf-Transfer-learning-in-NLP-9-320.jpg)