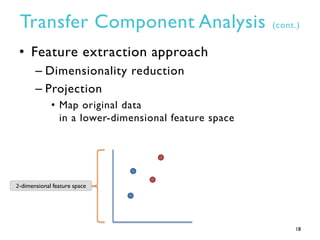
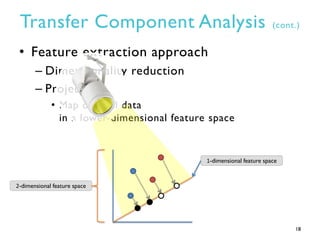
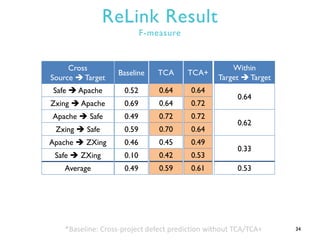
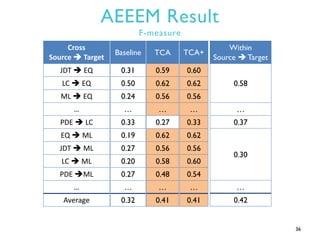
This document summarizes research on transfer defect learning to improve cross-project defect prediction. It presents Transfer Component Analysis (TCA) as a state-of-the-art transfer learning technique that maps data from source and target projects into a shared feature space to make their distributions more similar. It then proposes TCA+ which augments TCA with data normalization and decision rules to select the optimal normalization method based on characteristics of the source and target datasets. Experimental results on two cross-project defect prediction datasets show that TCA+ significantly outperforms traditional cross-project prediction and basic TCA.













![Data Normalization
• Adjust all feature values in the same scale
– E.g., Make Mean = 0 and Std = 1
• Known to be helpful for classification
algorithms to improve prediction
performance [Han et al. 2012].
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transferdefectlearningnewcompleted-130526123501-phpapp01/85/Transfer-defect-learning-14-320.jpg)
![Normalization Options
• N1: Min-max Normalization (max=1, min=0)
[Han et al., 2012]
• N2: Z-score Normalization (mean=0, std=1)
[Han et al., 2012]
• N3: Z-score Normalization only using source
mean and standard deviation
• N4: Z-score Normalization only using target
mean and standard deviation
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transferdefectlearningnewcompleted-130526123501-phpapp01/85/Transfer-defect-learning-15-320.jpg)