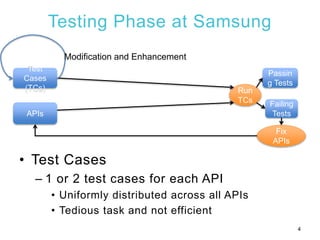
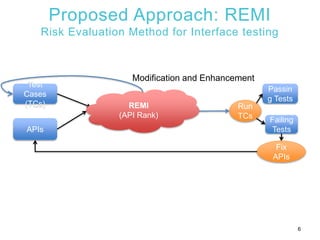
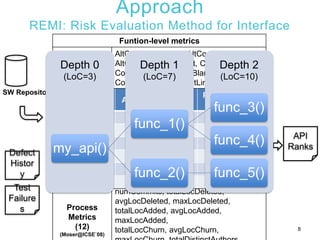
1) The document presents REMI, a method for applying software defect prediction to efficiently test APIs. REMI ranks APIs based on metrics to identify risky APIs and guide test case development and execution.
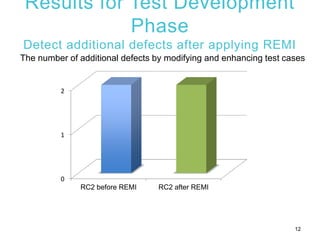
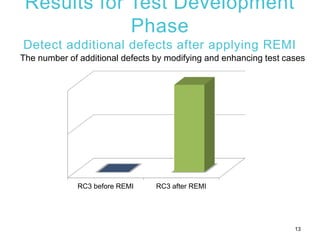
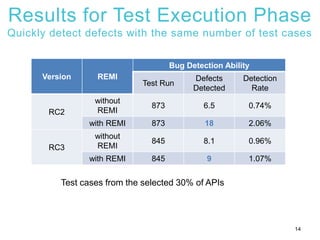
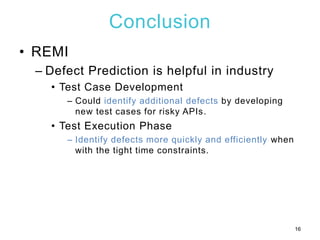
2) An experiment applying REMI to Tizen wearable APIs found that focusing test cases on risky APIs identified additional defects compared to uniform testing. REMI also found defects more quickly during test execution.
3) Developers providing feedback found the risky API rankings helpful for efficiently allocating limited testing resources, though REMI required some overhead to configure and execute. Labeling APIs as buggy/clean for the prediction model was also difficult without noise.