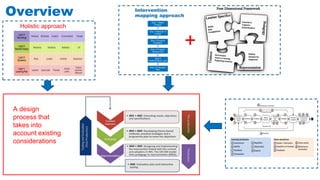
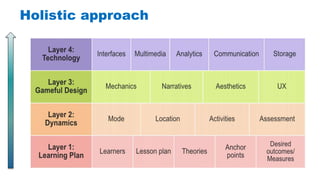
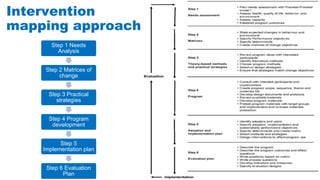
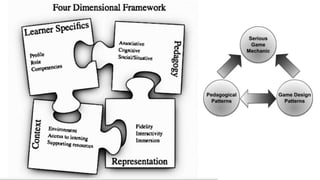
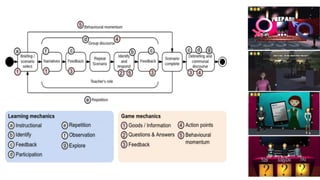
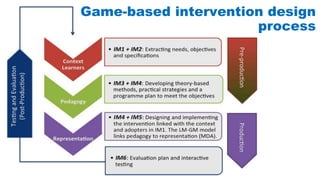
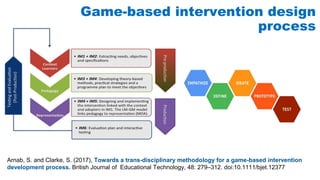
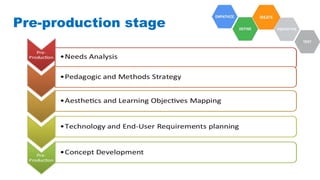
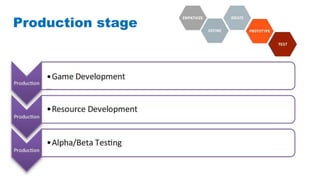
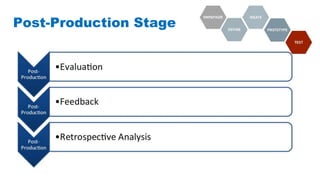
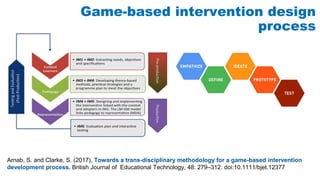
The document discusses the development of game-based learning interventions for children, emphasizing that there is no fixed formula or standard methodology for success. It outlines a holistic approach involving needs analysis, program development, and evaluation, focusing on objectives such as engagement and learning gains. Additionally, it highlights the importance of various strategies and educational goals in designing effective game-based interventions.