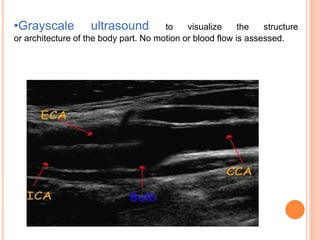
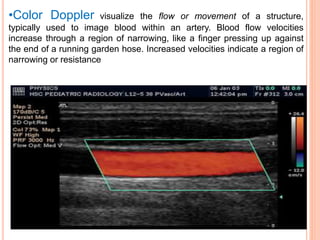
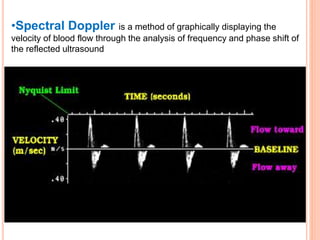
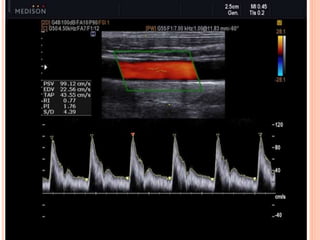
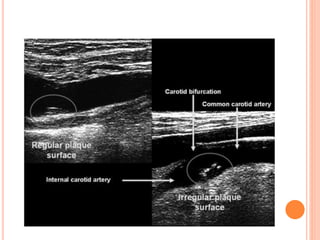
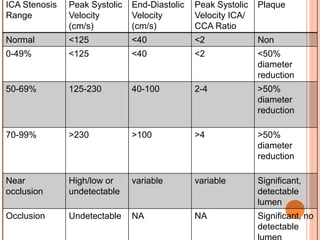
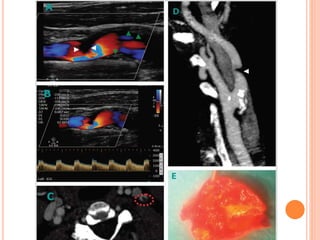
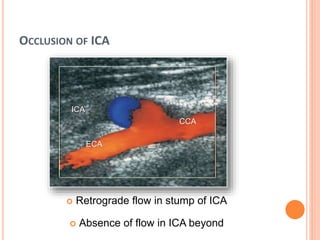
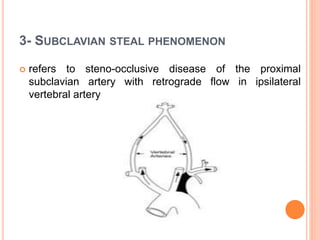
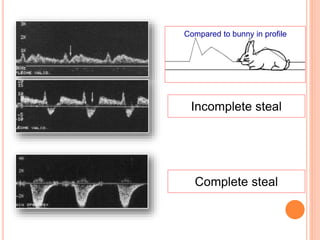
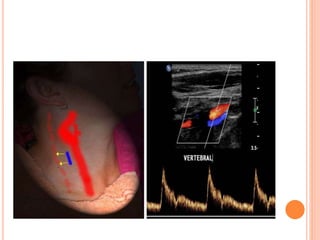
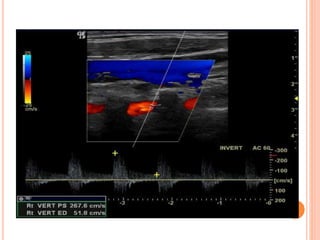
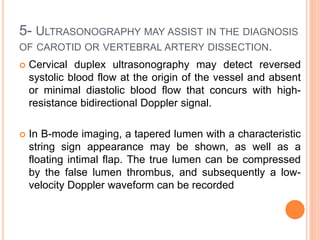
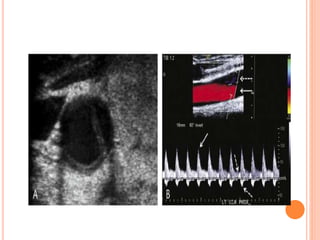
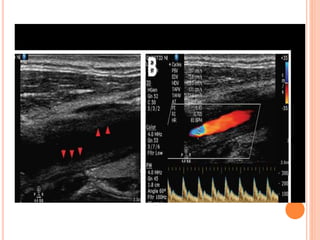
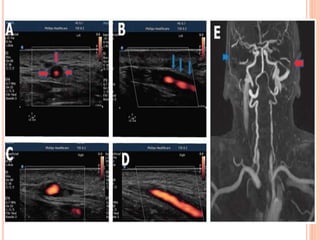
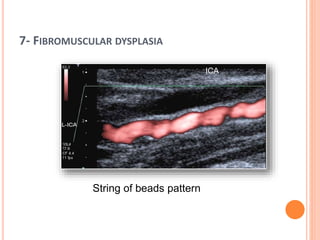
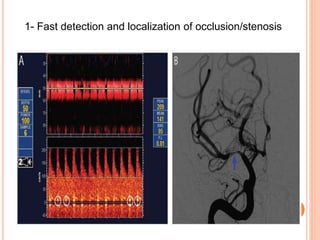
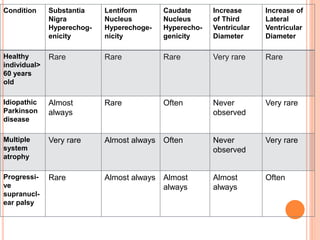
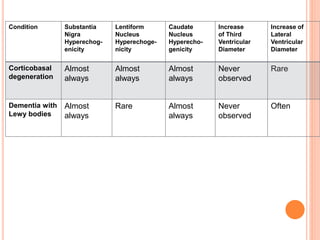
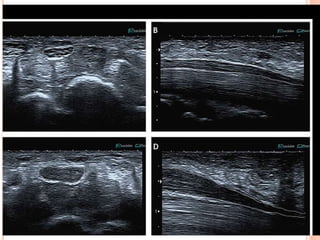
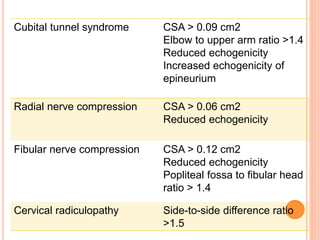
Ultrasonography provides several advantages in clinical neurology. It can be used to assess neurovascular structures like arteries and veins, detect abnormalities associated with movement disorders like increased substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in Parkinson's disease, and evaluate peripheral nerves for entrapment neuropathies. Ultrasonography techniques like duplex ultrasonography and transcranial Doppler allow visualization of vessel structures, plaque composition, and blood flow velocities to diagnose vascular diseases, monitor treatment, and detect vasospasm. Transcranial Doppler is also used to evaluate movement disorders, cerebral circulation in stroke and brain injury, and support a diagnosis of brain death. Peripheral nerve ultrasonography examines cross-sectional area, echogenicity,