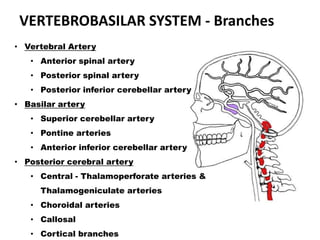
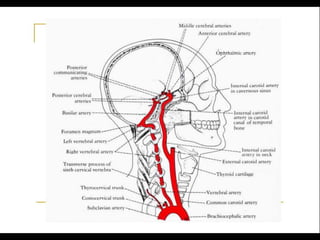
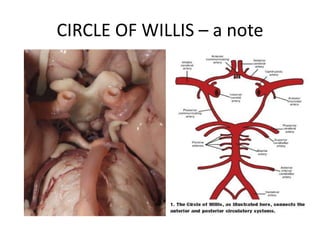
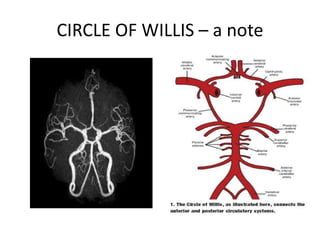
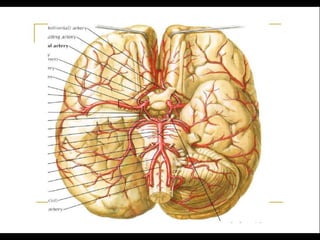
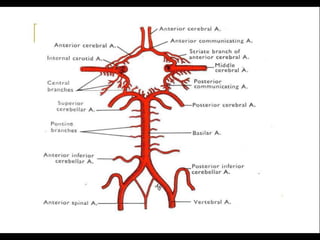
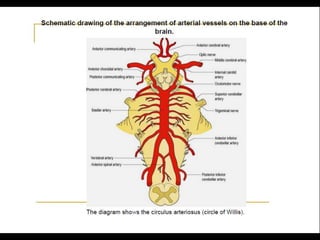
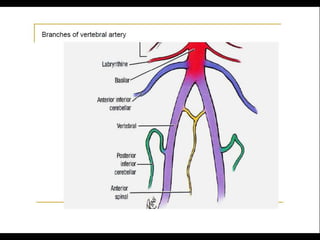
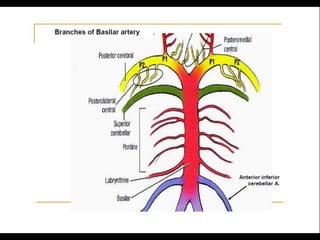
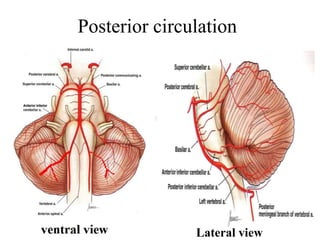
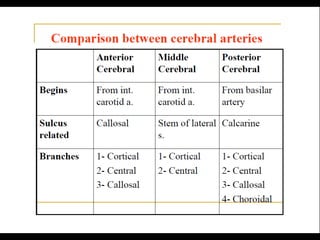
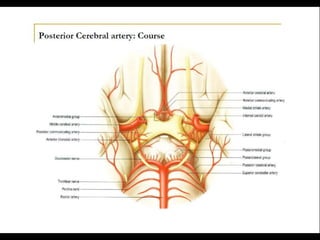
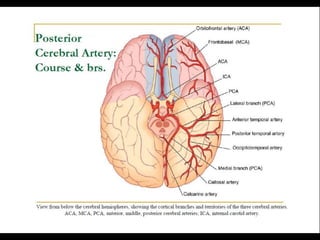
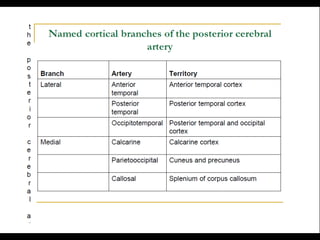
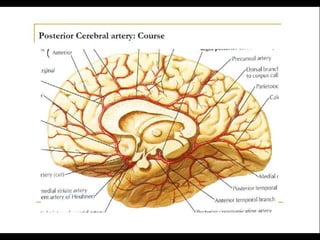
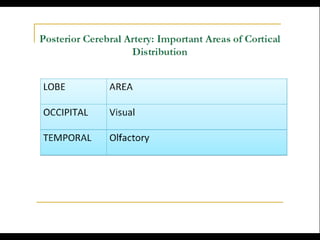
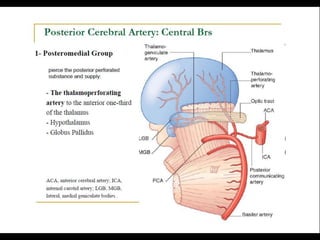
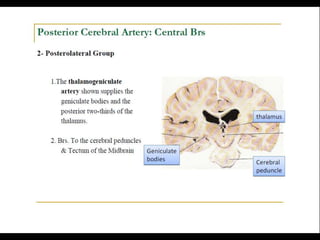
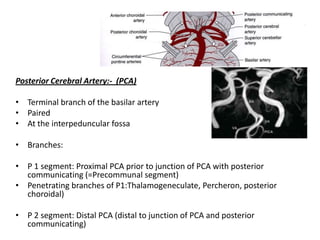
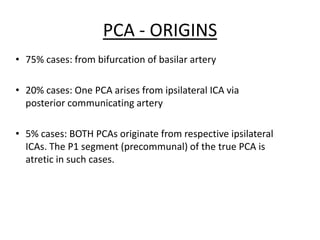
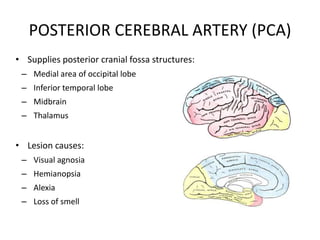
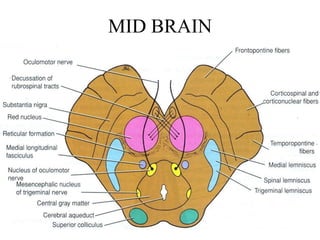
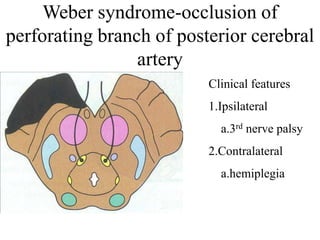
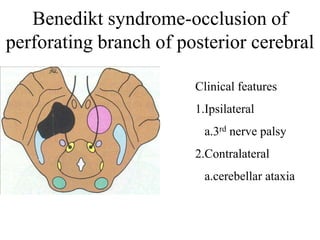
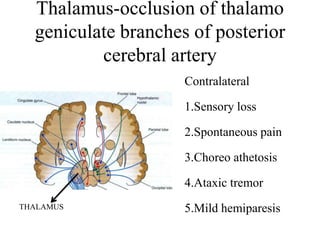
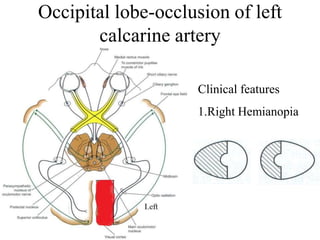
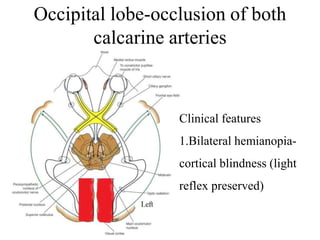
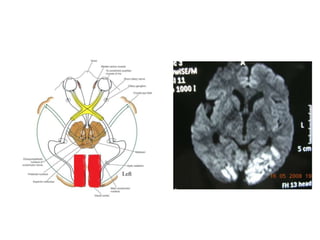
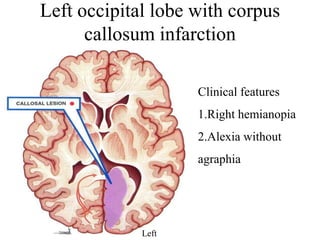
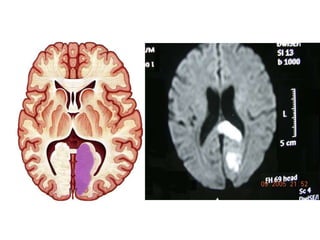
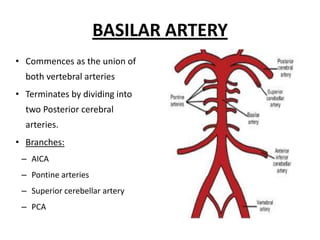
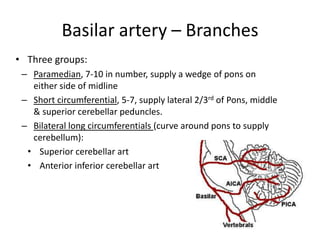
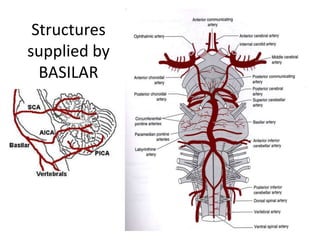
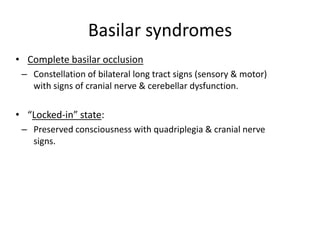
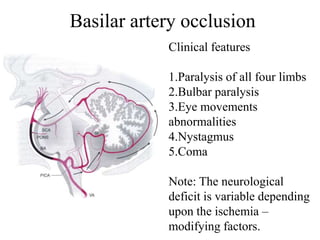
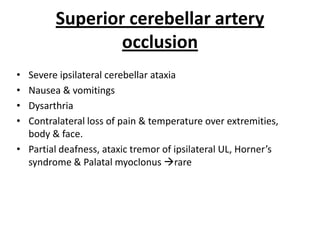
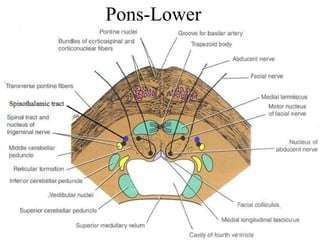
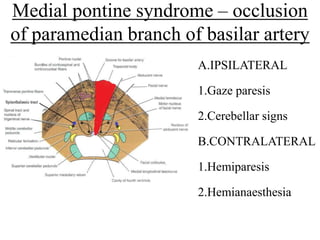
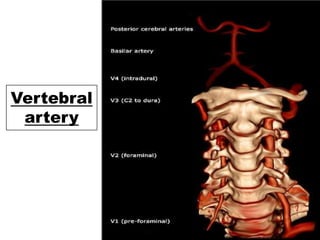
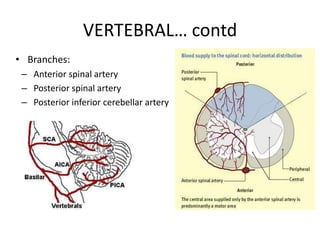
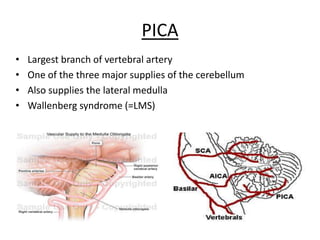
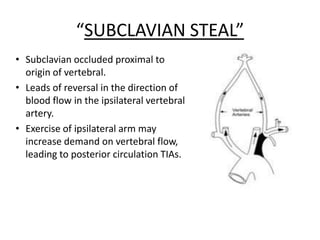
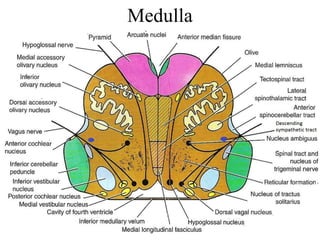
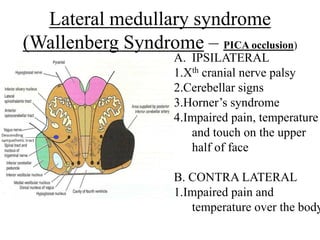
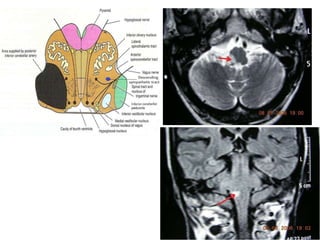
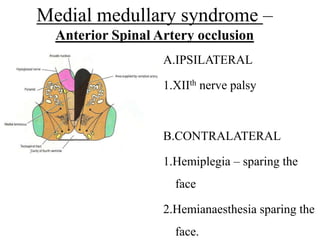
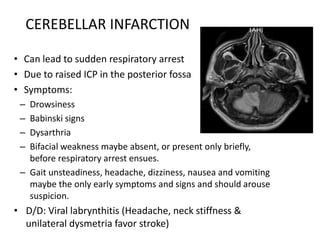
Posterior circulation strokes can be differentiated from anterior circulation strokes based on clinical features. Posterior circulation strokes often present with vertigo, unsteadiness, crossed hemiplegia, bilateral deficits, cerebellar signs, ocular findings, dissociated sensory loss, and Horner's syndrome. The vertebrobasilar system supplies structures such as the cerebellum, medulla, pons, midbrain, thalamus, and occipital and temporal lobes. Common syndromes include lateral medullary syndrome and superior cerebellar artery occlusion. Infarctions in different vascular territories can produce characteristic clinical deficits.