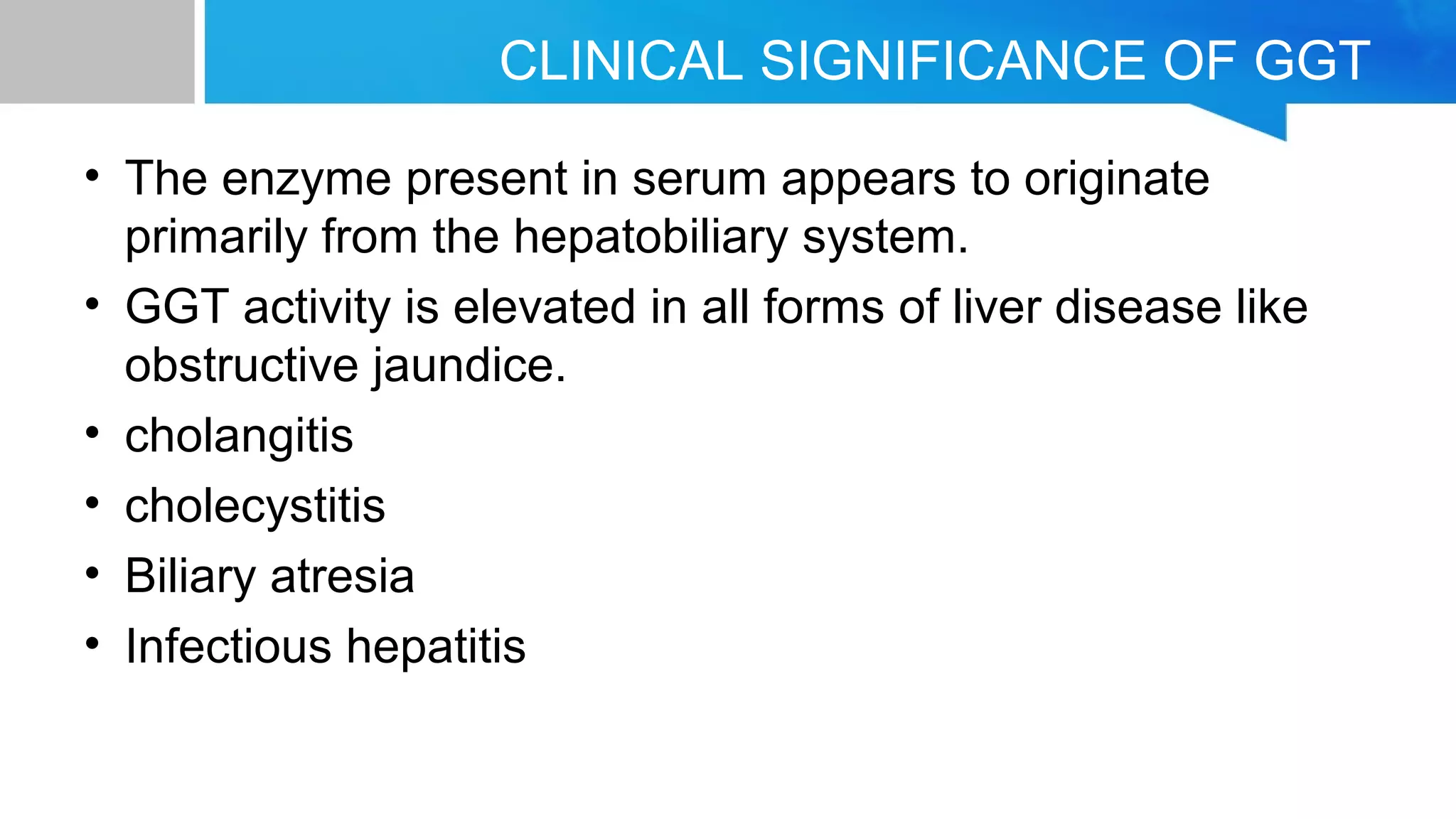
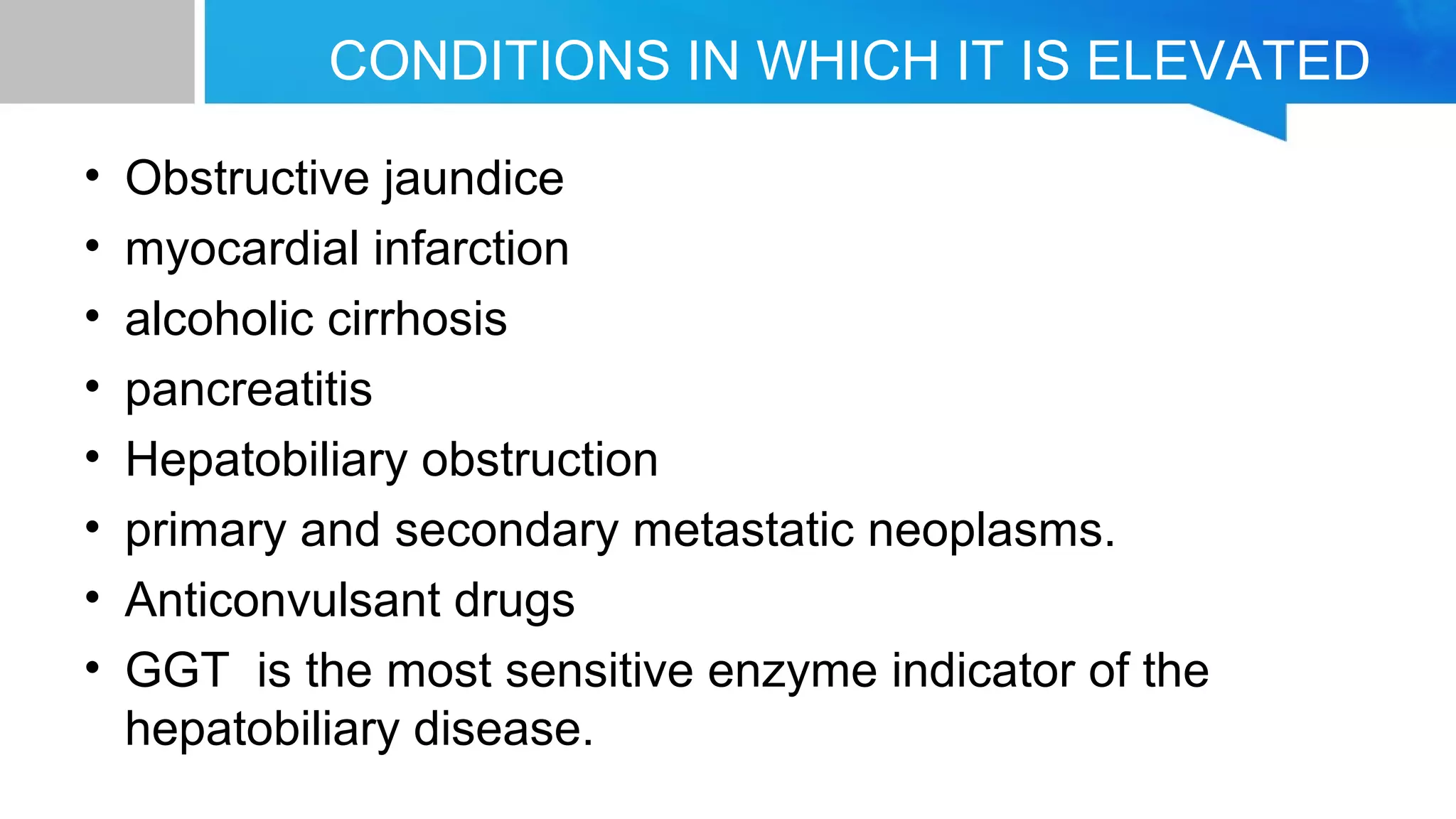
Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) is an enzyme related to glutathione metabolism and is primarily found in the hepatobiliary system, with the highest activity in organs such as the kidneys and pancreas. Normal GGT levels differ by gender, ranging from 10-50 U/L for males and 7-35 U/L for females, and its elevation indicates liver disease and other medical conditions. GGT is considered the most sensitive enzyme indicator for hepatobiliary diseases, including obstructive jaundice and alcoholic cirrhosis.