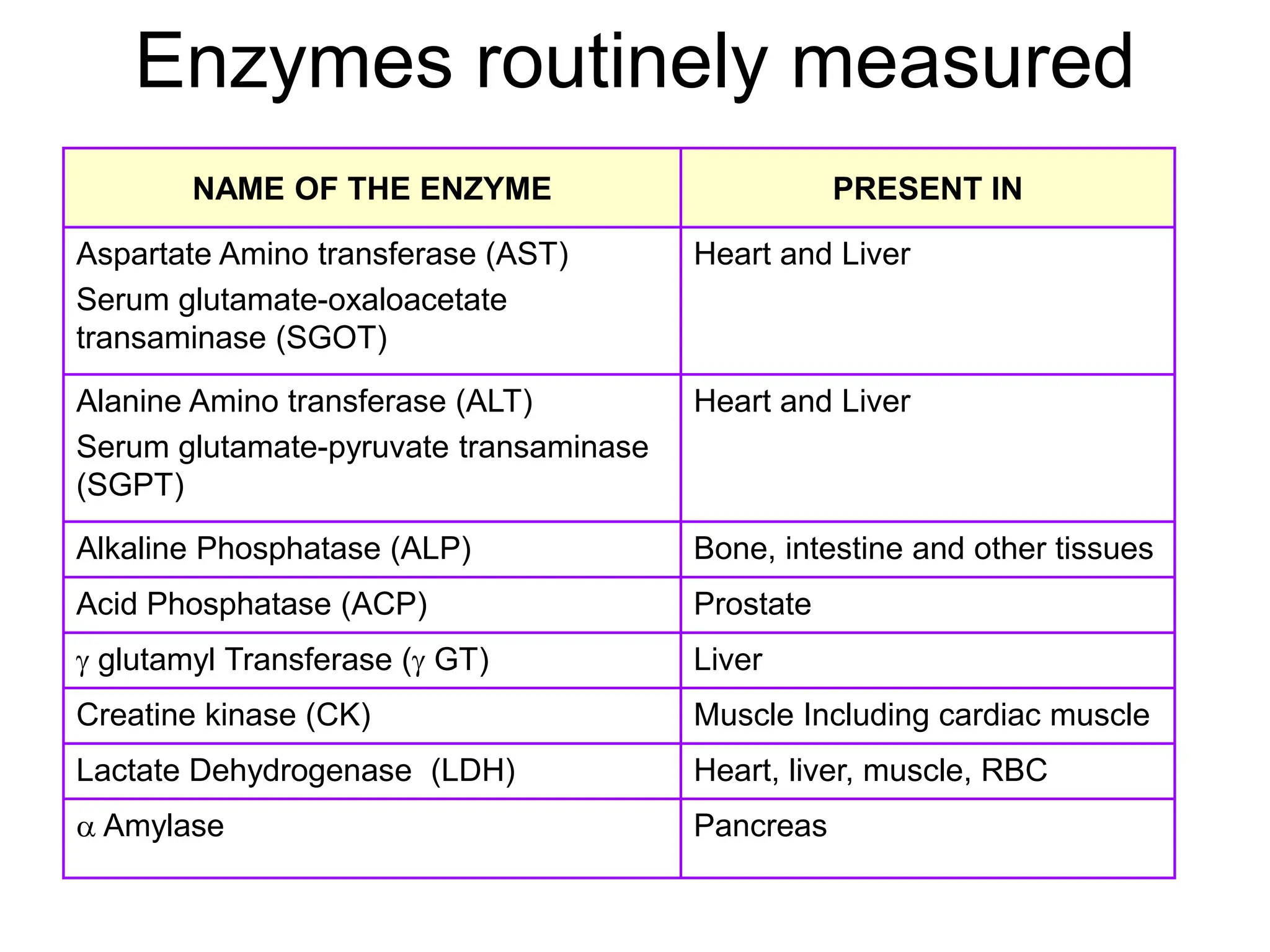
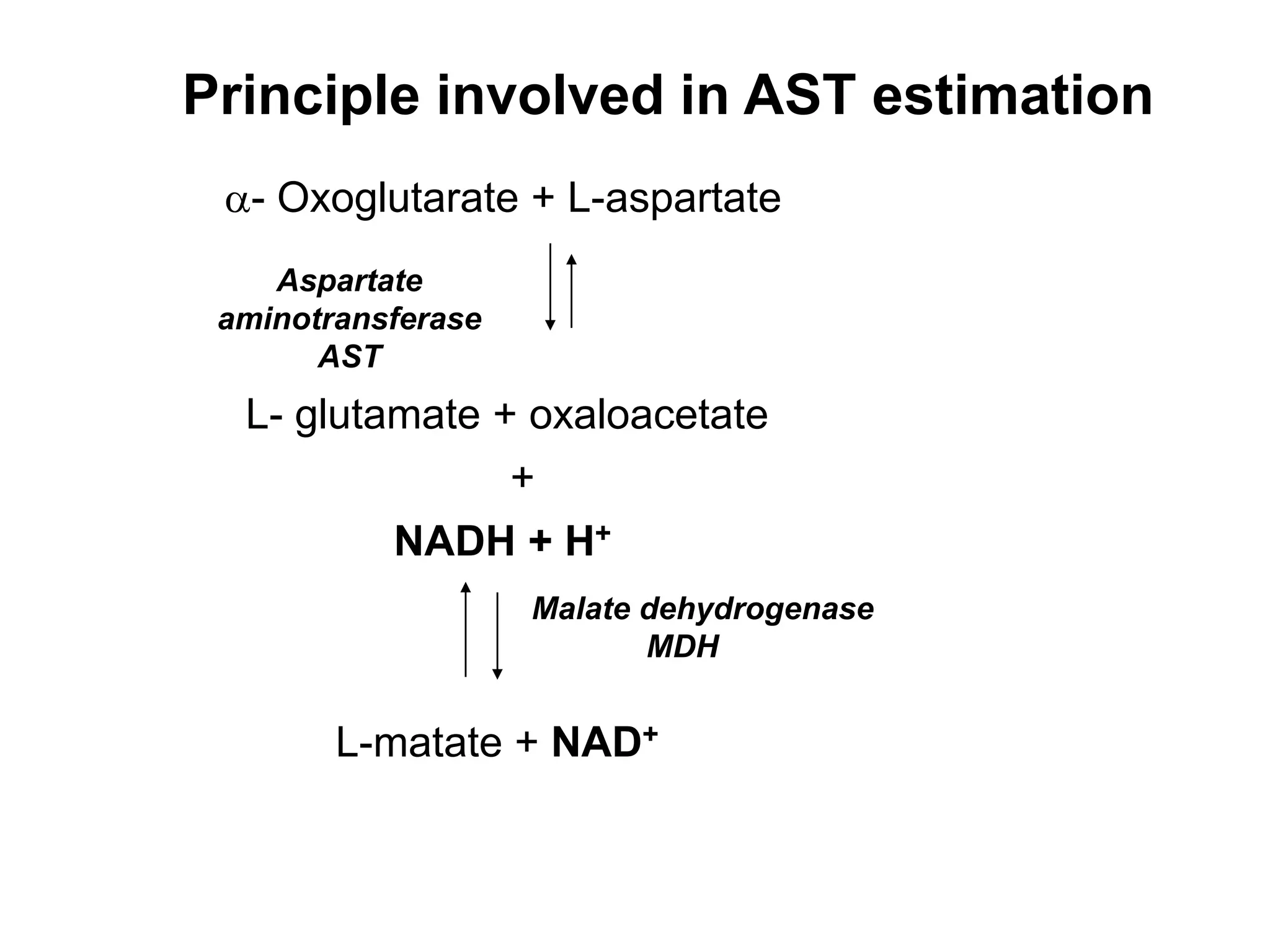
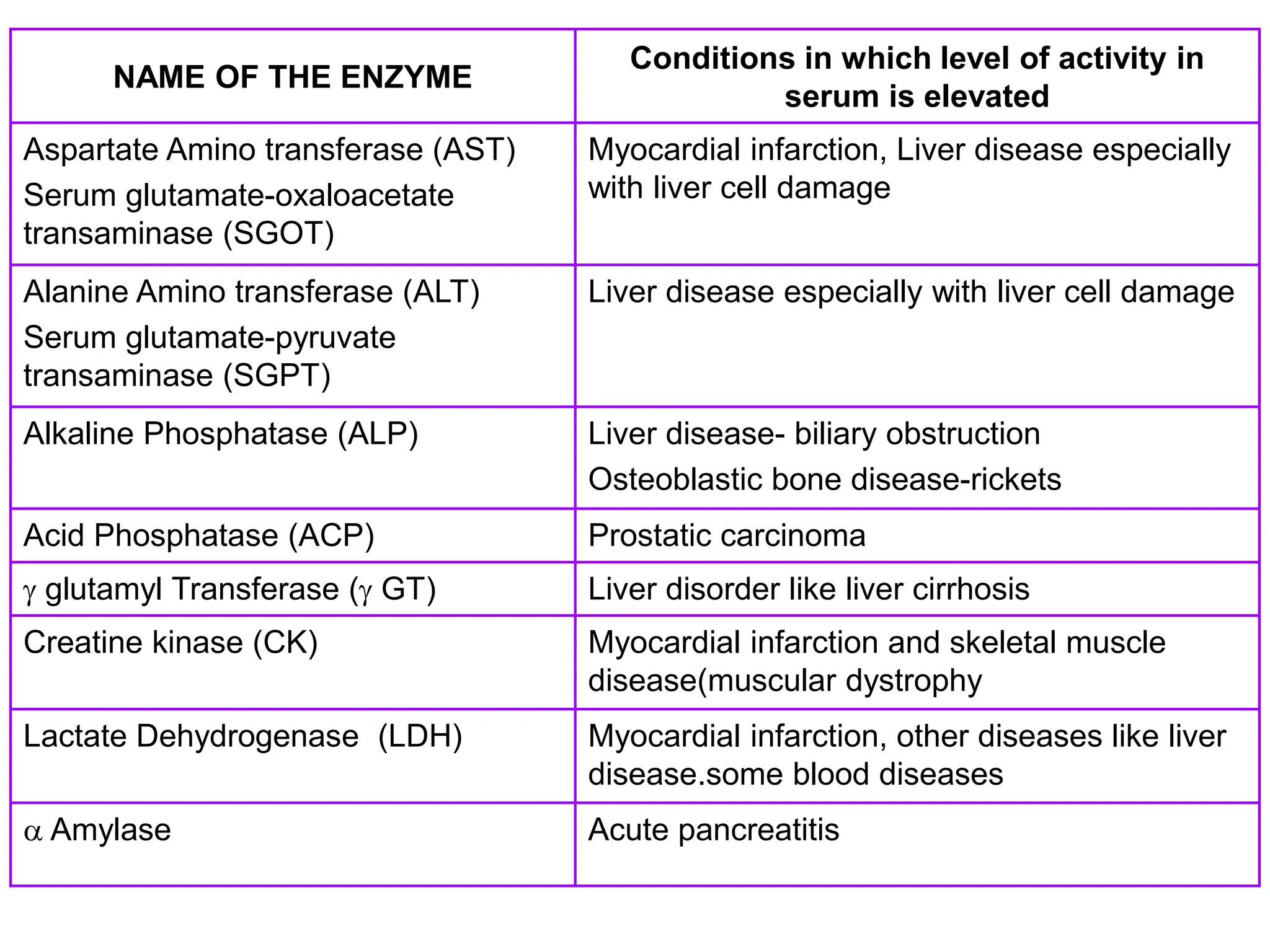
- Enzymes act as biological catalysts and are important for clinical diagnosis when their levels are abnormal. Important enzymes include AST, ALT, CK, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, and GGT.
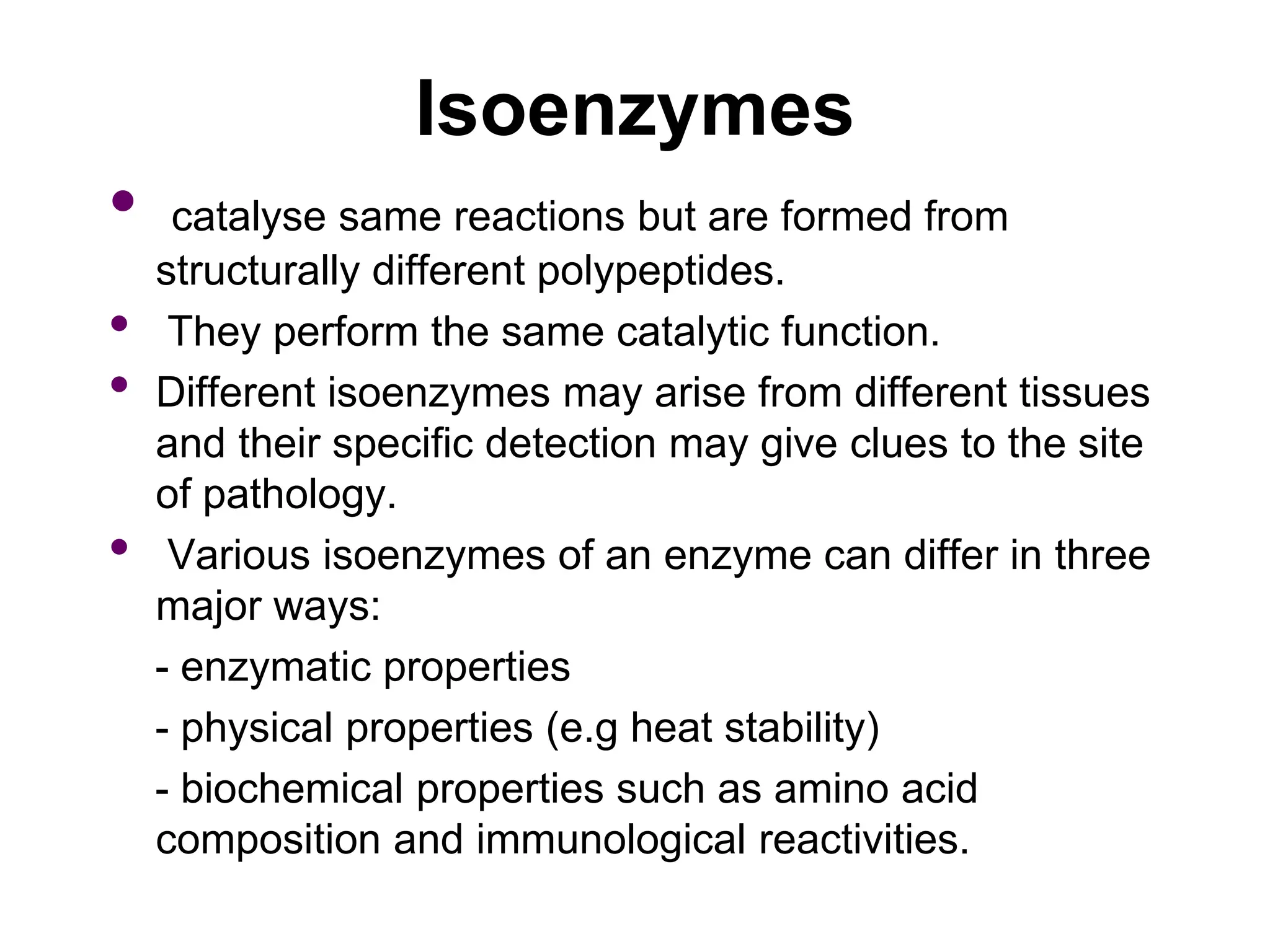
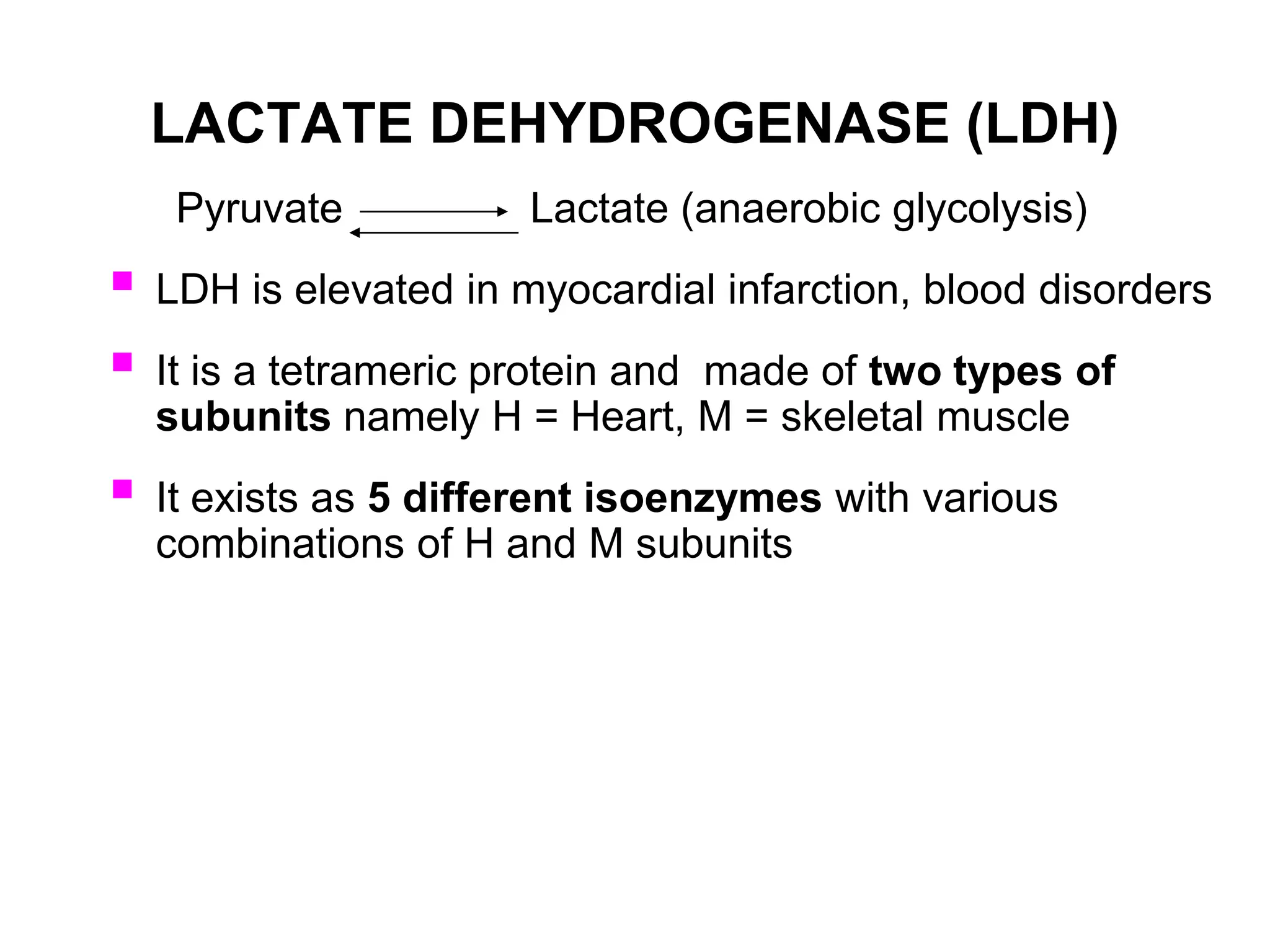
- Isoenzymes are genetic variants of enzymes produced in specific tissues, and their patterns can provide information about organ-specific diseases. For example, the three CK isoenzymes indicate heart, brain, or muscle involvement.
- Elevated levels of cardiac enzymes like CK-MB and LDH indicate heart damage as seen in myocardial infarction, while elevated AST, ALT, and GGT suggest liver disease or damage. Alkaline phosphatase is useful for investigating liver and bone diseases