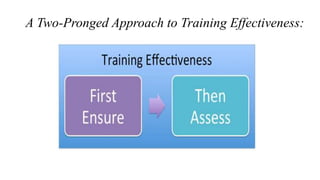
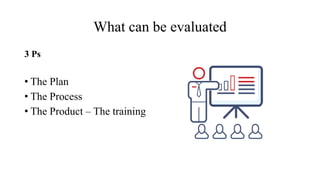
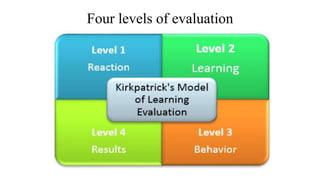
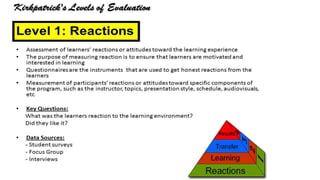
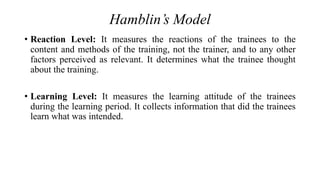
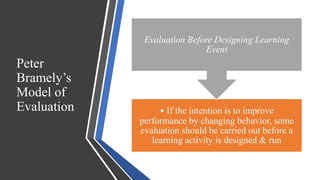
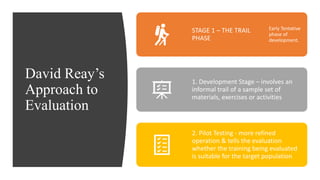
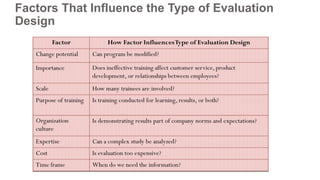
Training effectiveness examines the degree to which training improves employee knowledge, skills, and behaviors. It assesses whether employees learned what was taught and can apply it on the job. Organizations use a two-pronged approach: 1) ensuring training effectiveness through best practices in design, development and delivery; and 2) periodically assessing training effectiveness through reviews and continuous improvement. Evaluation models like Kirkpatrick's assess training at multiple levels from reaction to results to determine the impact on individual and organizational outcomes.