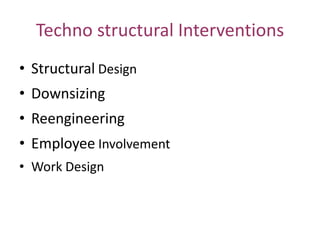
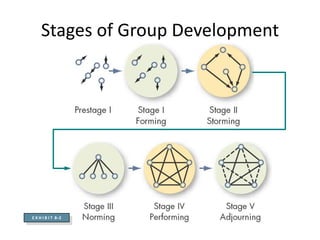
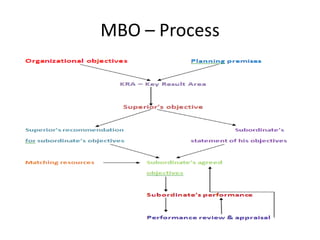
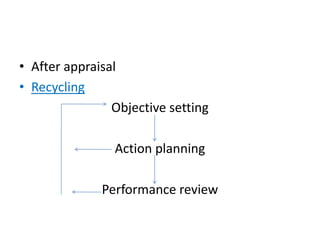
The document discusses various types of organizational development interventions including sensitivity training, team building, management by objectives, coaching, and training. It describes the characteristics of effective interventions and outlines factors to consider in the design of interventions. Examples are provided of different human process, techno-structural, human resources, and strategic interventions that can be used to help organizations increase their effectiveness.