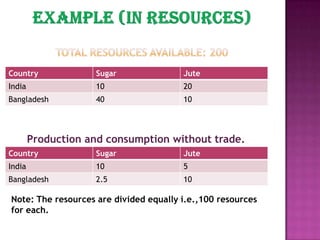
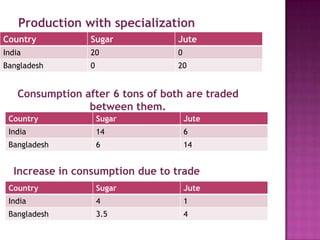
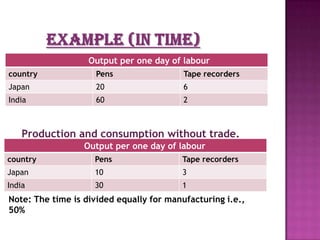
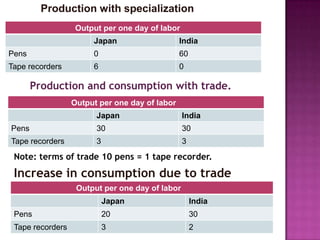
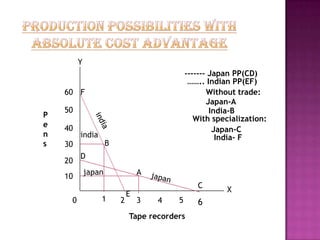
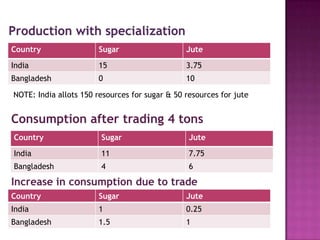
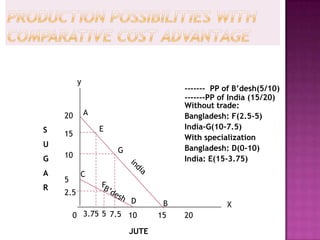
The document discusses several theories of international trade. It begins by explaining mercantilism, which held that countries should maintain a trade surplus. It then explains Adam Smith's theory of absolute advantage, which argues that countries should specialize in what they can produce most efficiently. David Ricardo further developed this with his theory of comparative advantage, which showed that even if one country is more efficient in all products, both can still benefit from trade by focusing on their comparative advantages. The theories aim to achieve efficient allocation of global resources and maximize production at lowest cost through international specialization and trade.