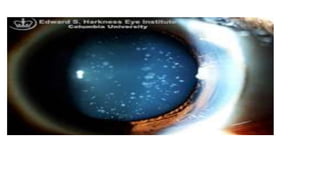
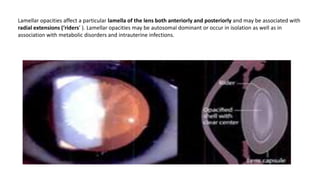
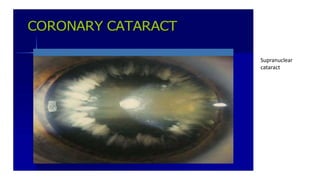
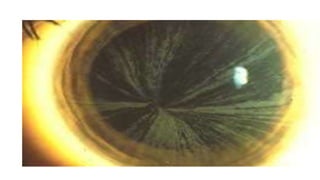
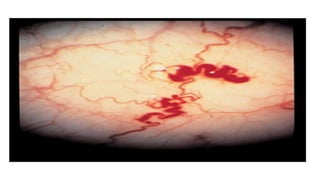
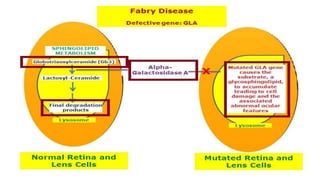
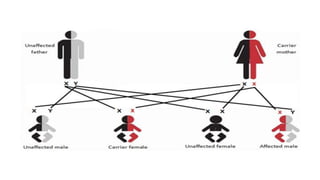
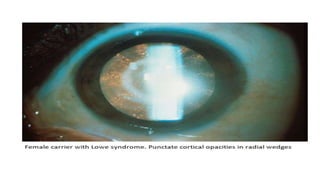
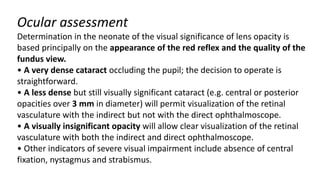
Congenital cataracts are present at birth or develop in the first year, with various etiologies including infections, metabolic disorders, trauma, and genetic conditions. The document details different types of cataracts, their associations with systemic diseases, and the management of infants with cataracts, emphasizing the importance of visual assessment and early intervention. A thorough clinical evaluation is essential, as dense cataracts can lead to irreversible visual impairment, and careful history-taking and examination can prevent misdiagnosis and poor outcomes.