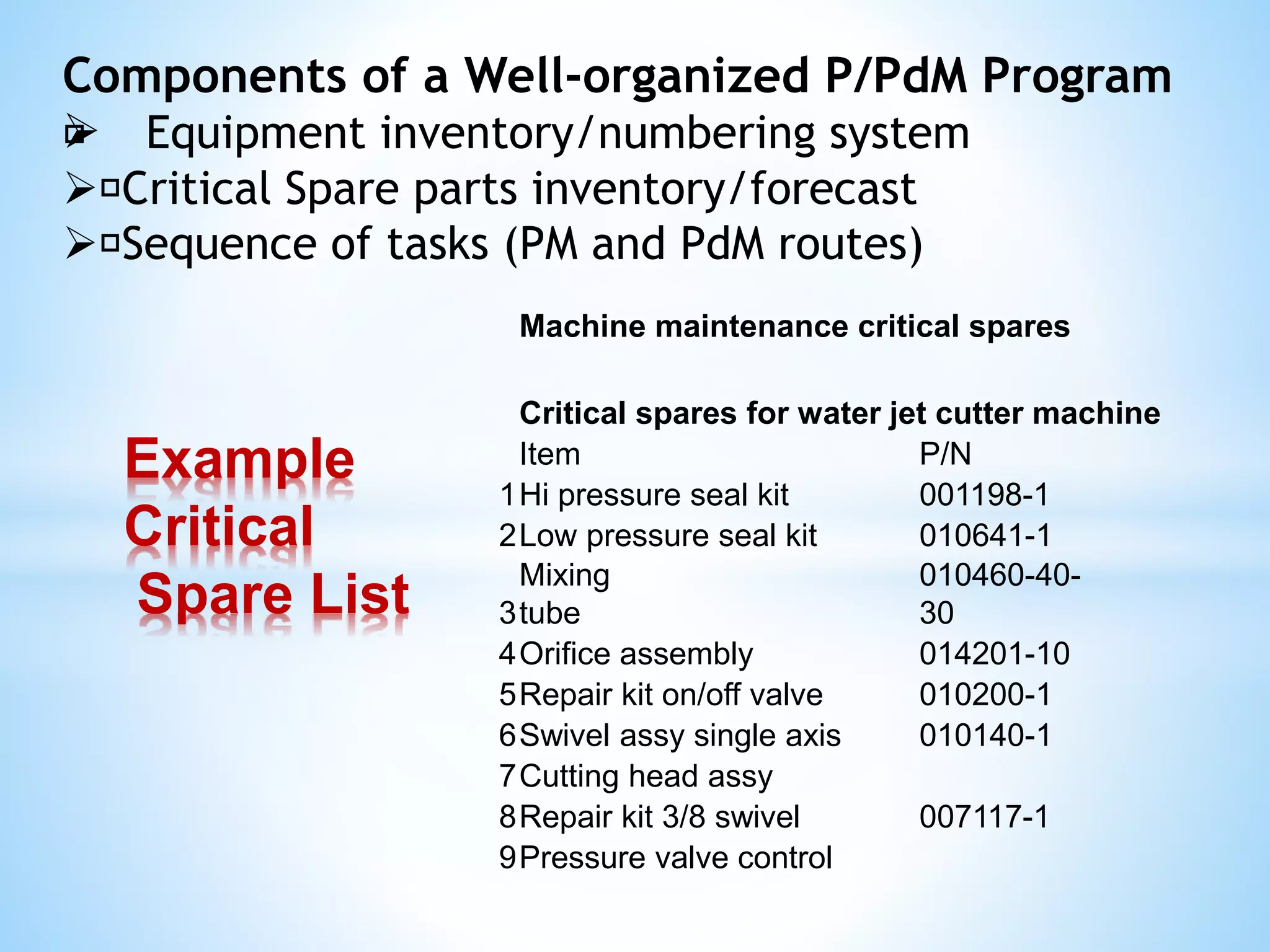
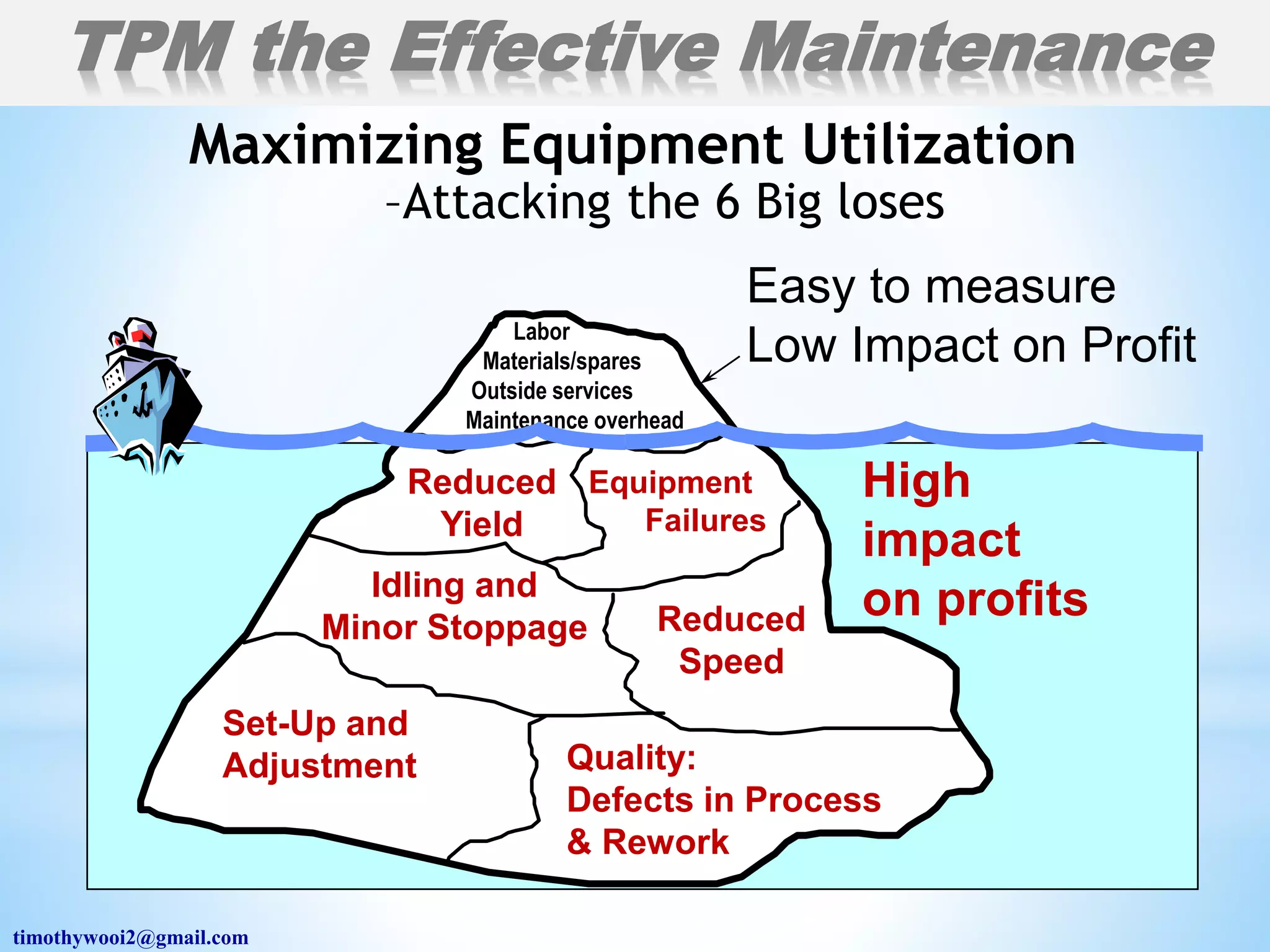
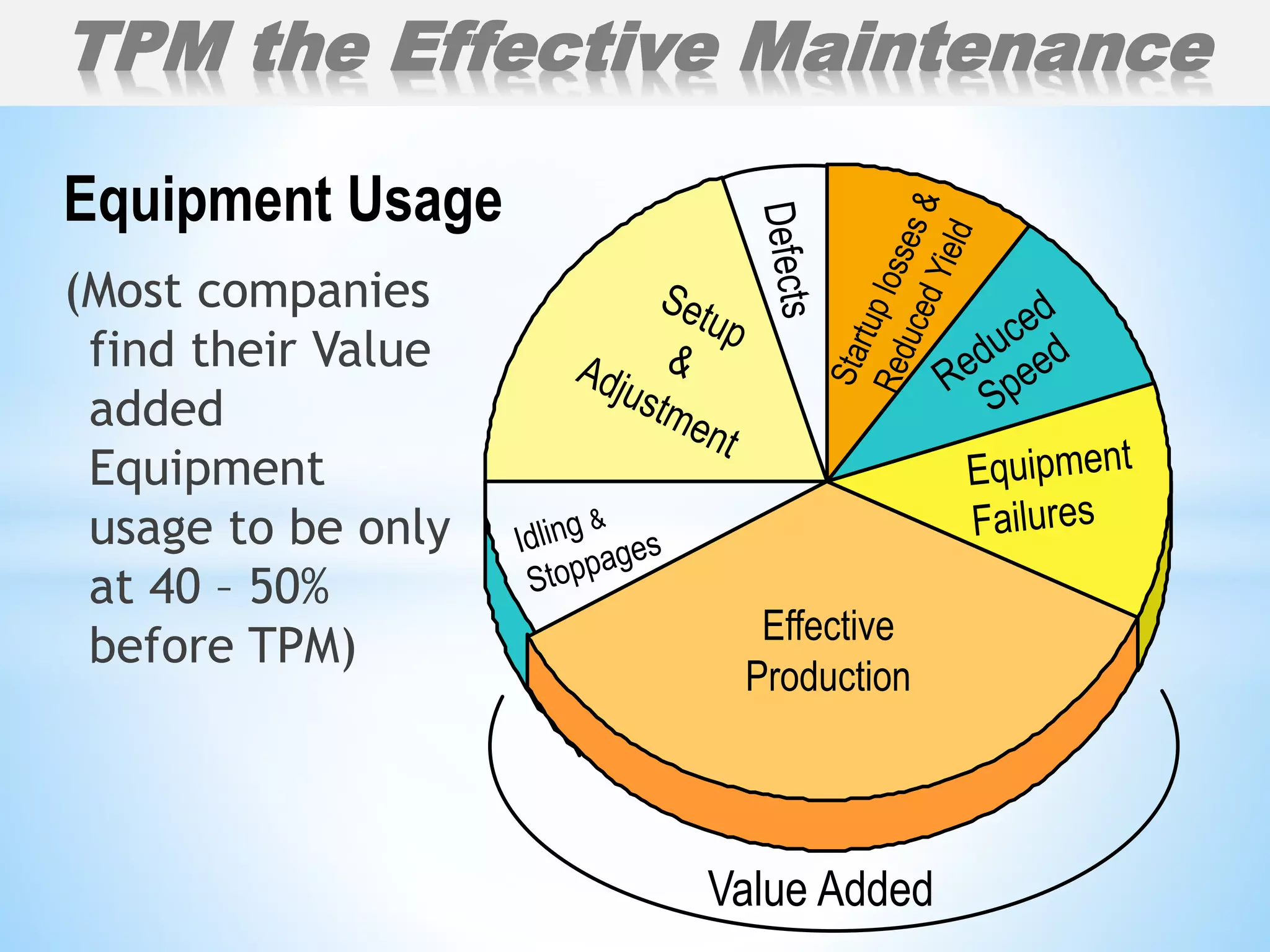
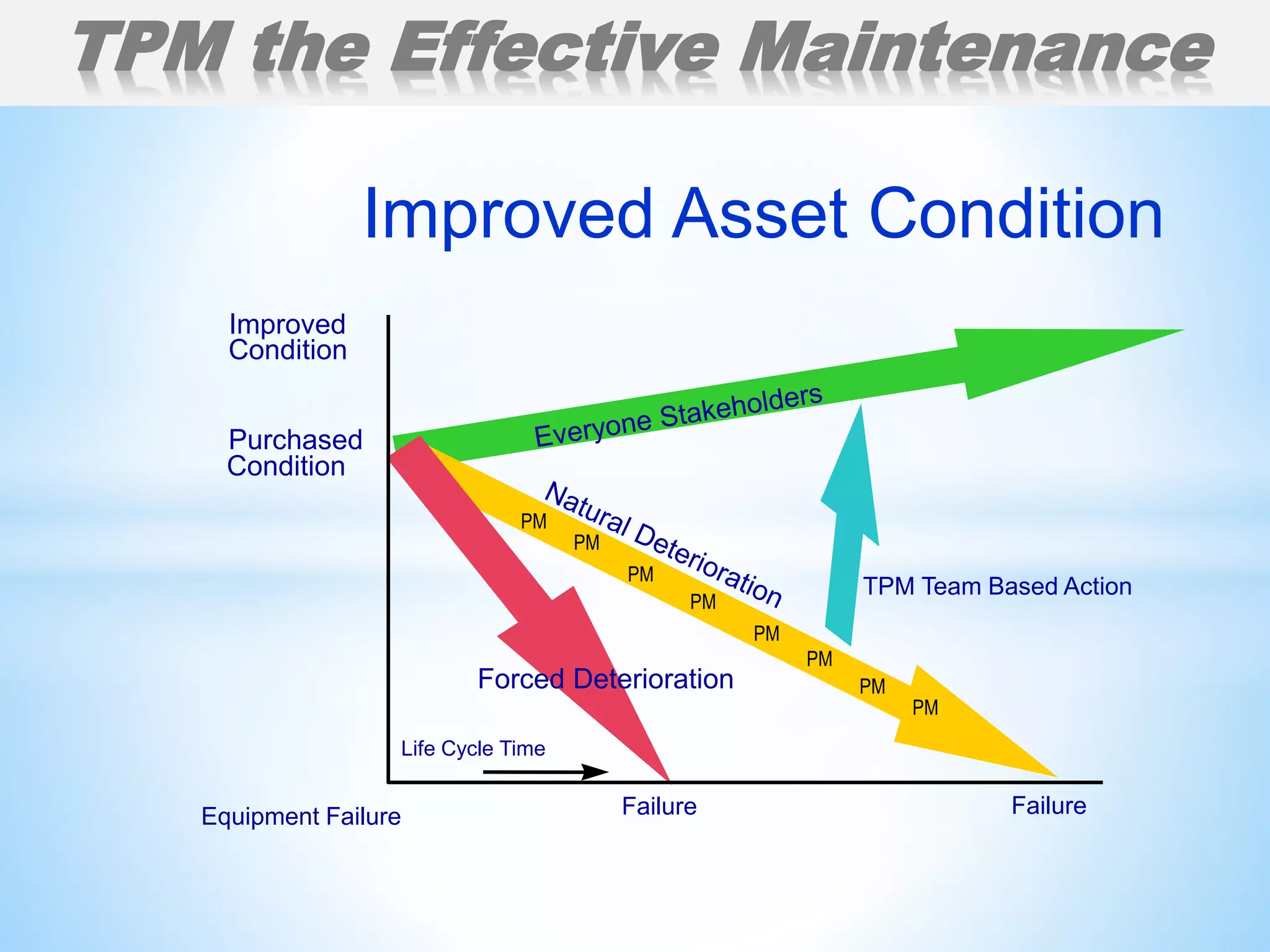
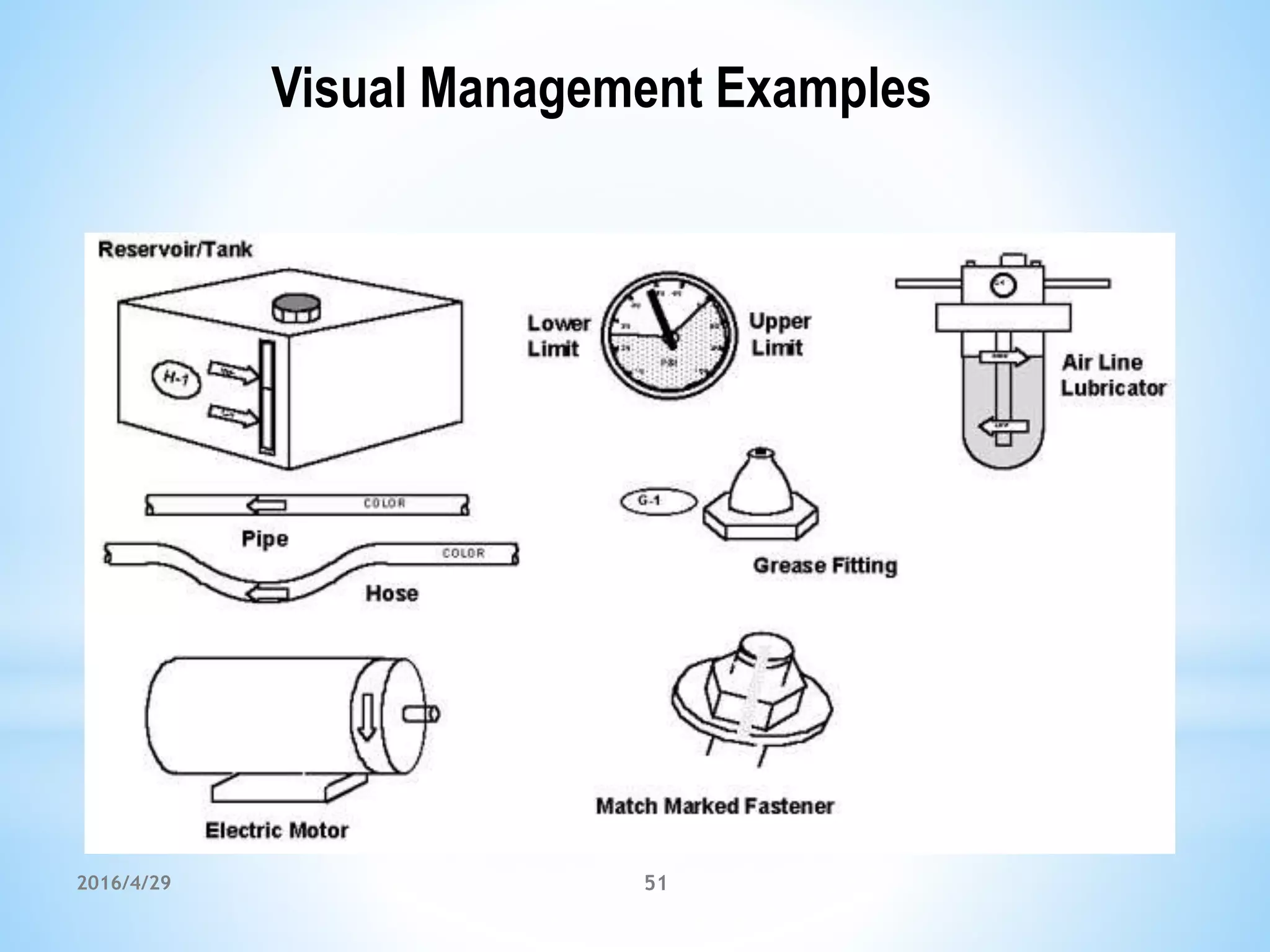
The document outlines a training workshop on Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) for Kotak Malaysia, focusing on minimizing equipment downtime and enhancing maintenance strategies through a structured 12-step approach. Key topics include proactive maintenance, equipment management, and effective training to transition from reactive to preventive modes of maintenance, ultimately aiming for zero breakdowns and zero defects. Emphasis is placed on management support, continuous improvement, and team collaboration to achieve overall operational effectiveness and efficiency.