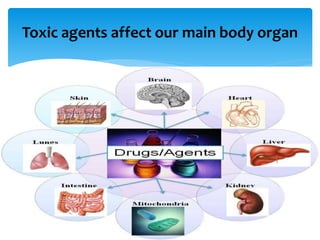
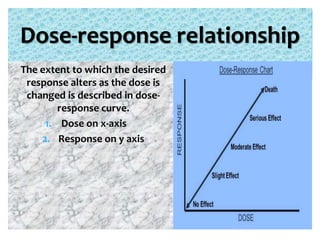
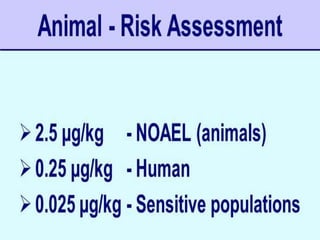
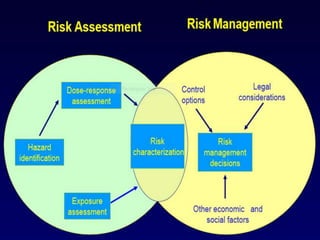
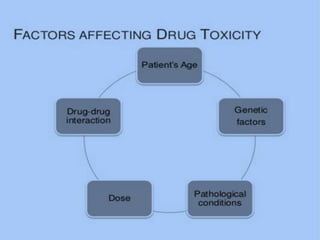
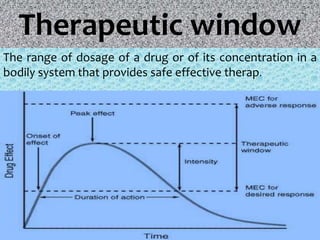
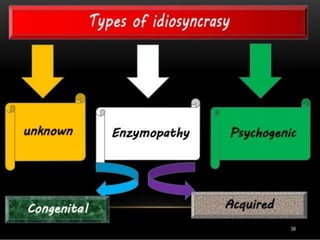
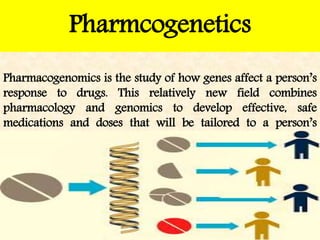
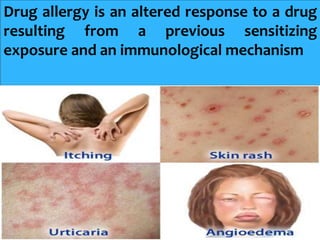
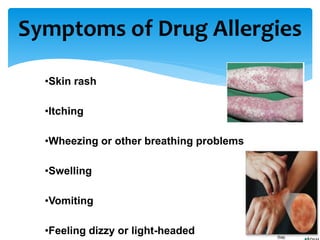
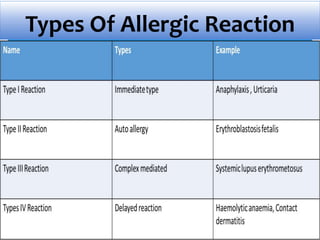
The presentation on toxicology discusses the adverse effects of chemicals on living organisms, focusing on principles such as the dose-response relationship and the risk equation. It covers drug toxicity, including the therapeutic index, idiosyncrasy, and drug allergies, outlining their classifications and symptoms. The document also highlights the role of pharmacogenomics in tailoring medications based on individual genetic responses.