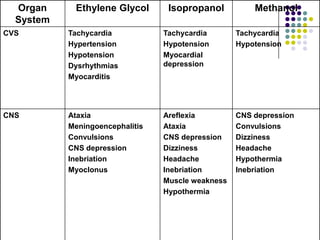
This document discusses toxic alcohols including ethanol, methanol, ethylene glycol, and isopropanol. It provides details on the sources, metabolism, clinical effects, diagnosis, and treatment of toxic alcohol poisoning for each substance. Key points include the different metabolic pathways, symptoms based on serum concentration levels, use of antidotes like ethanol or fomepizole to prevent metabolism, and indications for hemodialysis in severe poisonings.