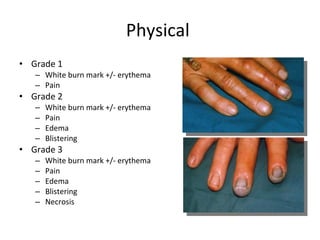
Hydrofluoric acid is a colorless, fuming liquid or gas that is used for glass etching, metal cleaning, and rust removal. Exposure can occur through inhalation, skin contact, eye contact, or ingestion. It causes local corrosive injury and can lead to systemic fluoride poisoning. Fluoride binds to tissue calcium and magnesium ions, causing pain, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia. Treatment involves removal of contaminated clothing, decontamination, calcium gluconate for skin or eye exposure and systemic poisoning, and monitoring for hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, and hypomagnesemia.