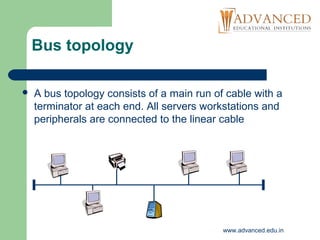
This document discusses different network topologies including bus, star, ring, and tree or hybrid topologies. It describes the basic characteristics of each topology including their advantages and disadvantages. It also discusses network operating systems, describing peer-to-peer and client/server models. Peer-to-peer networks have no central file server while client/server networks centralize functions and applications on dedicated file servers.