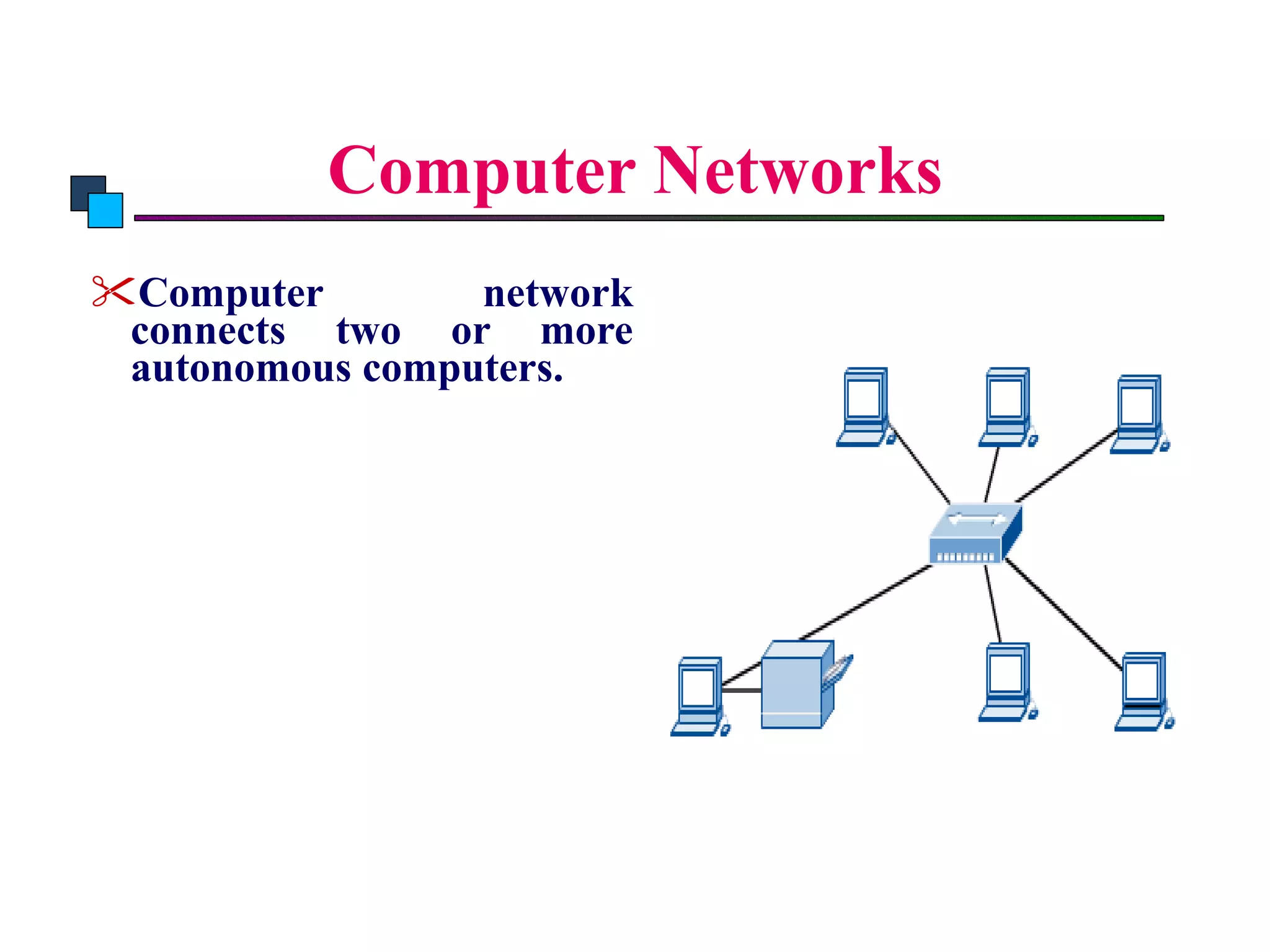
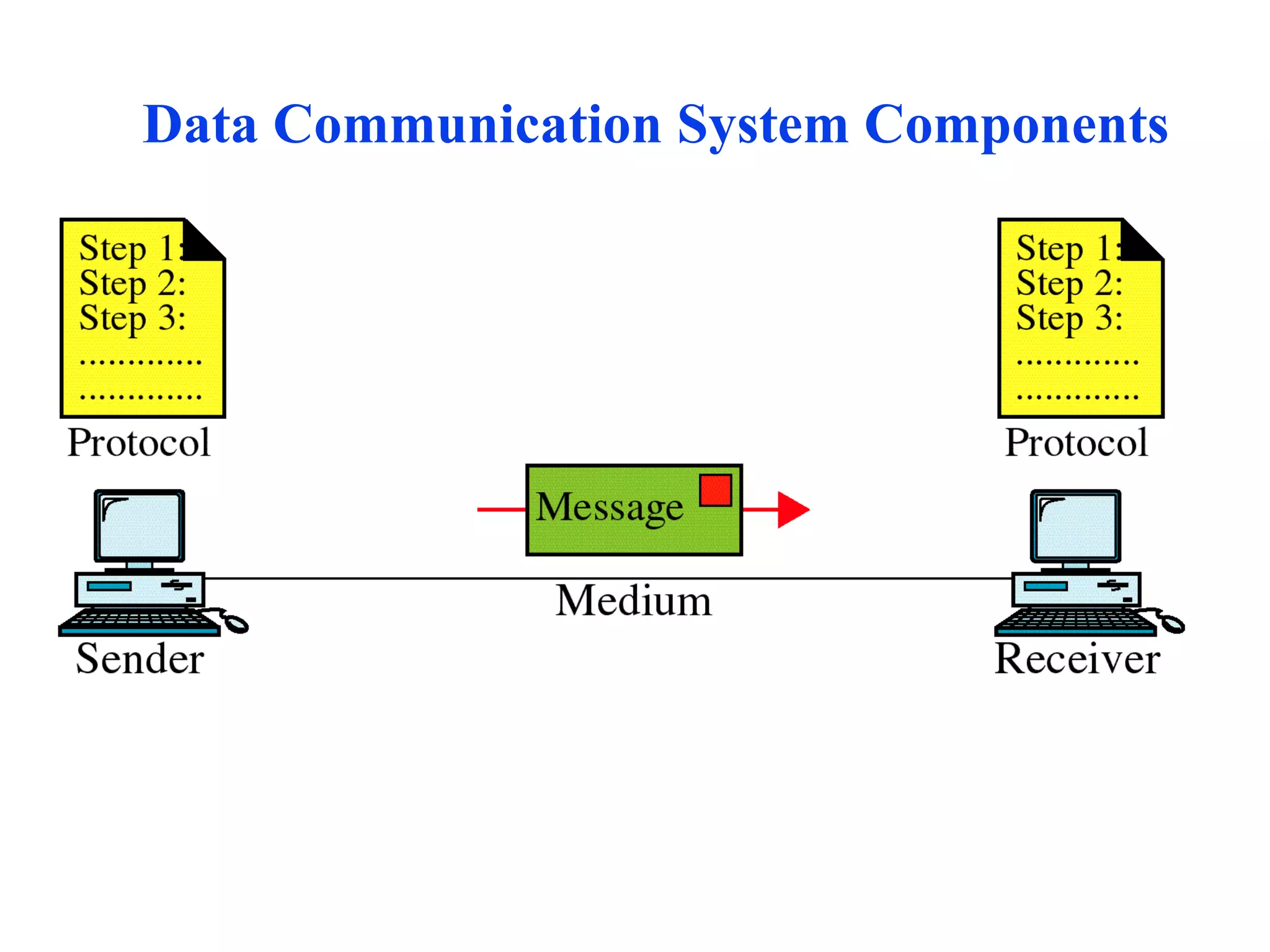
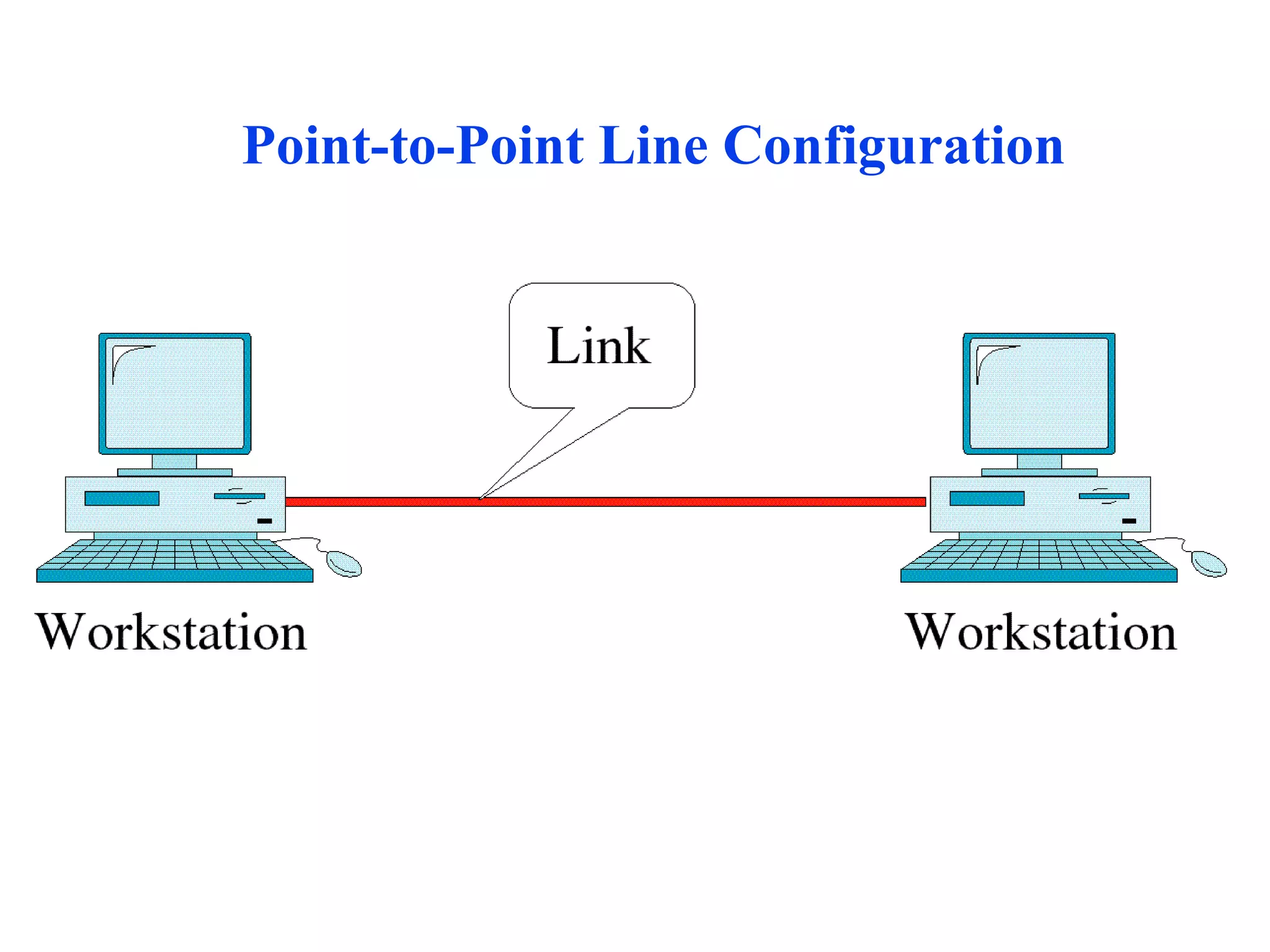
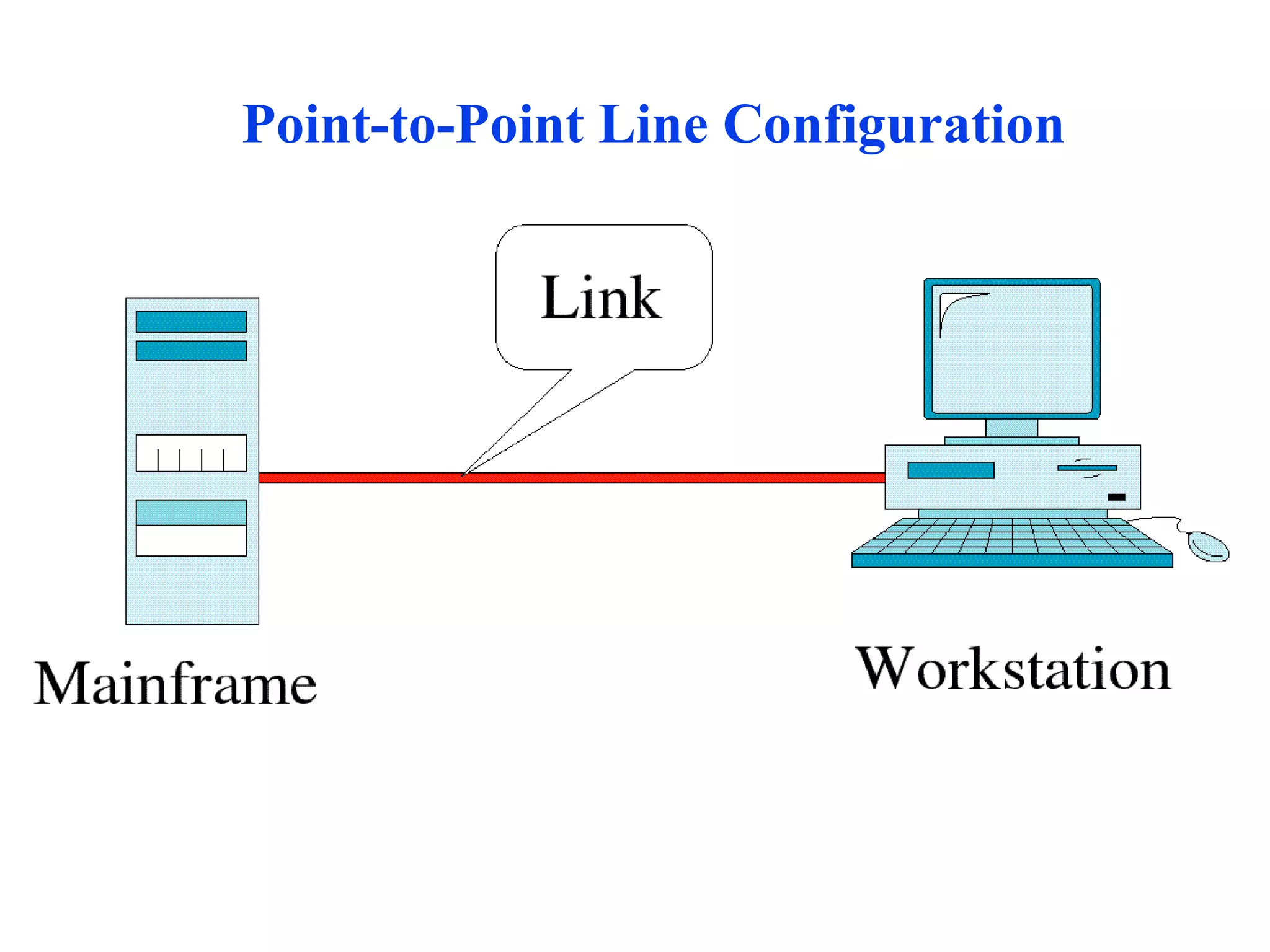
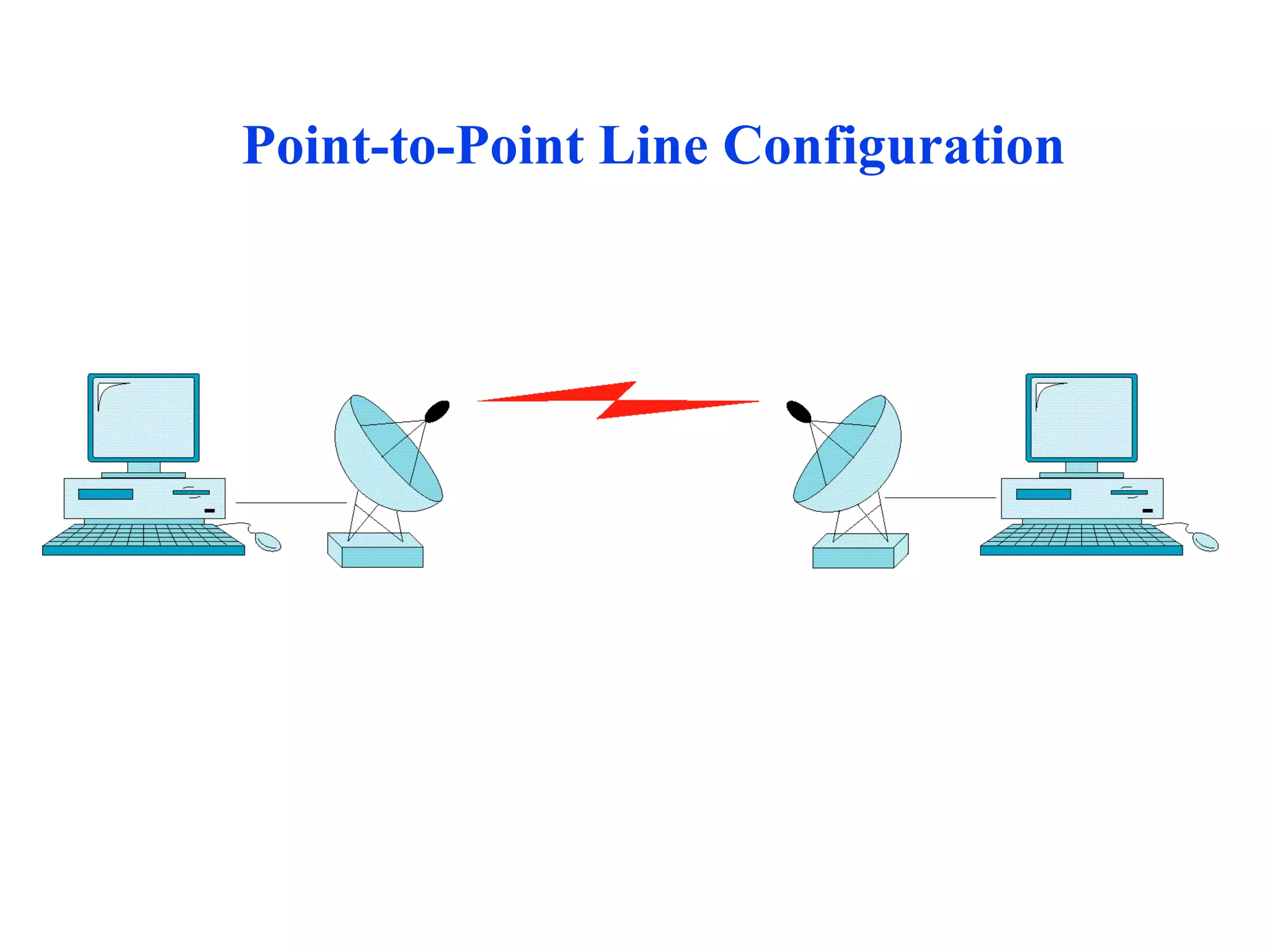
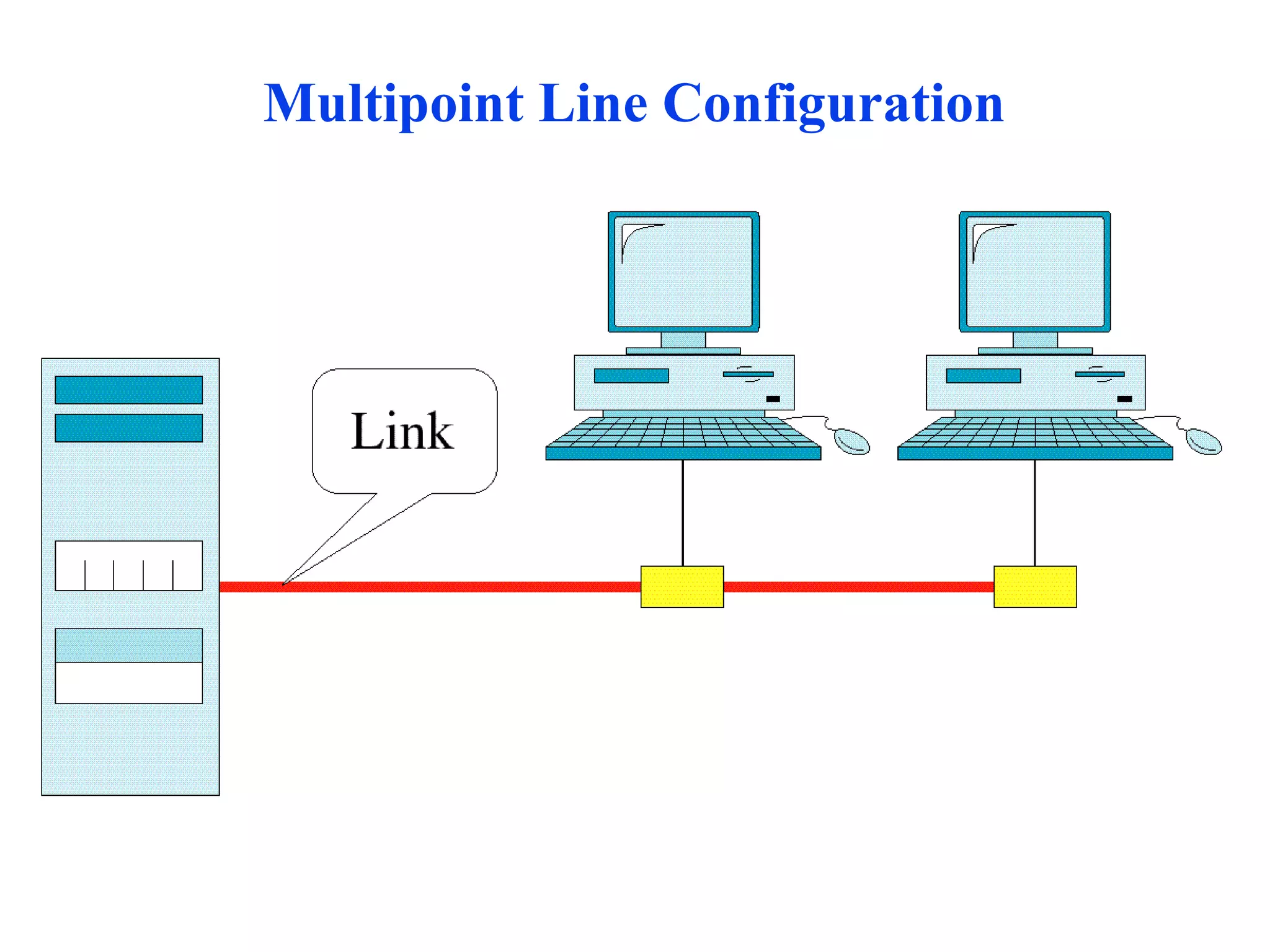
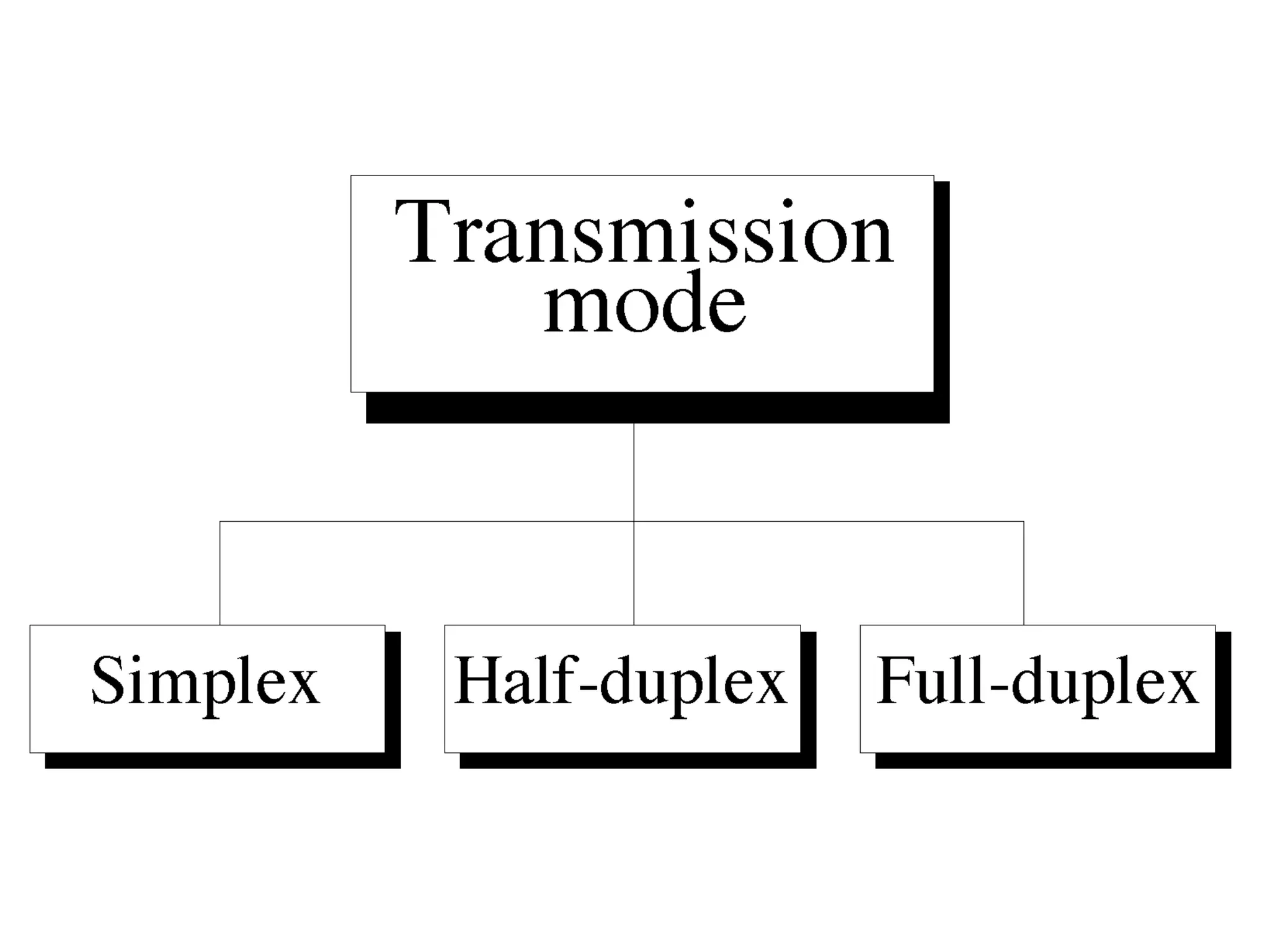
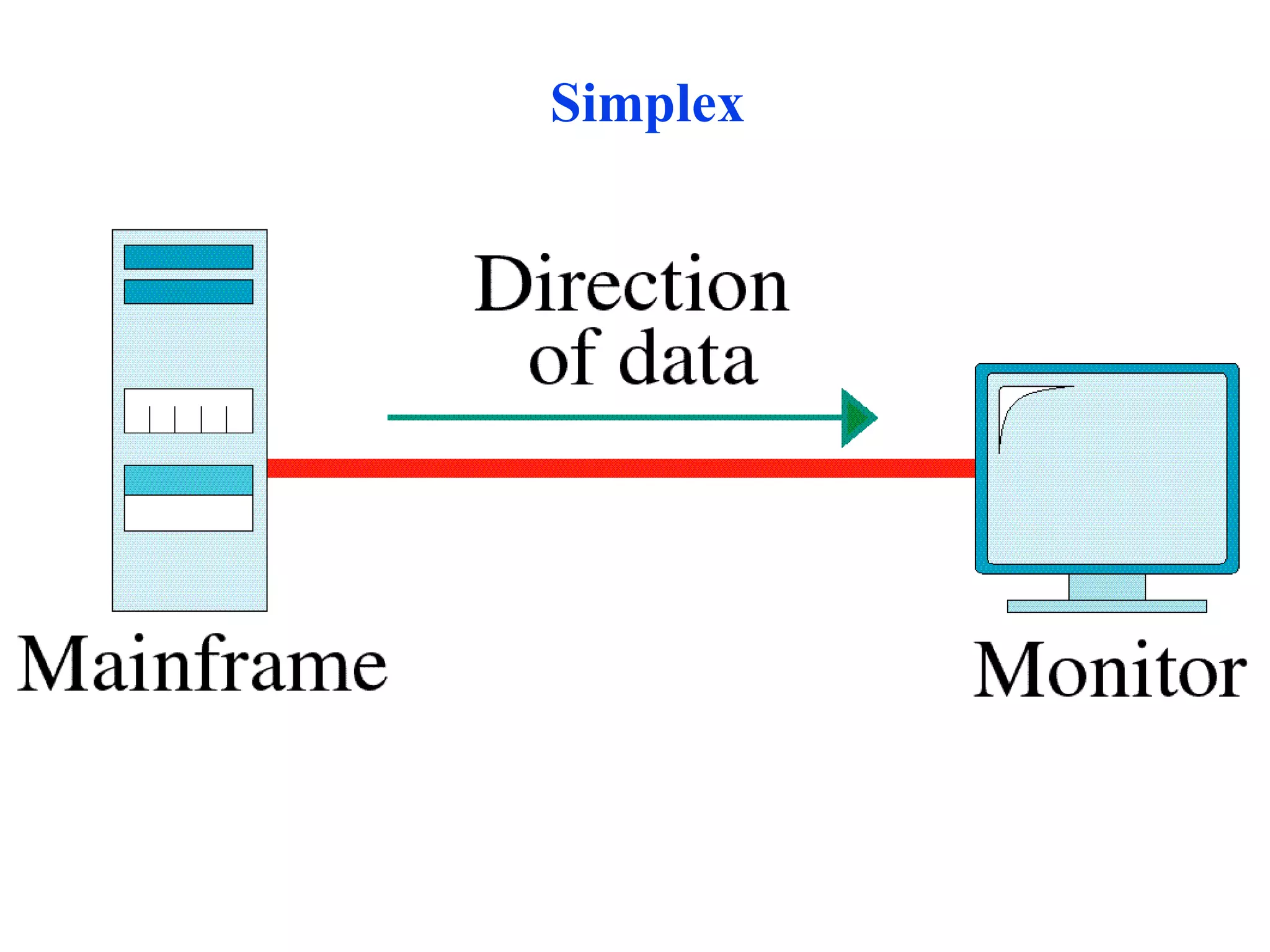
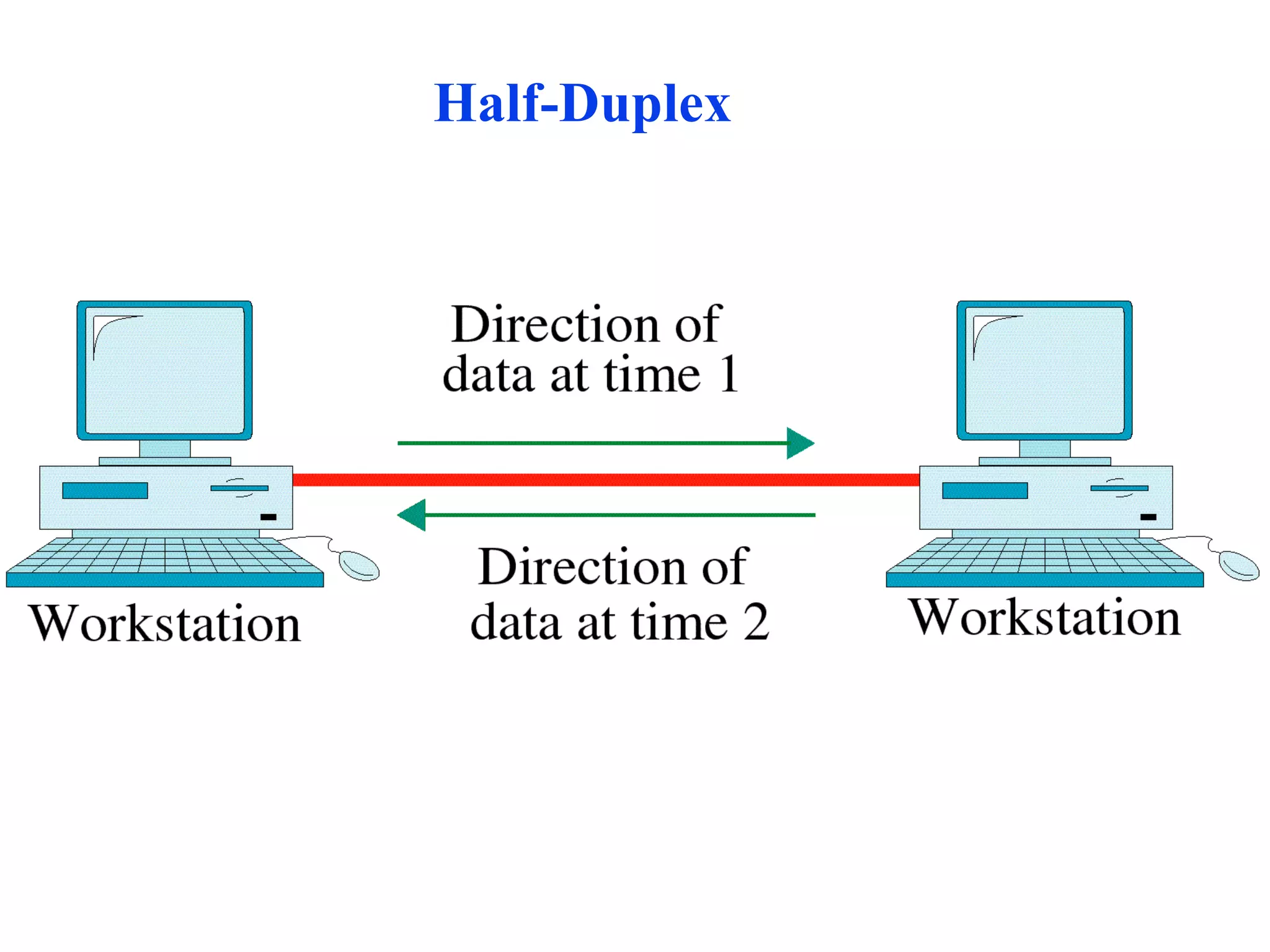
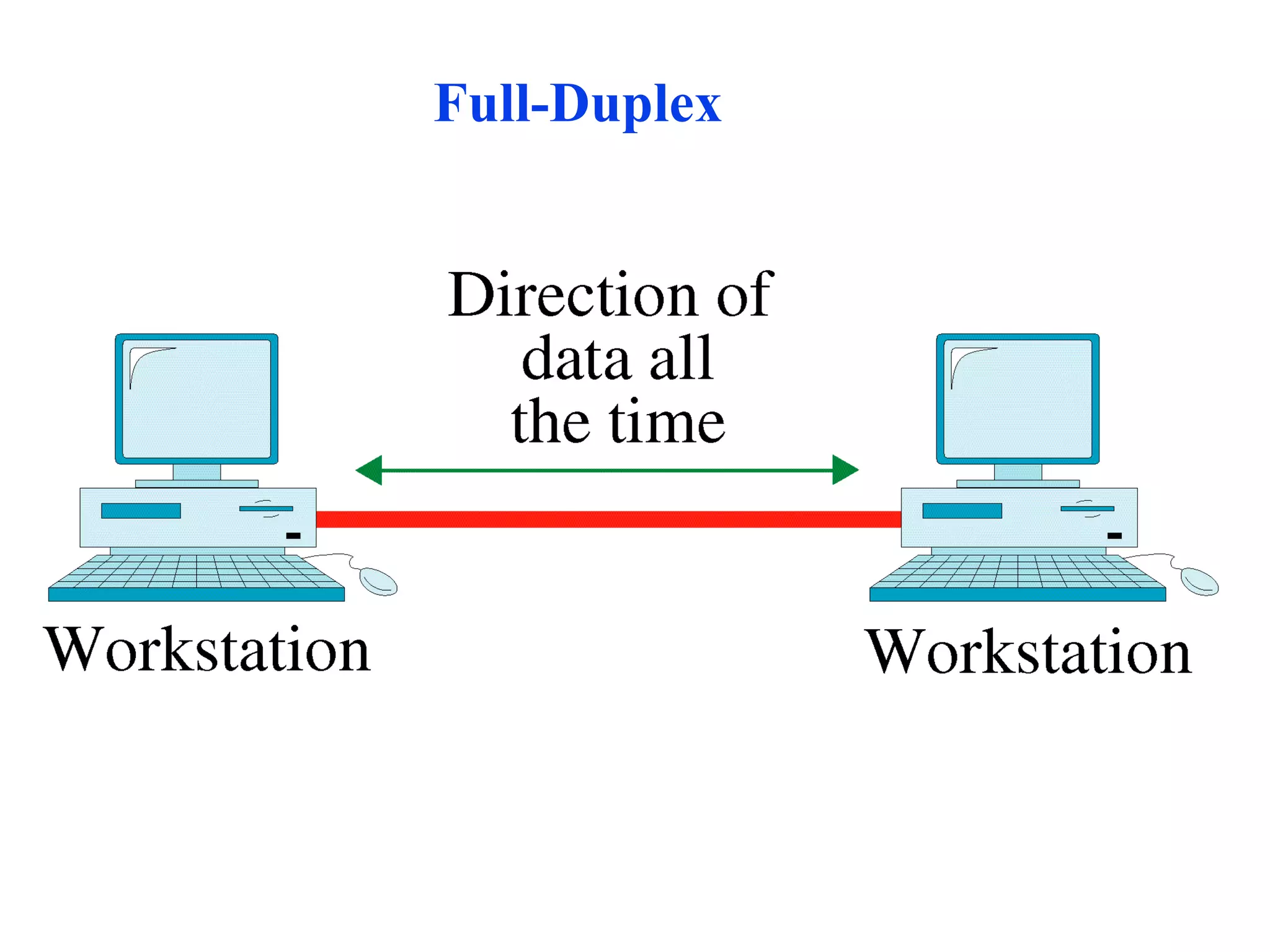
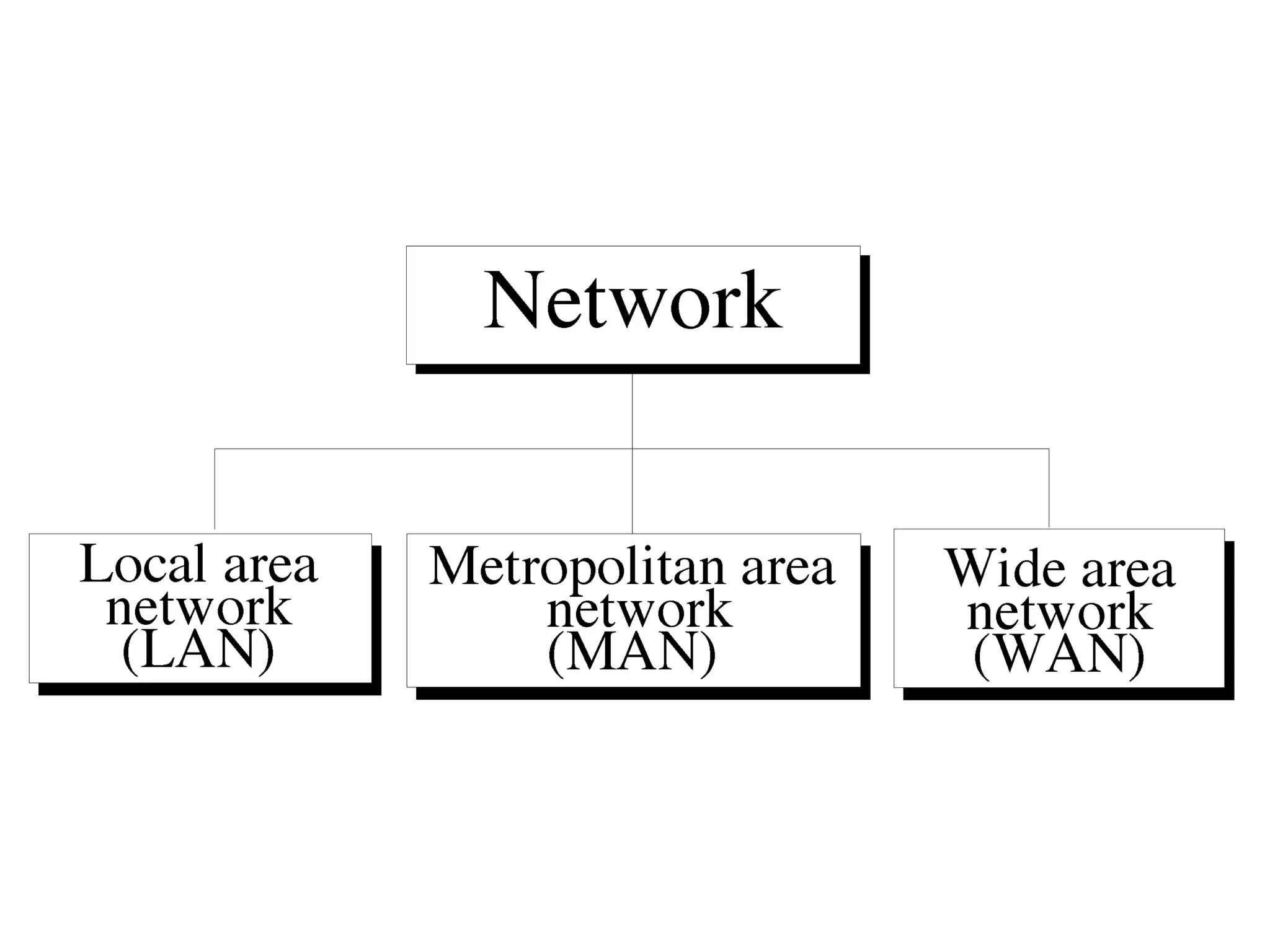
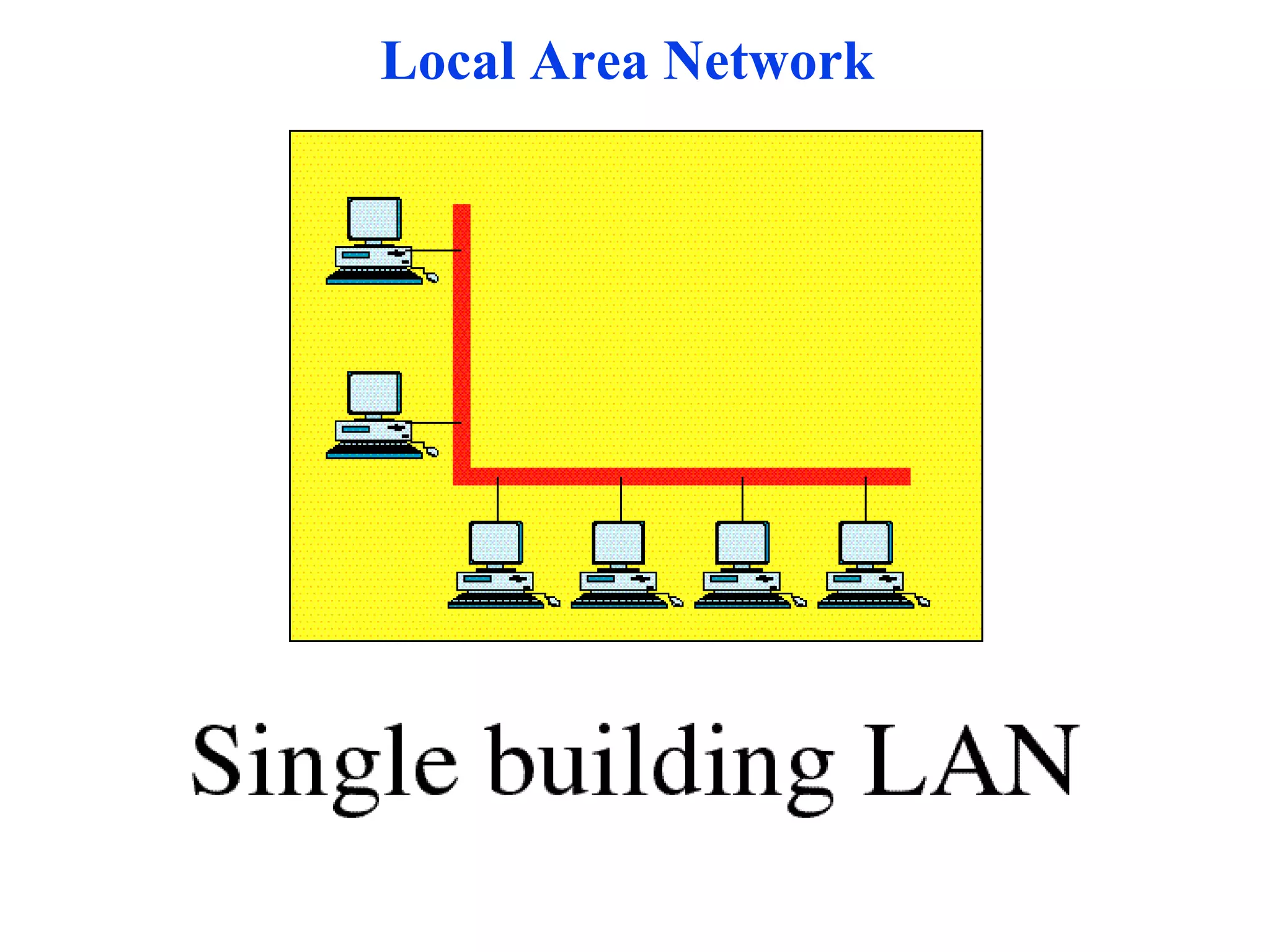
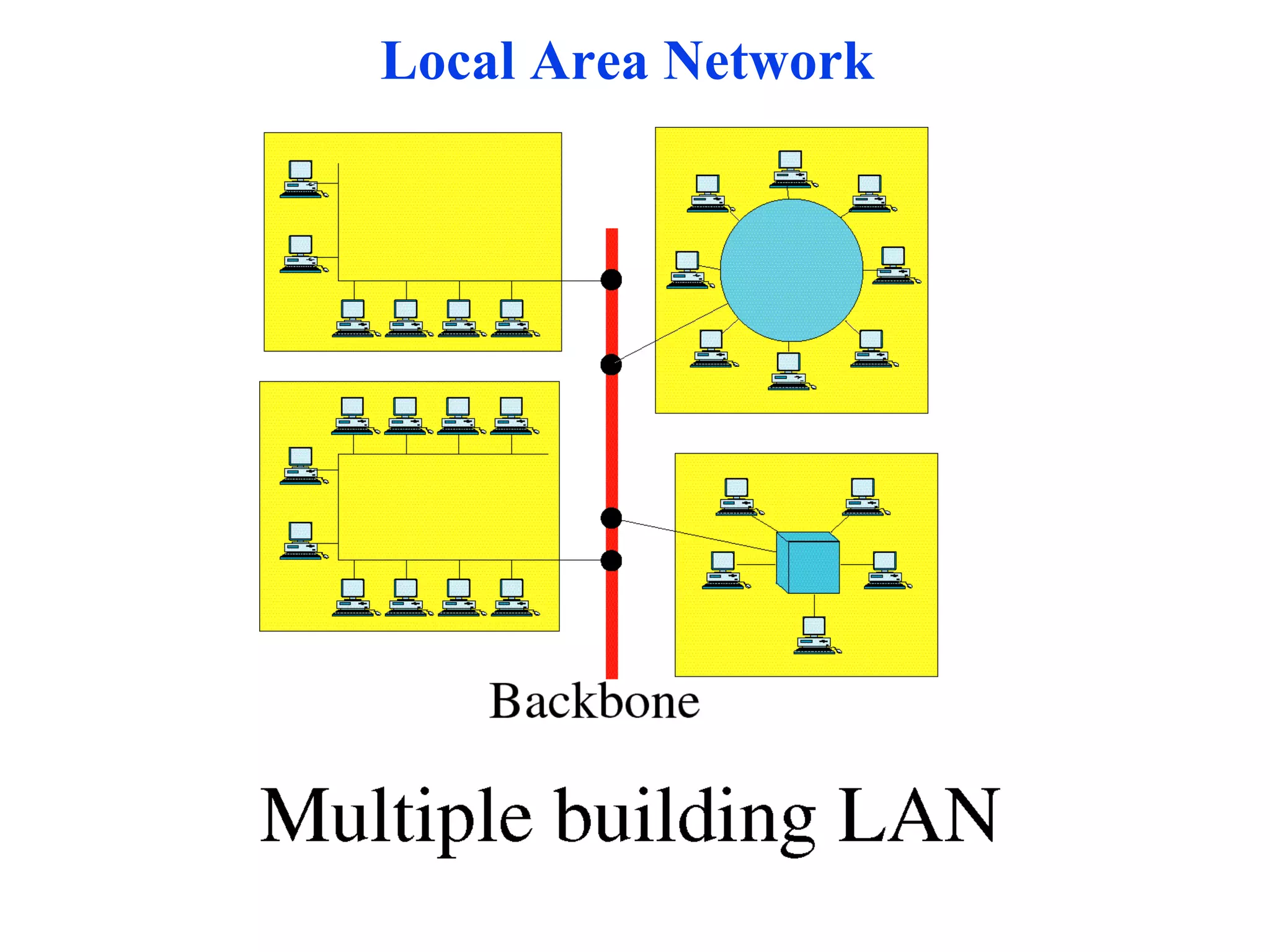
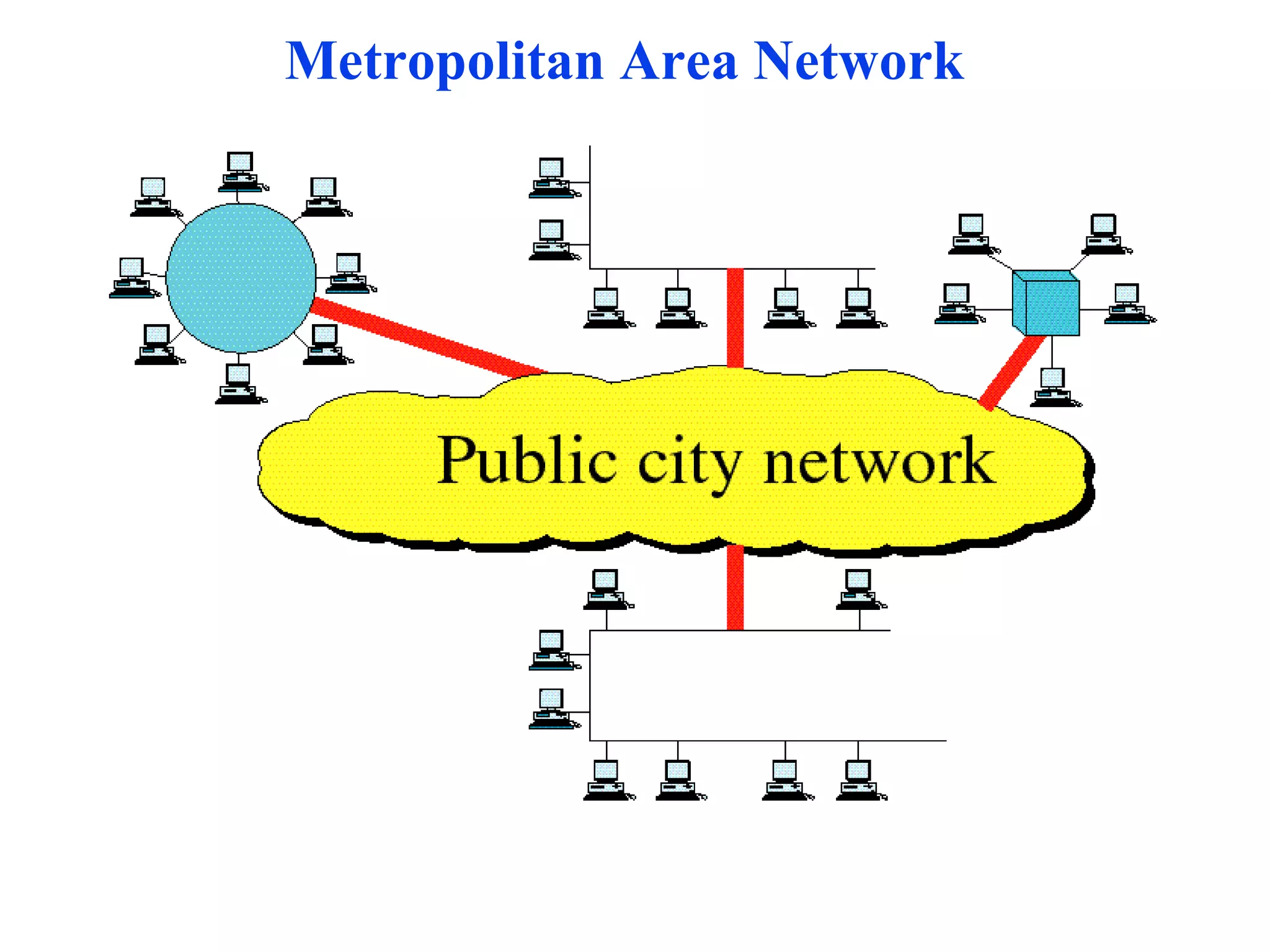
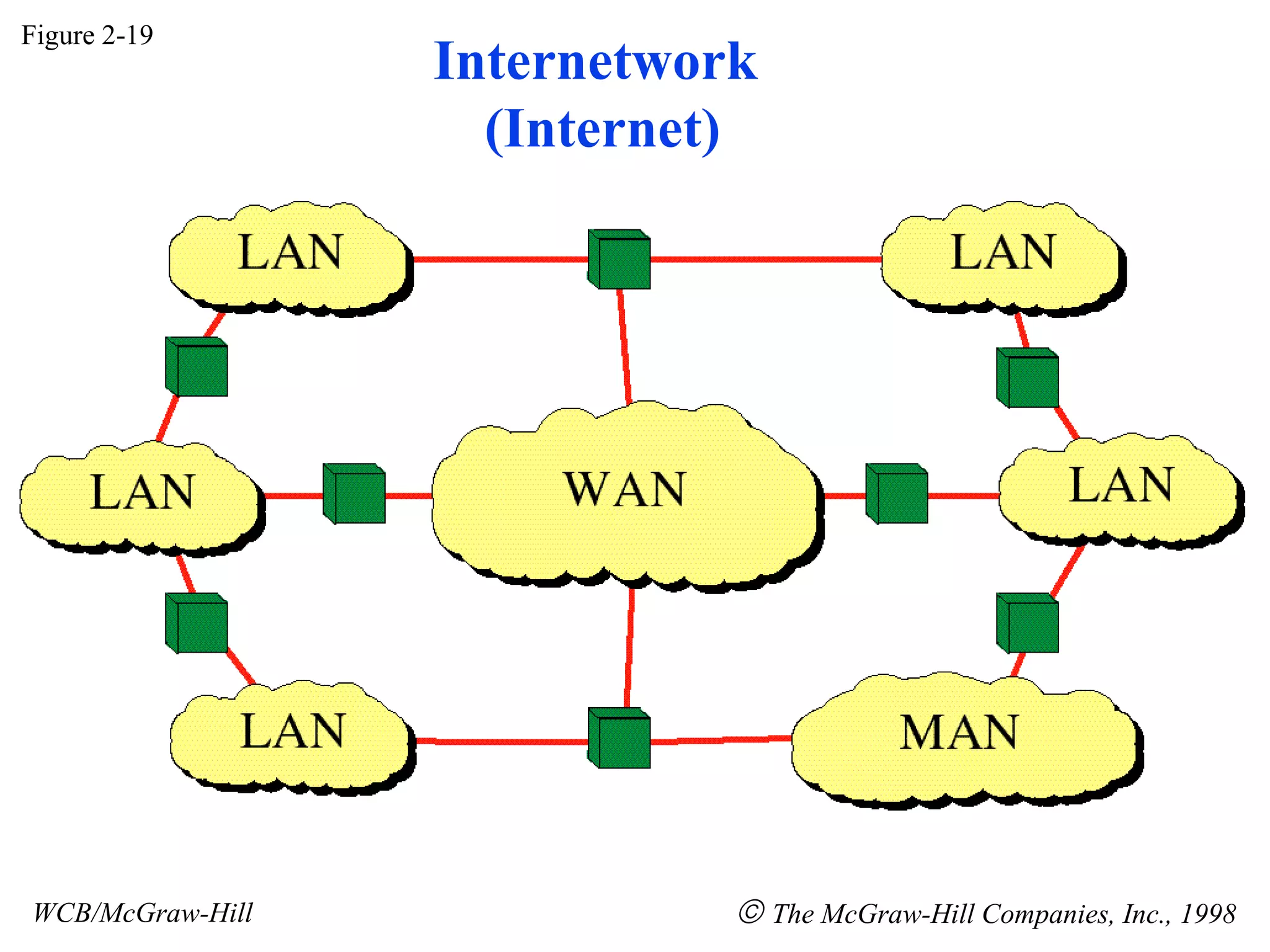
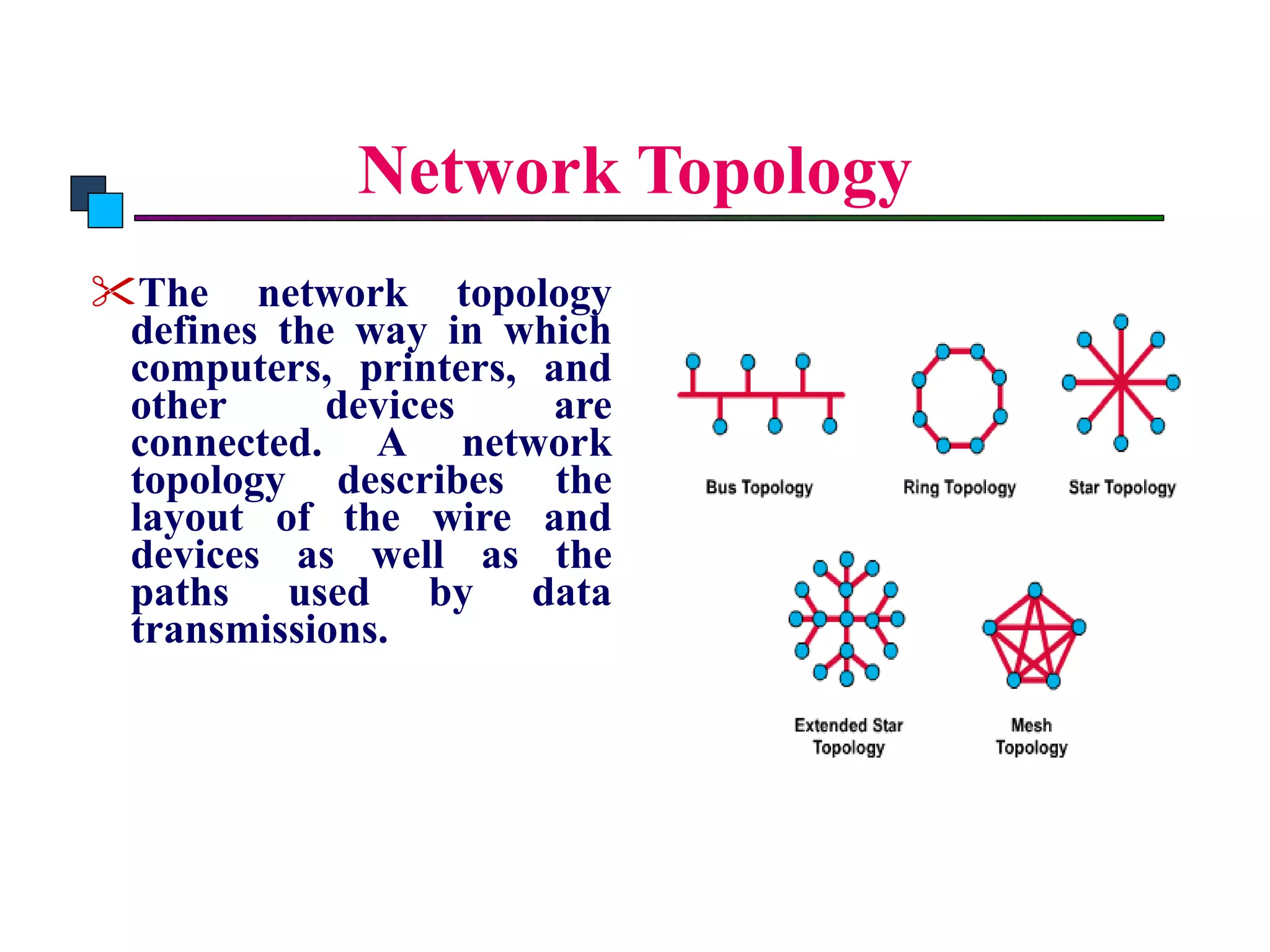
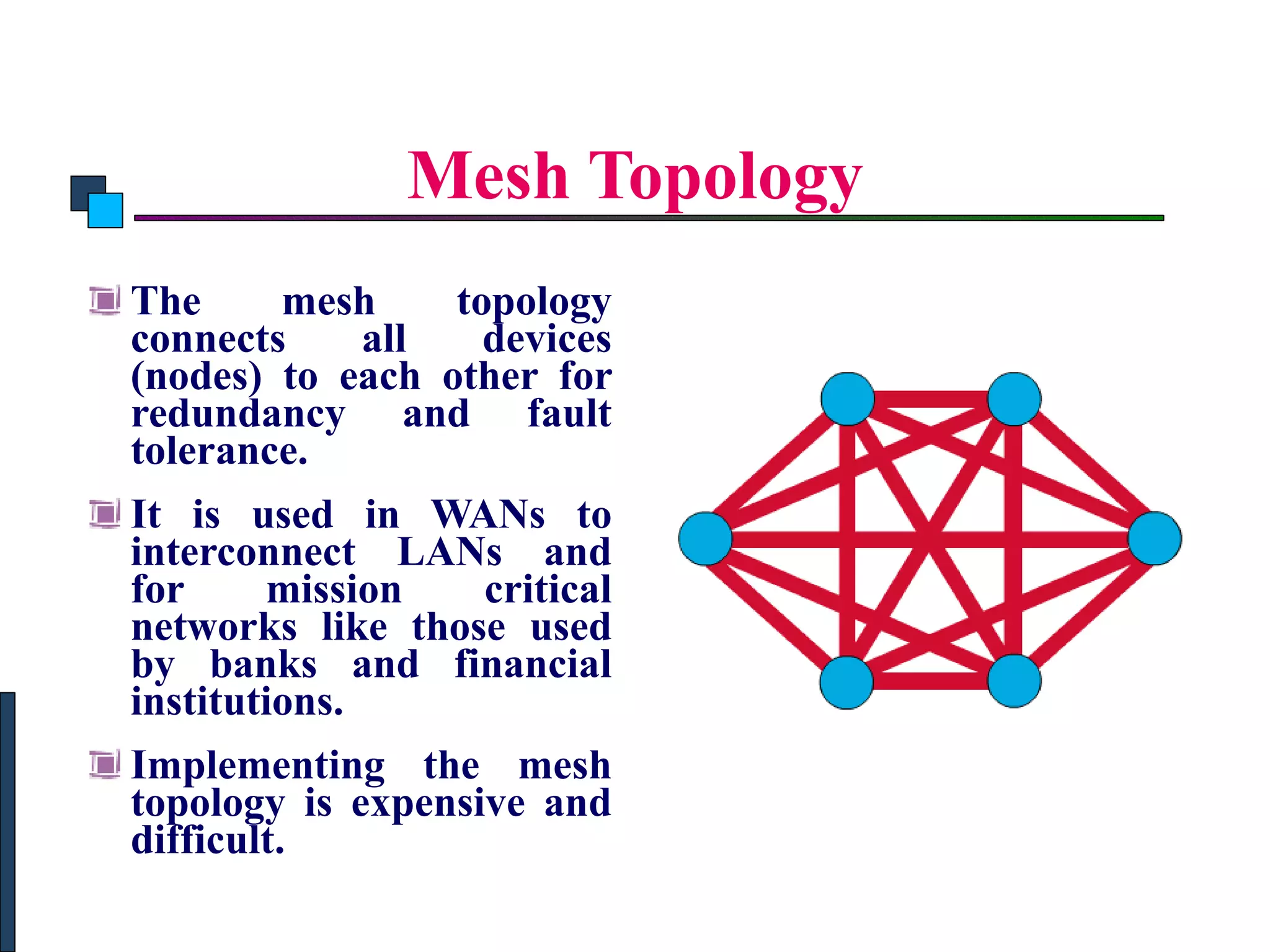
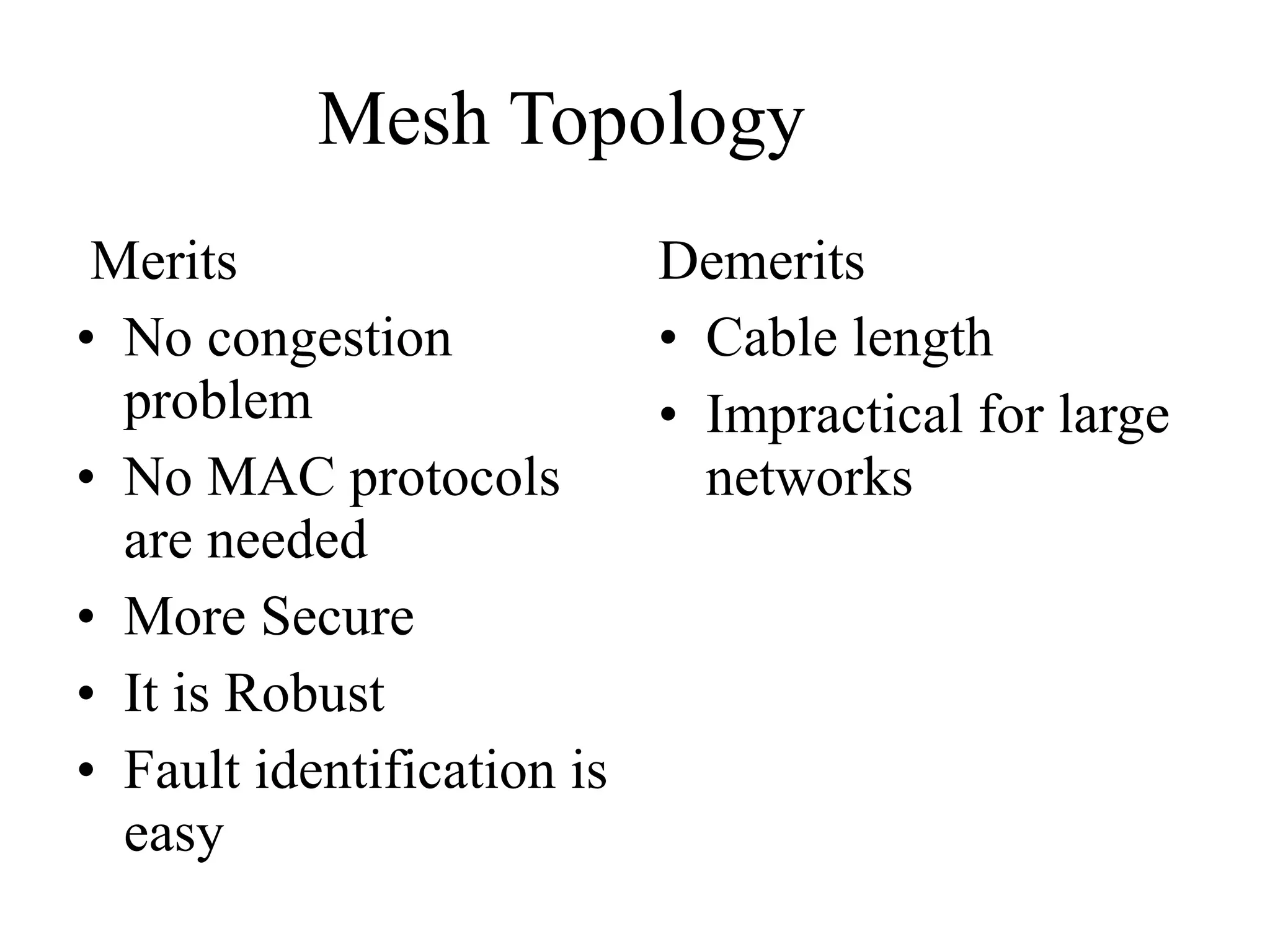
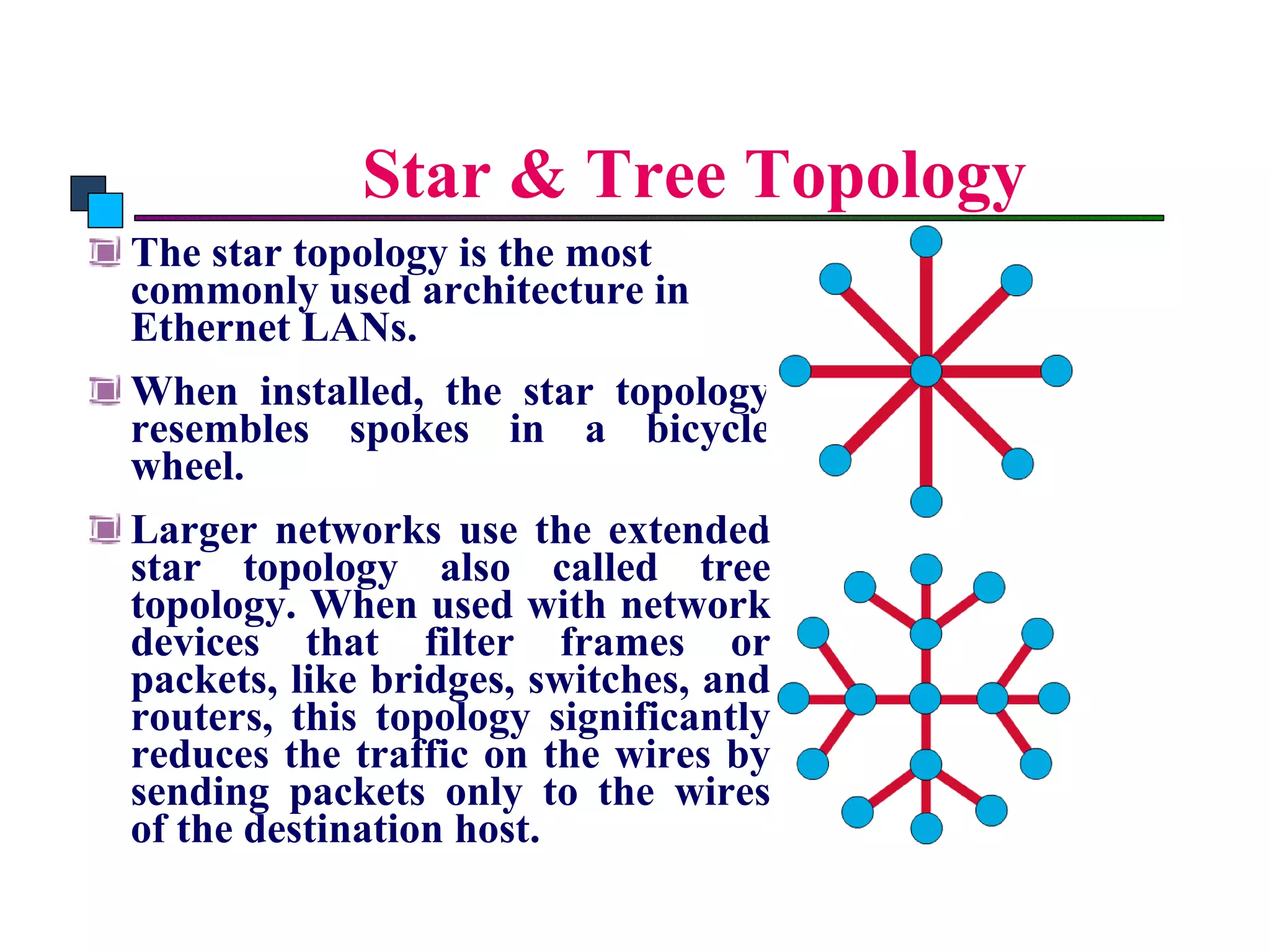
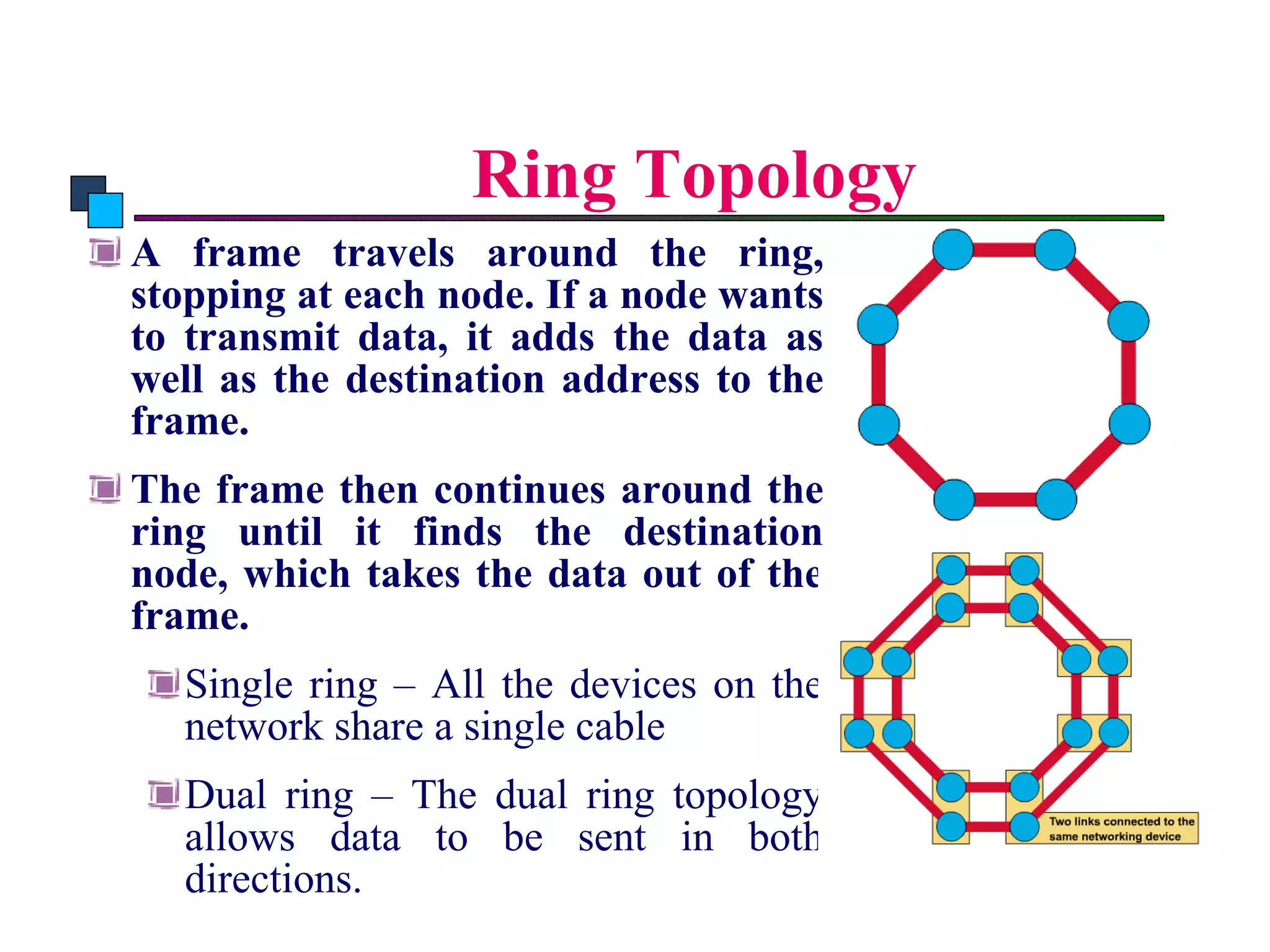
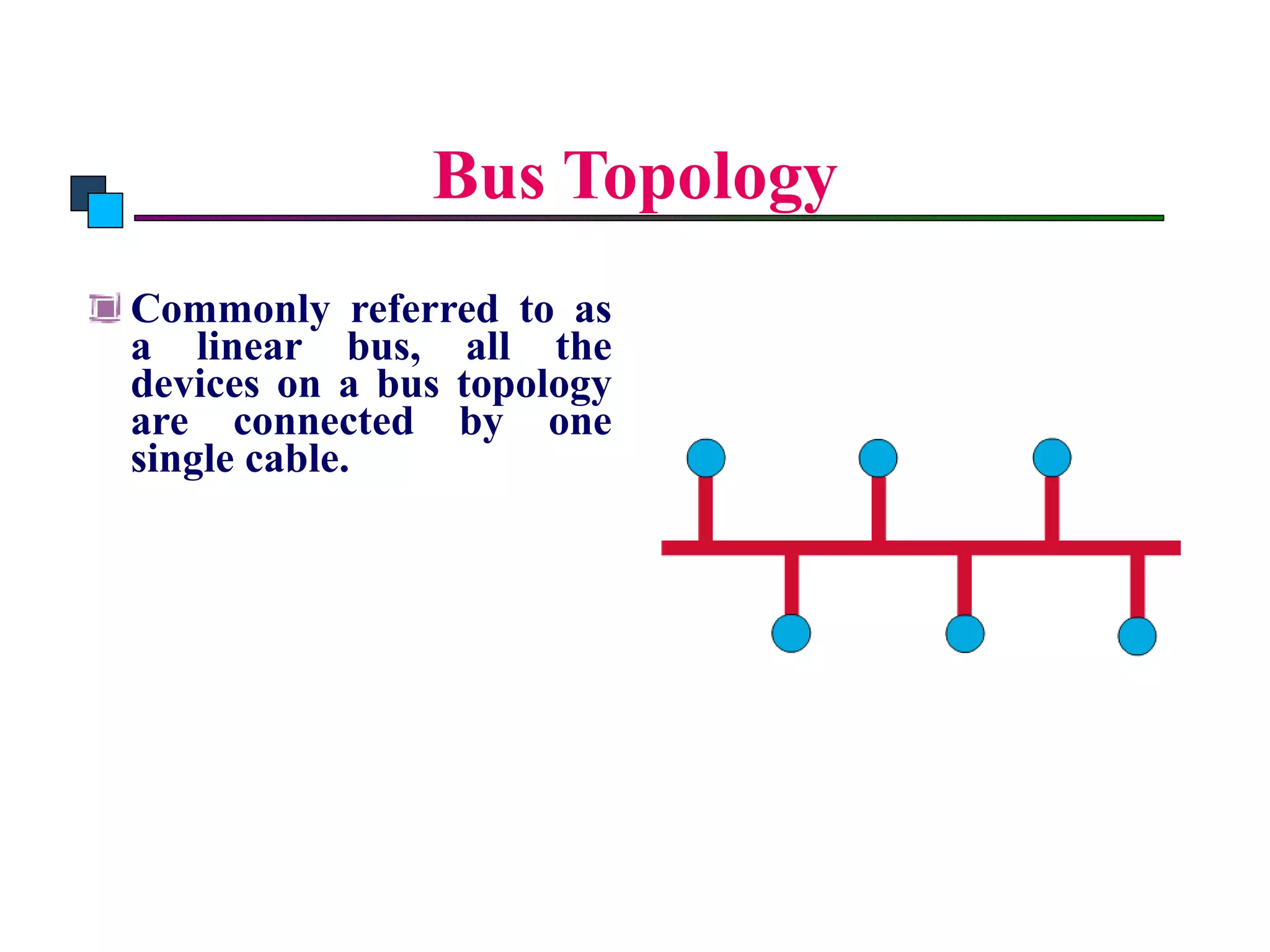
The document discusses different types of network topologies including point-to-point, multipoint, mesh, star/tree, ring, and bus topologies. It provides details on the characteristics of each topology such as how the devices are connected, advantages and disadvantages of each approach, and examples of applications where different topologies may be used.