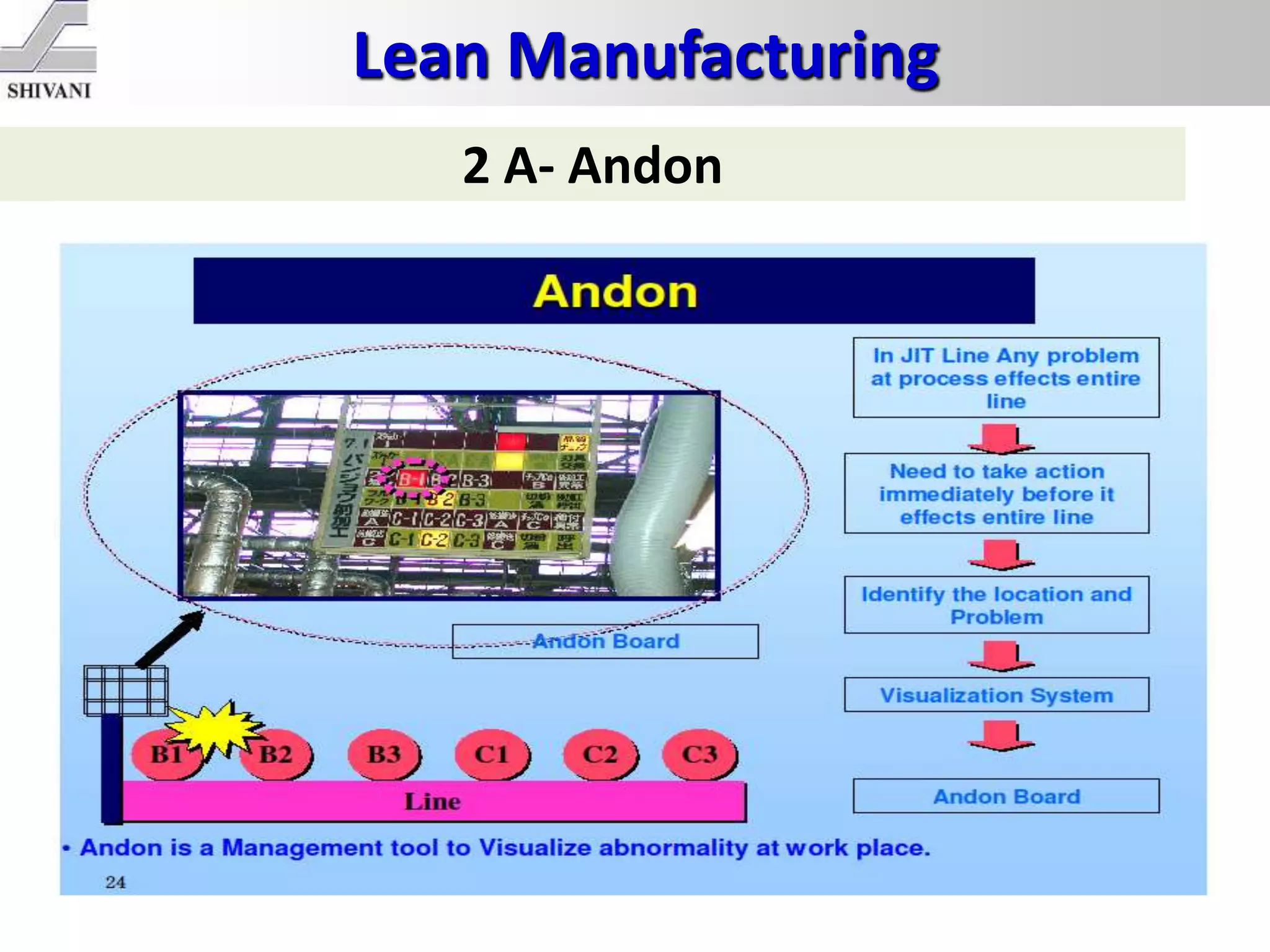
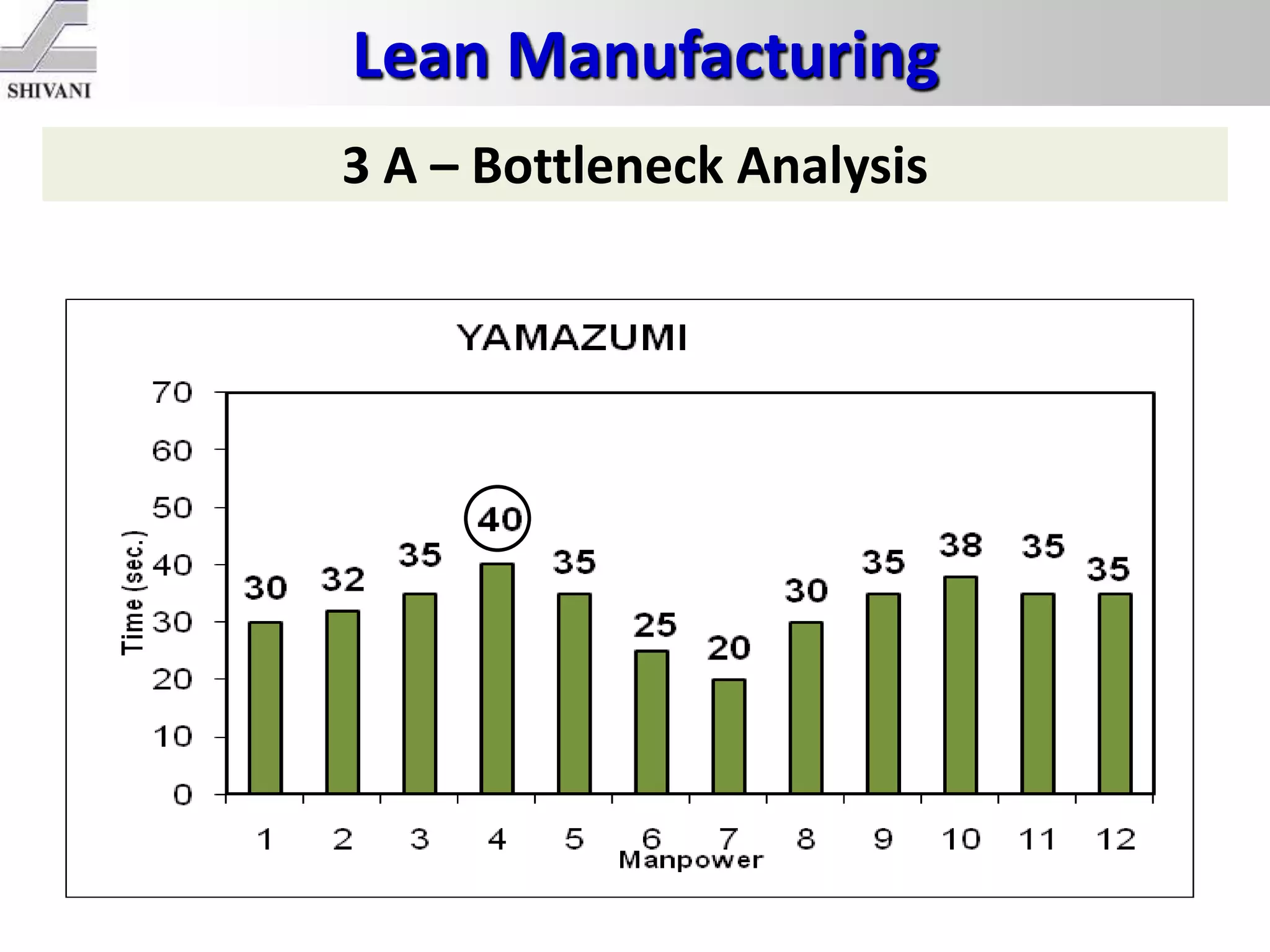
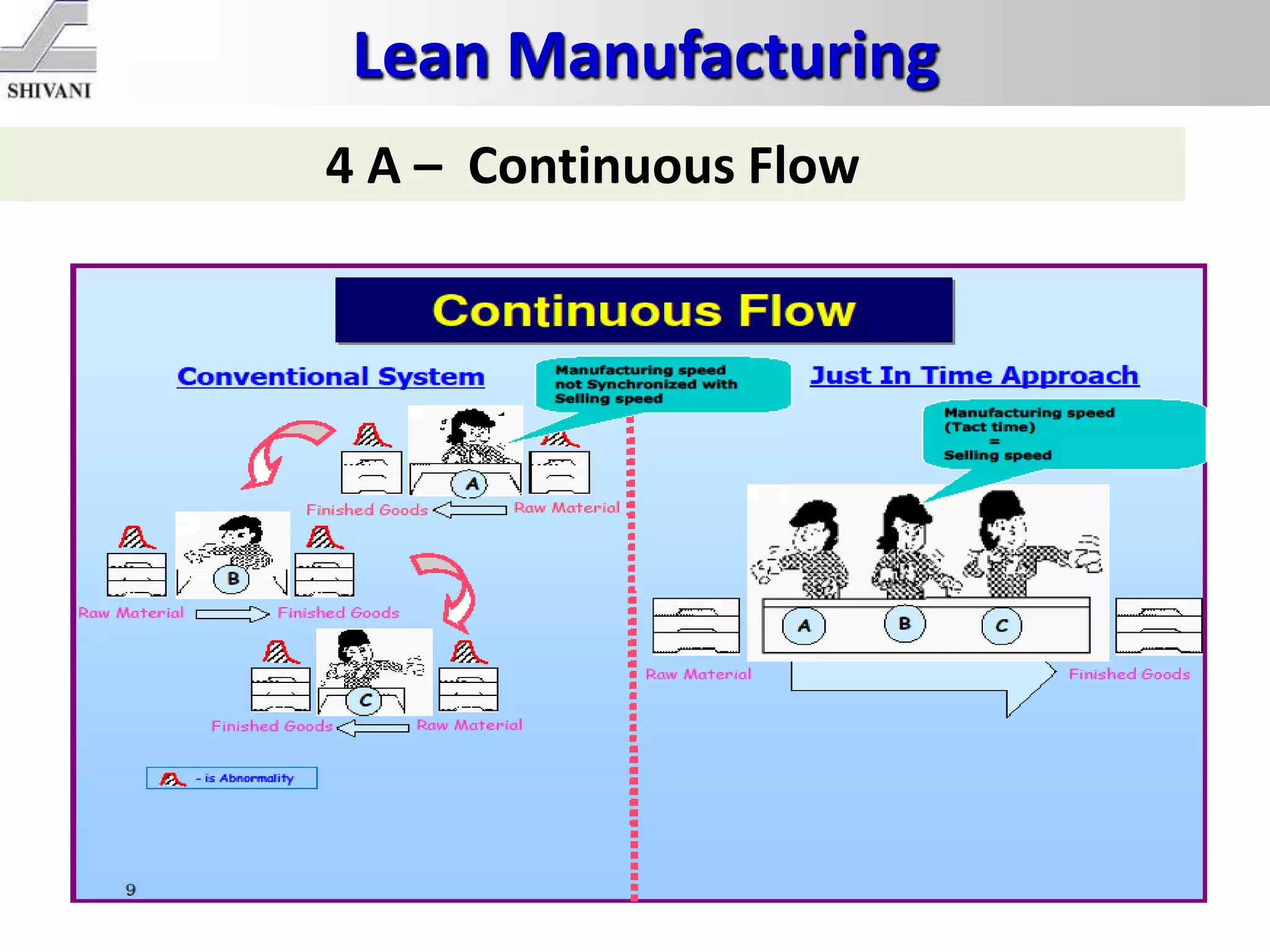
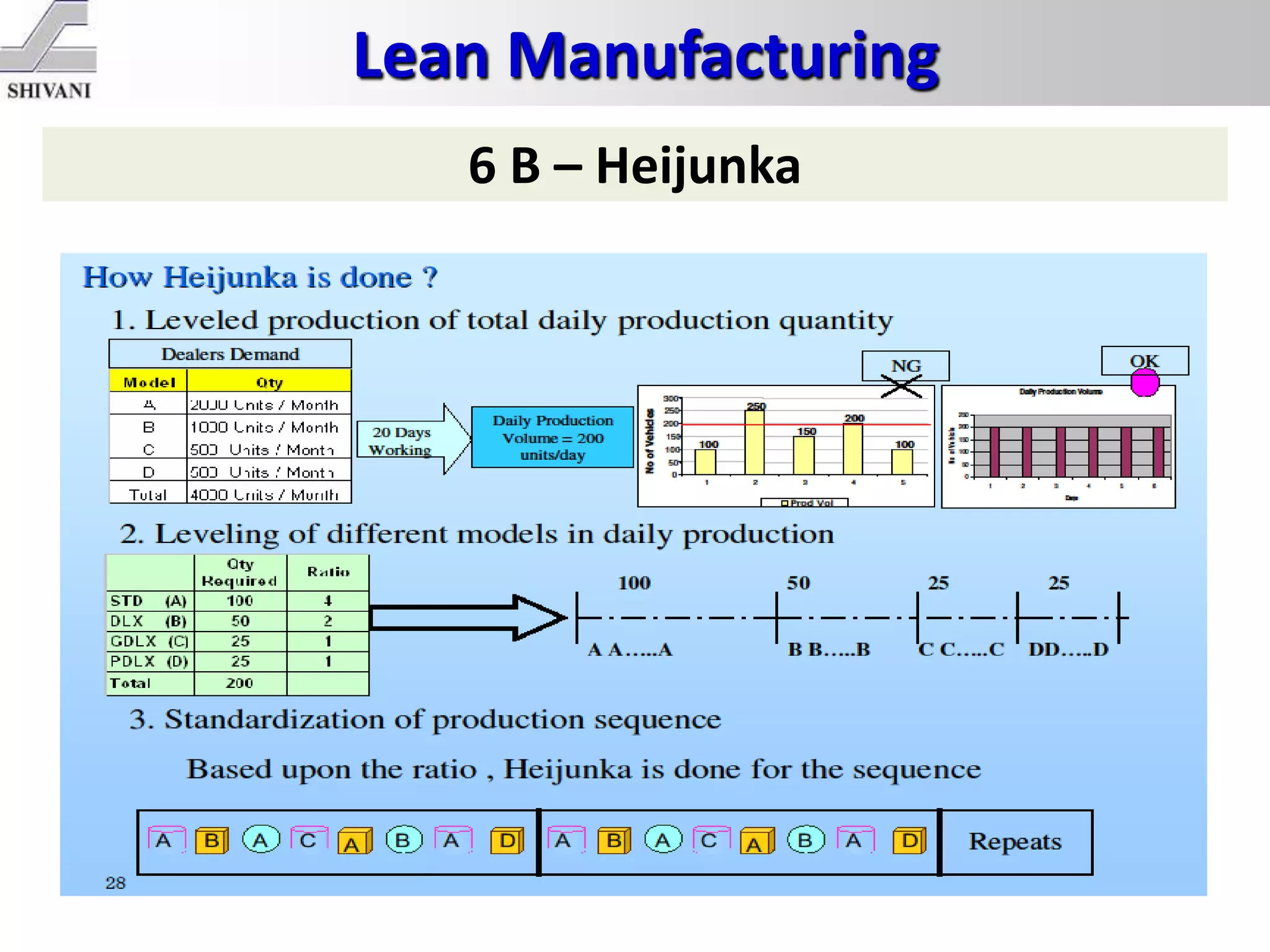
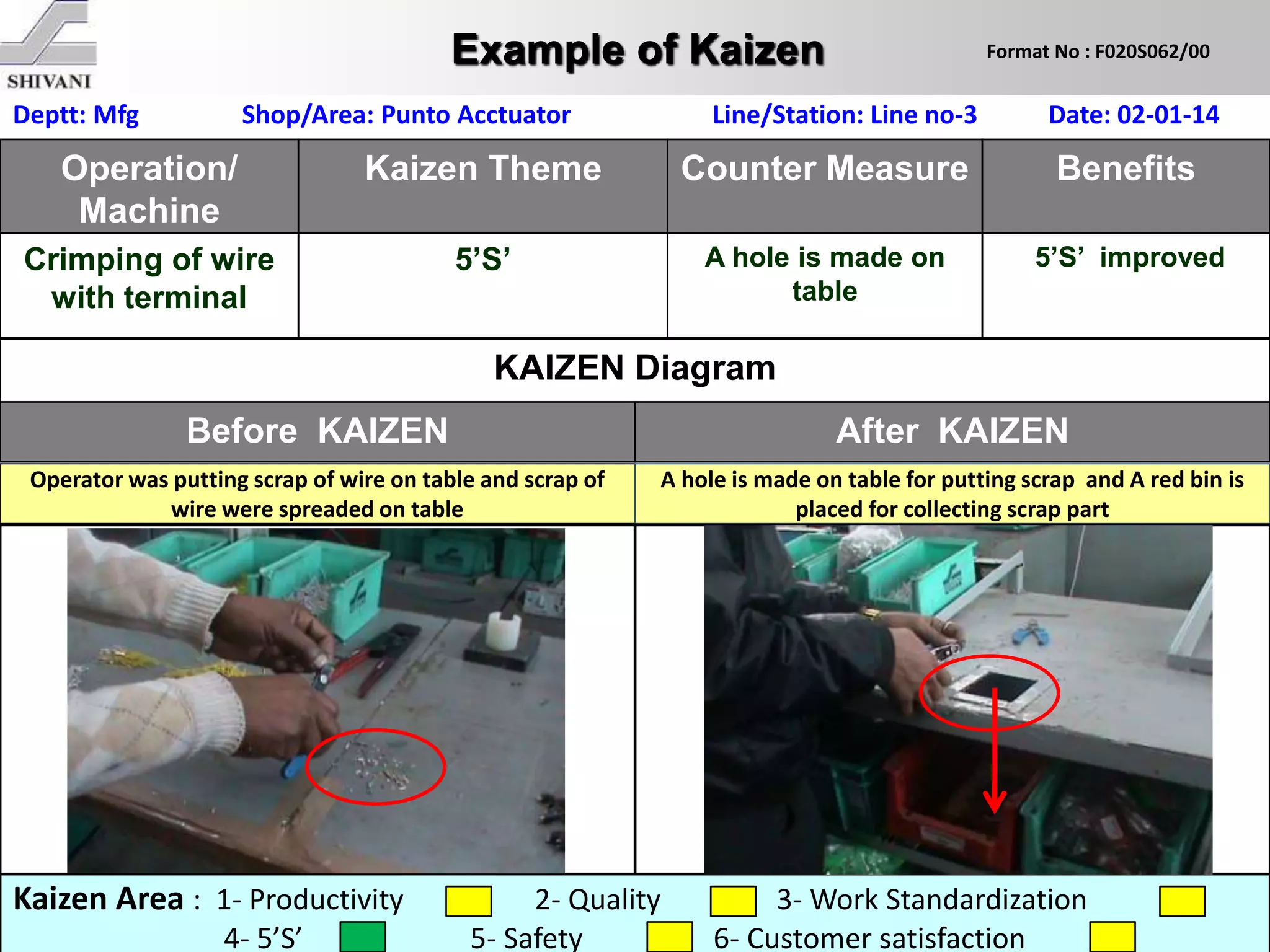
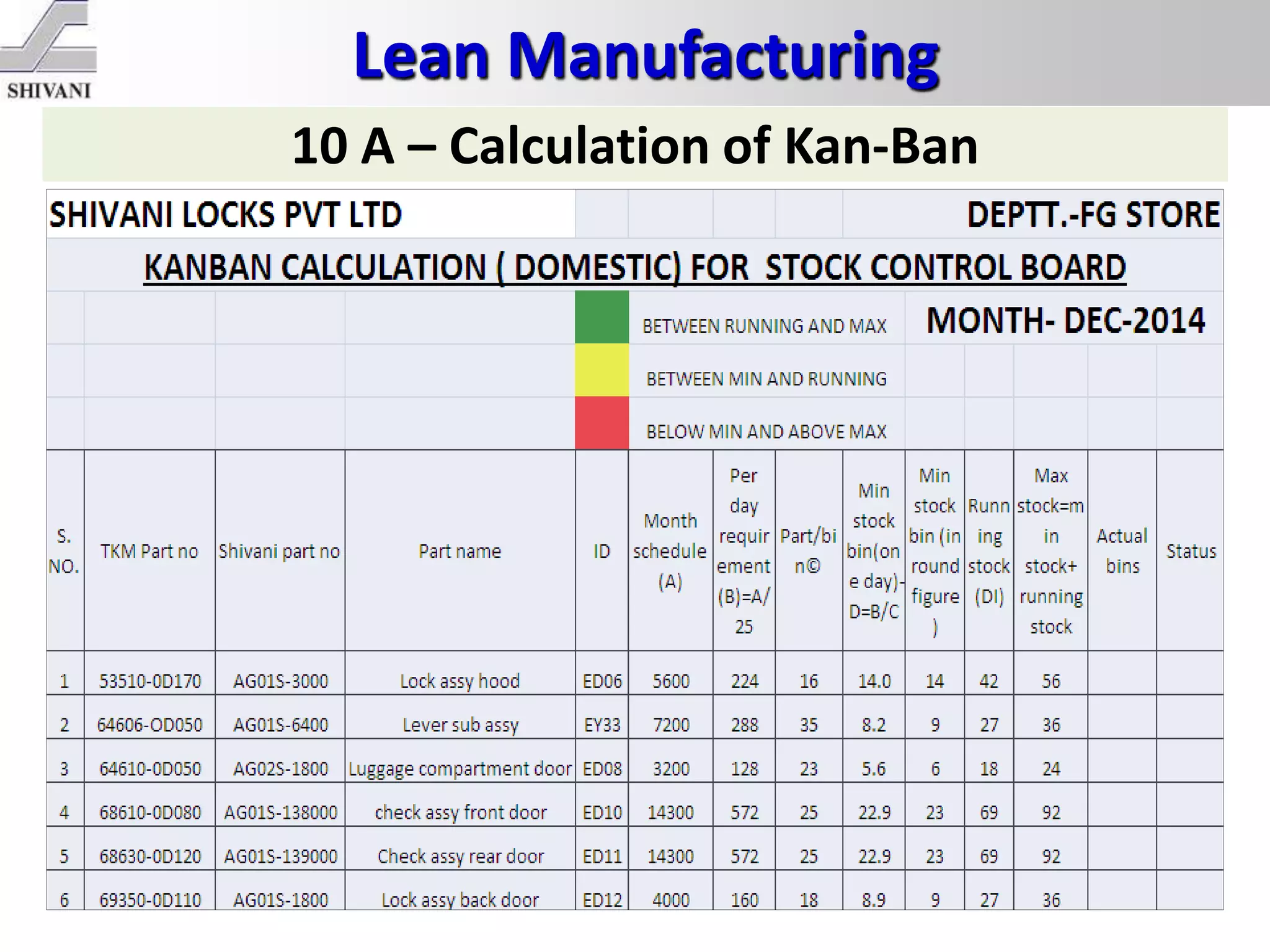
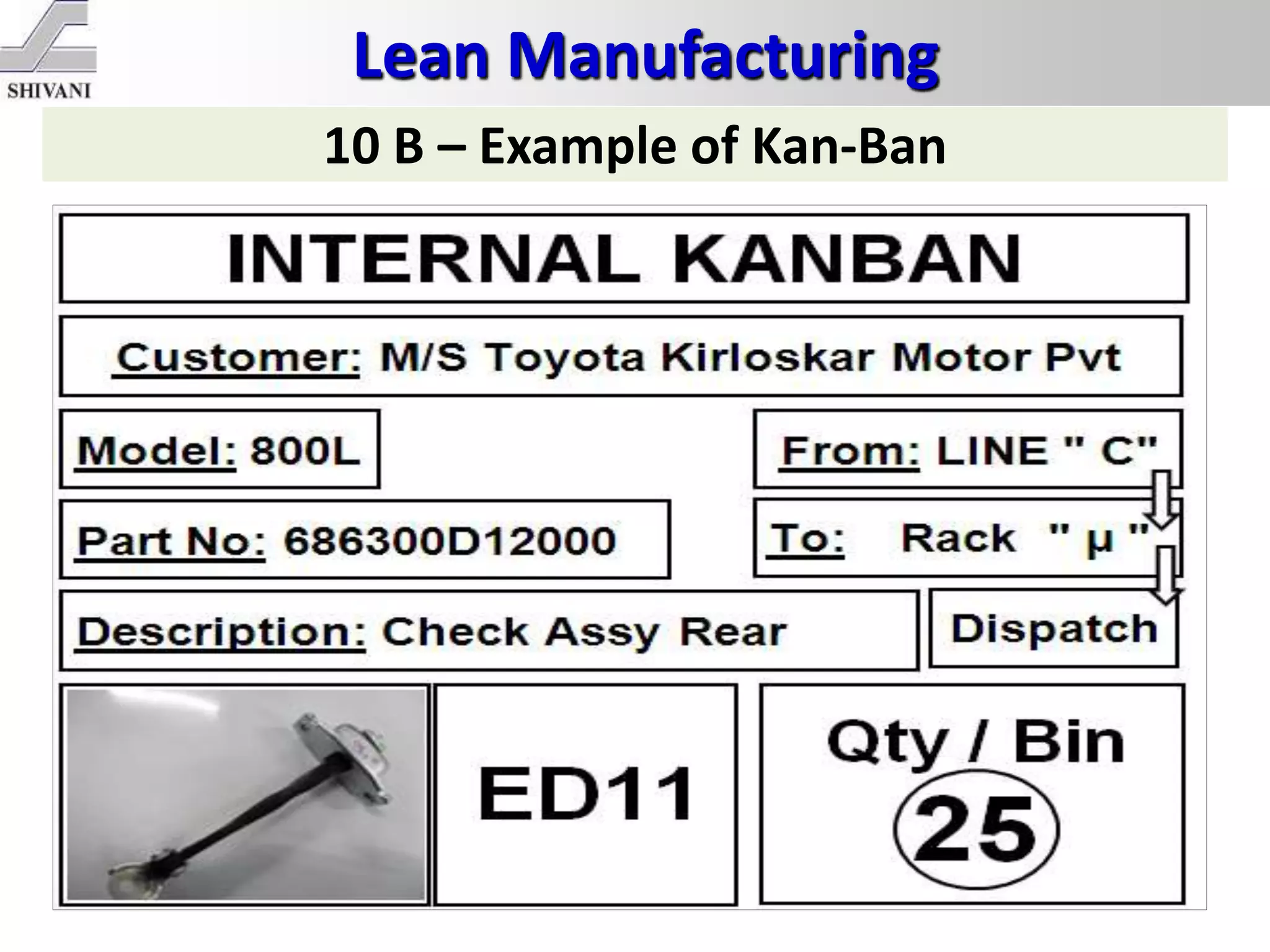
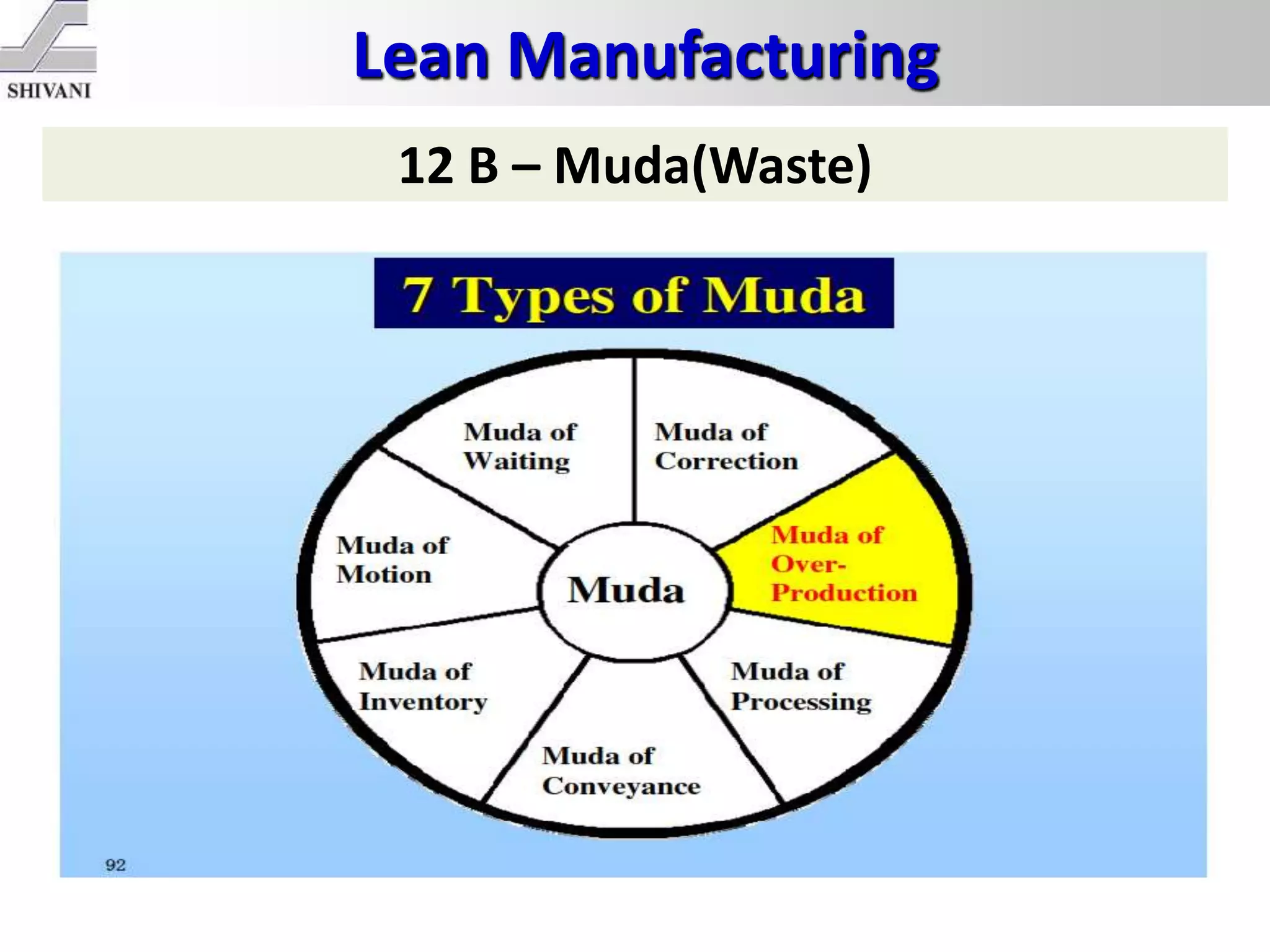
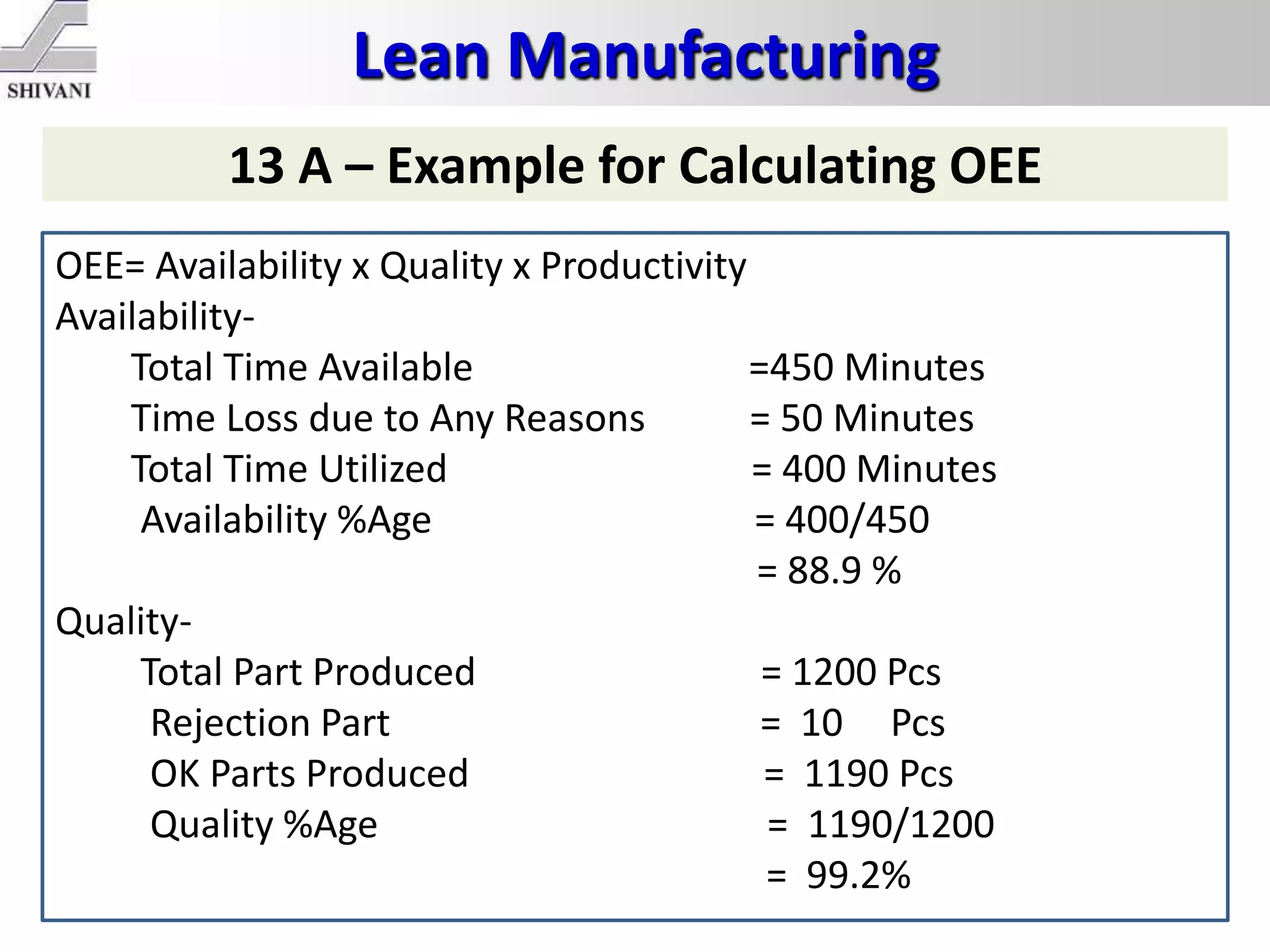
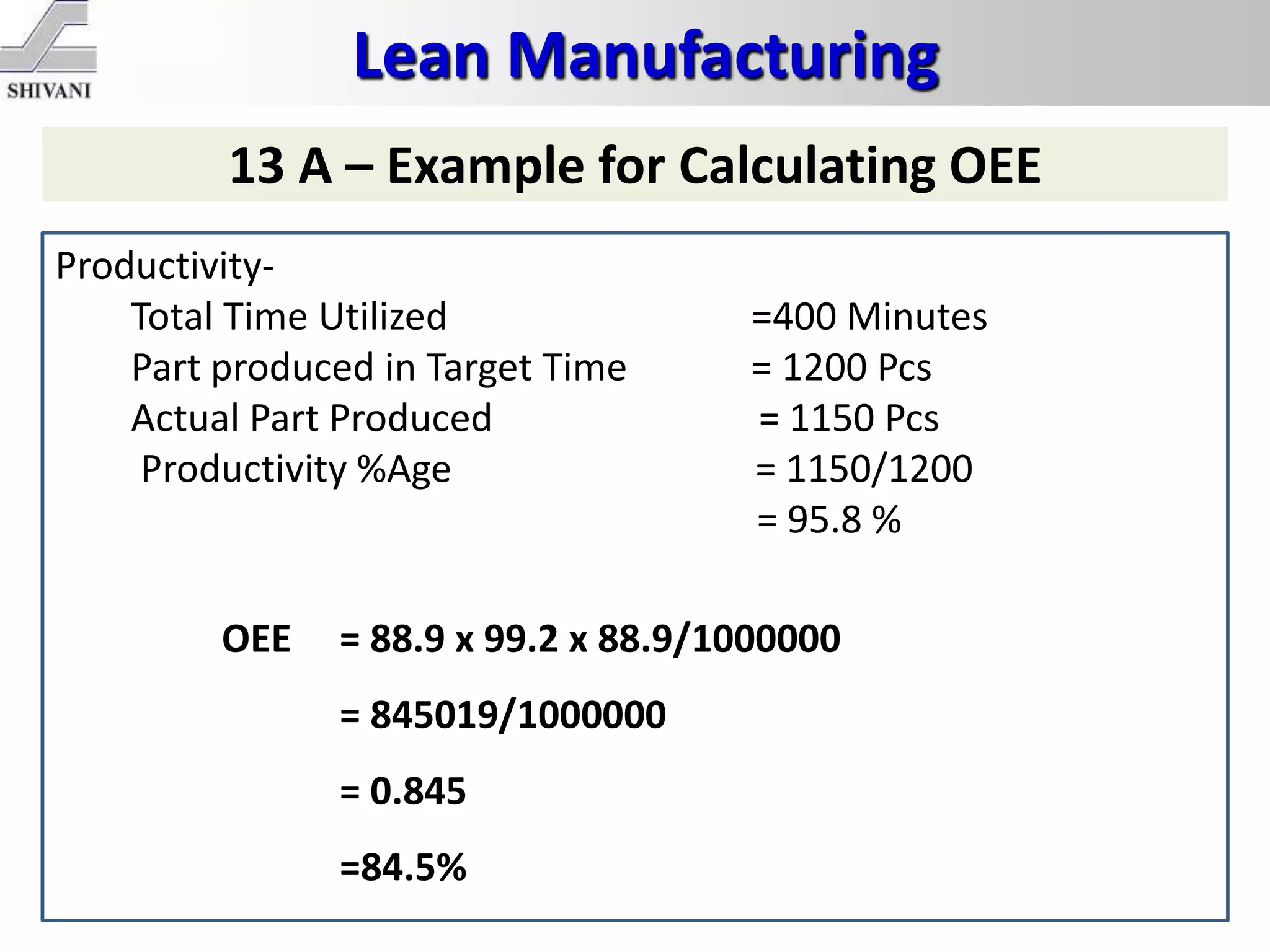
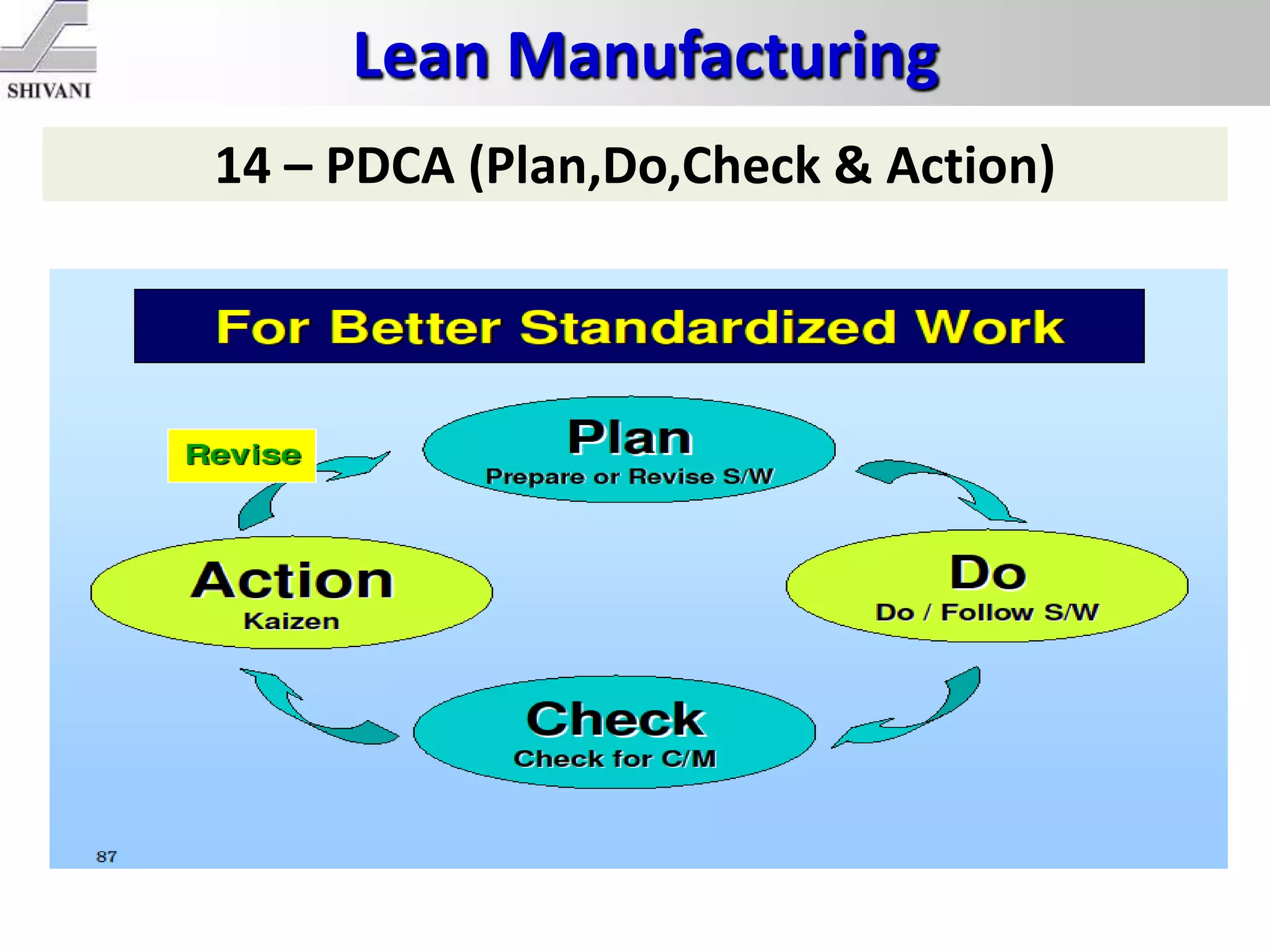
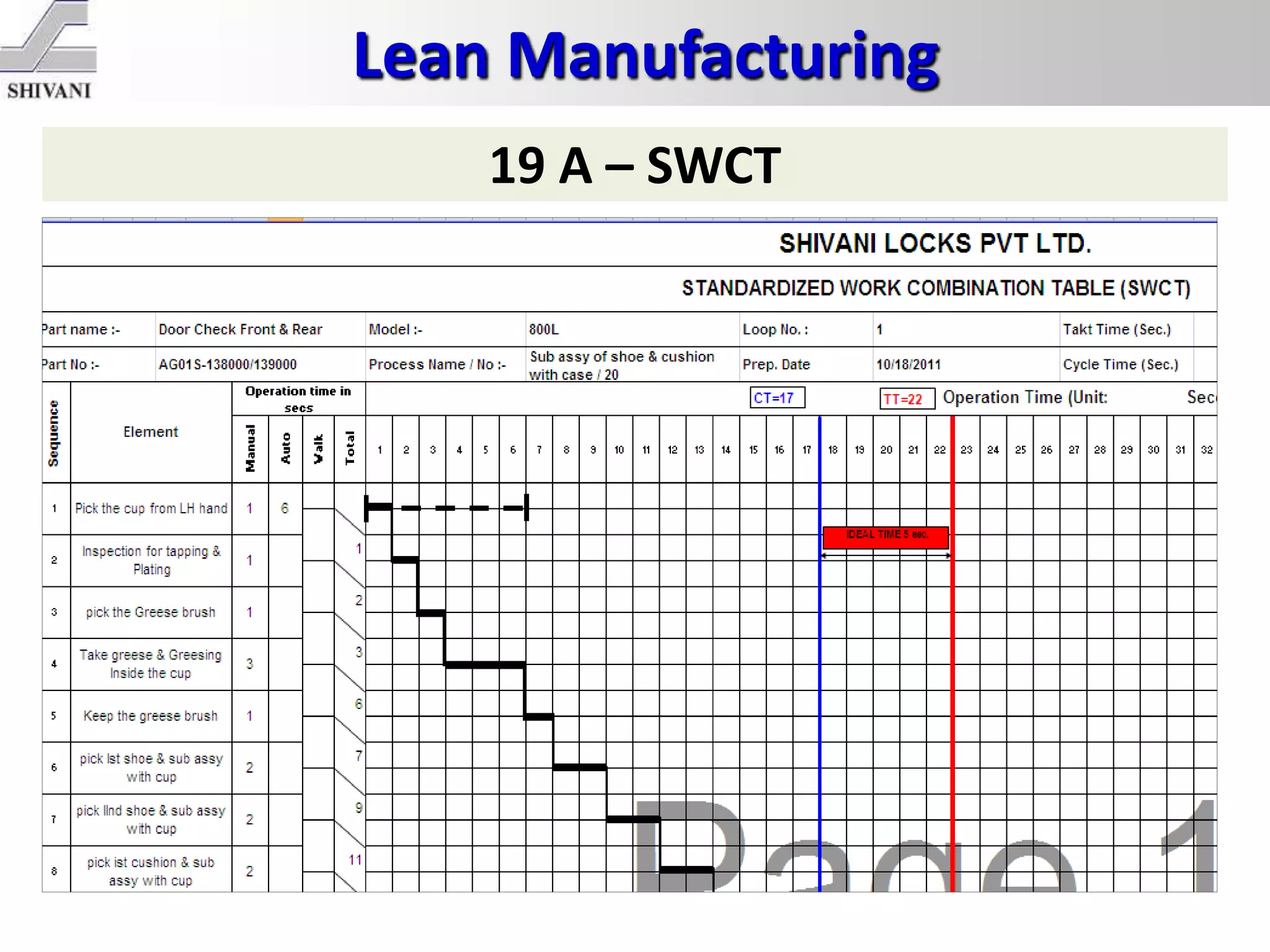
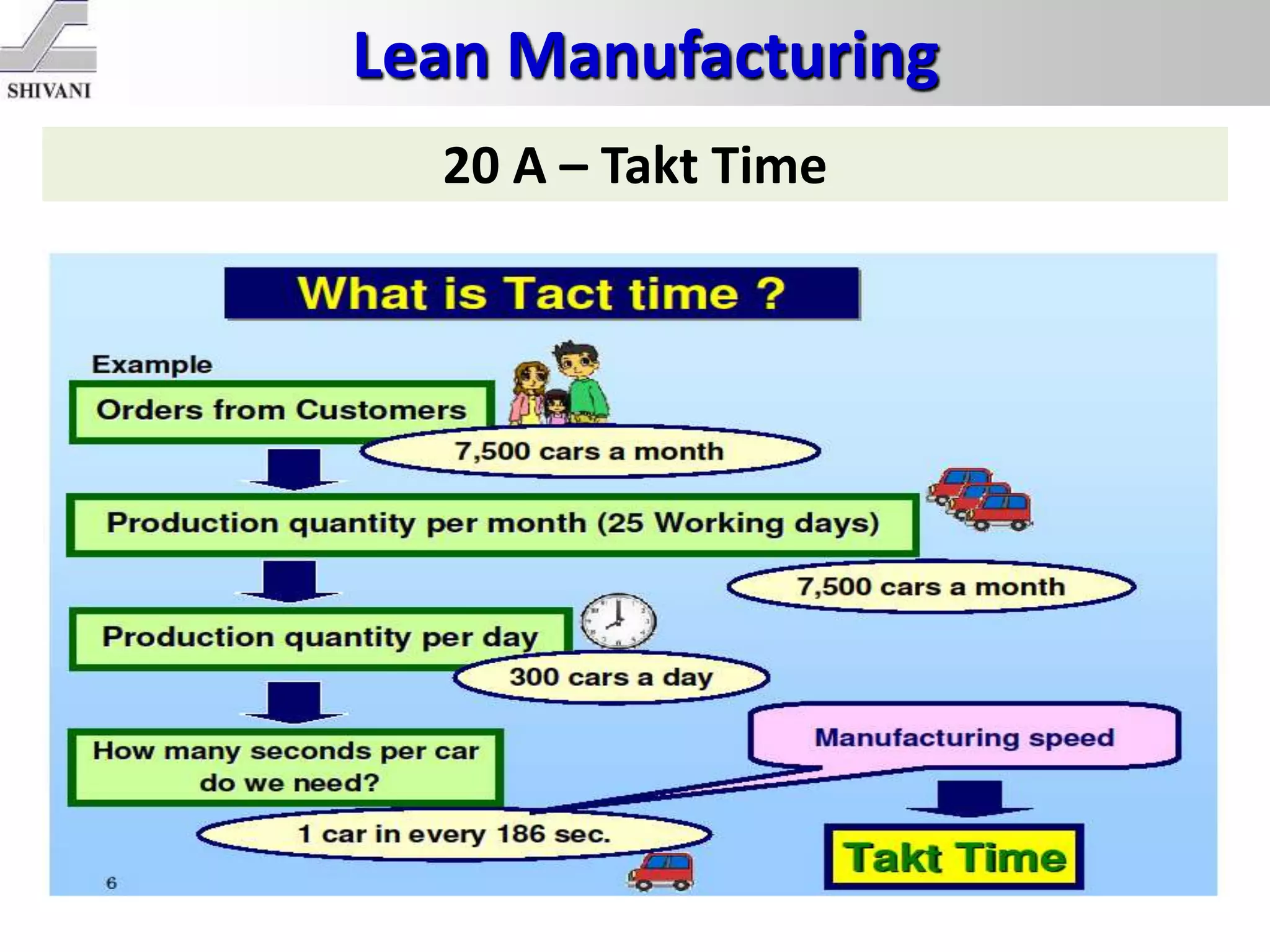
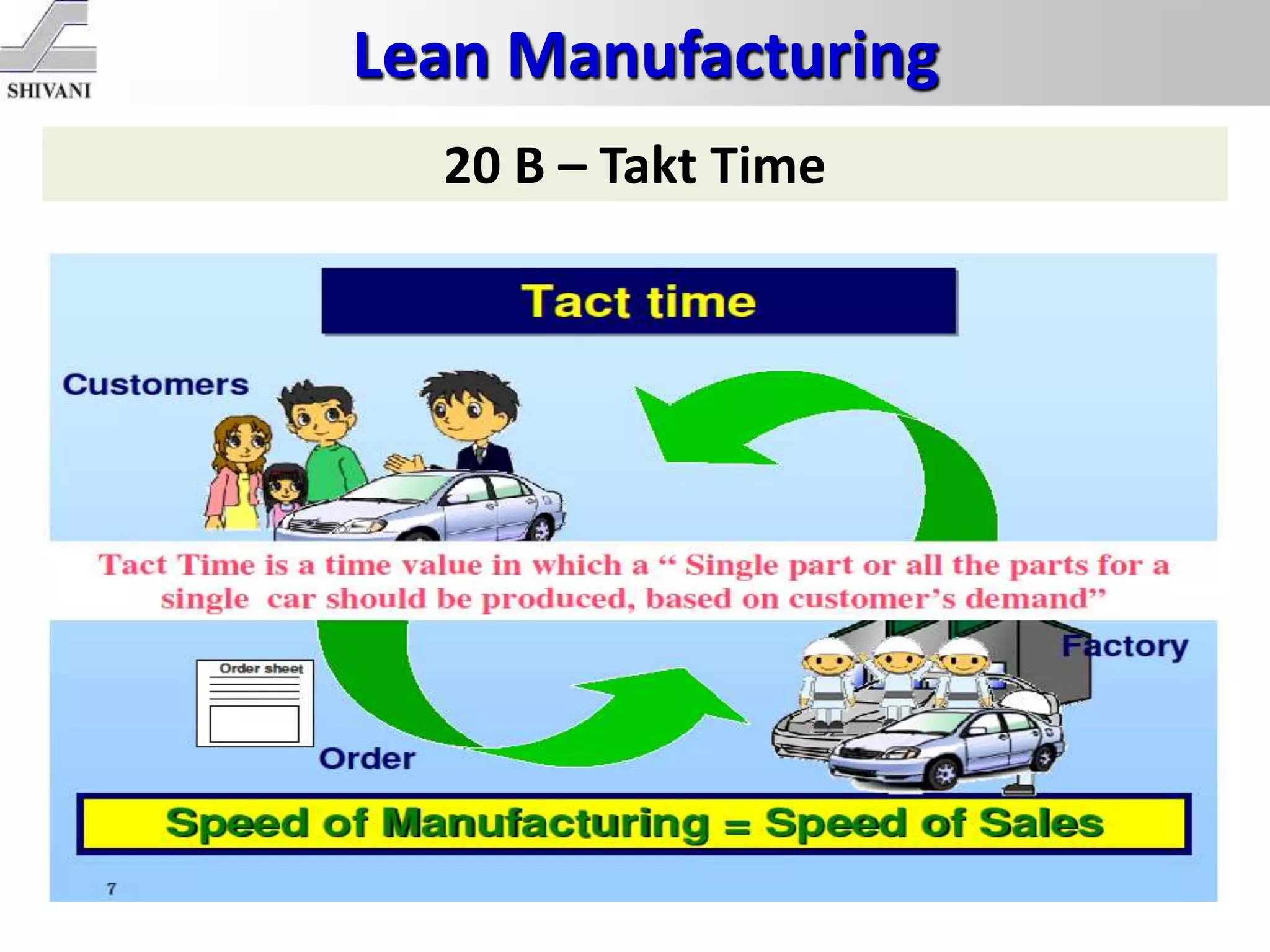
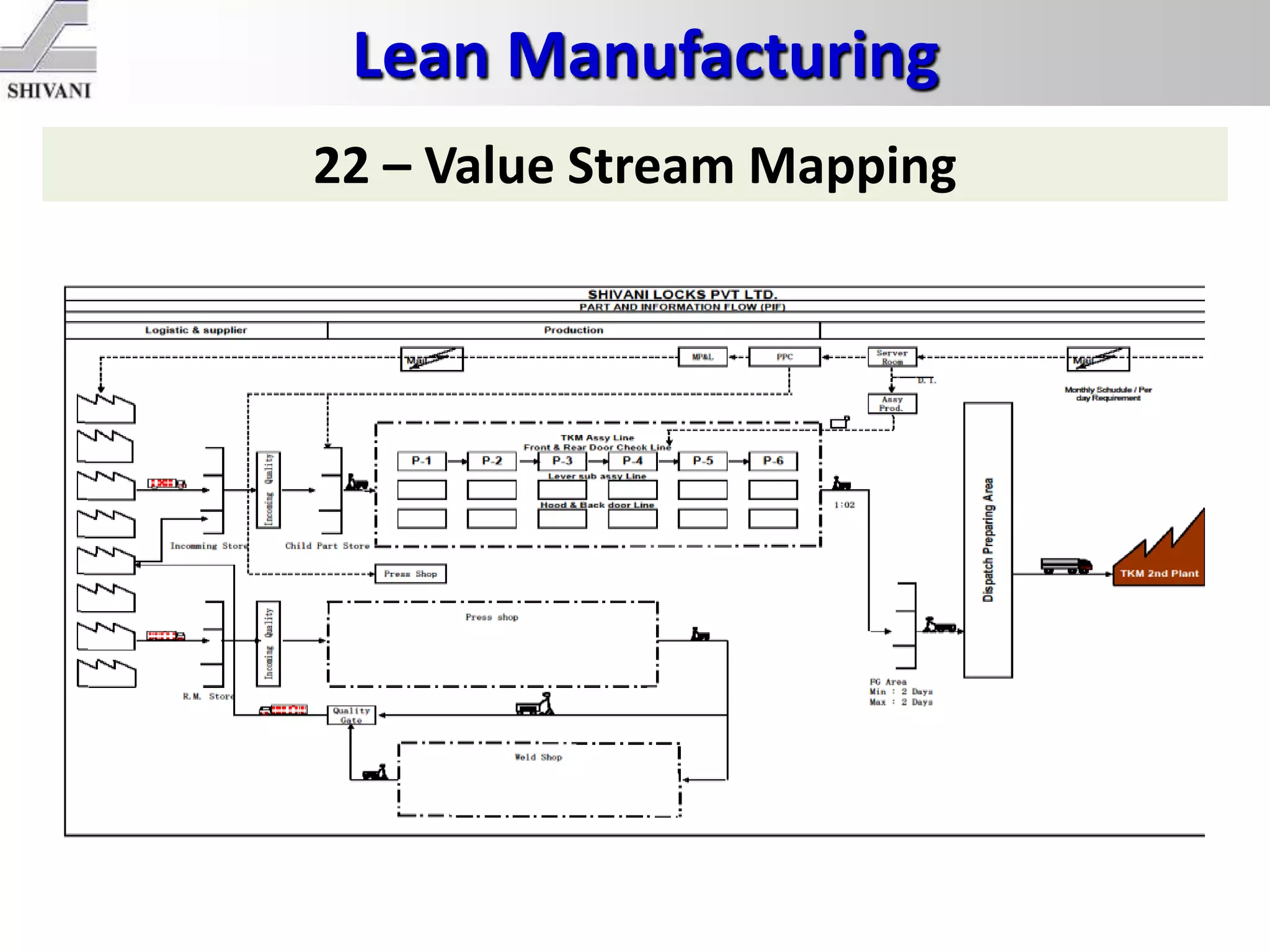
Lean manufacturing is a systematic method for eliminating waste within the manufacturing process. It aims to maximize customer value and minimize waste. Some key tools of lean manufacturing include 5S, continuous flow, just-in-time production, kaizen, value stream mapping, total productive maintenance, and standard work. The ultimate goal of lean is to produce only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the amount needed to eliminate waste and reduce costs.