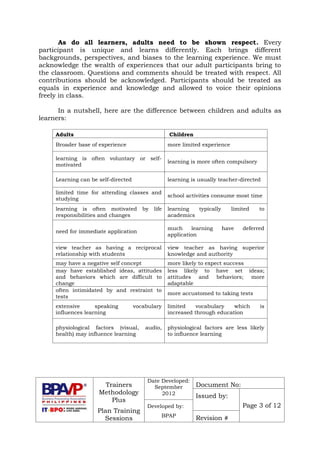
- The document discusses key characteristics of adult learners and how they differ from child learners. Adults are self-directed, goal-oriented, and draw on life experiences. They want learning to be relevant and applicable.
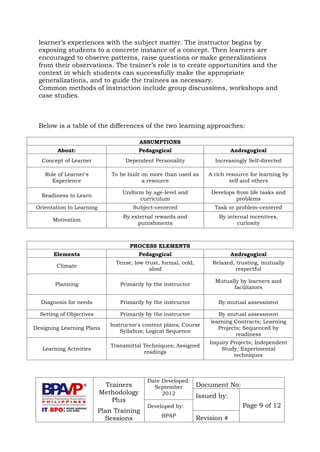
- Two approaches to teaching are described: instructor-centered pedagogy and learner-centered andragogy. Pedagogy relies on lectures while andragogy emphasizes collaboration. The best approach depends on the subject and learner characteristics.
- Motivating adult learners involves understanding their reasons for learning and addressing barriers. Social relationships, career advancement, and cognitive interest can drive motivation. Lack of time, money and confidence can block motivation.