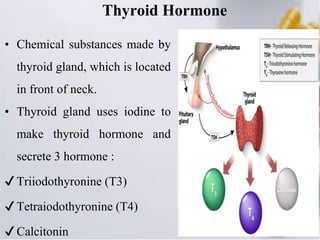
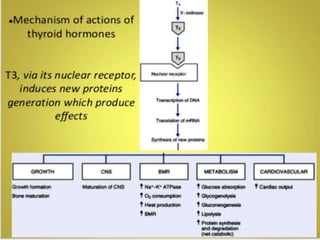
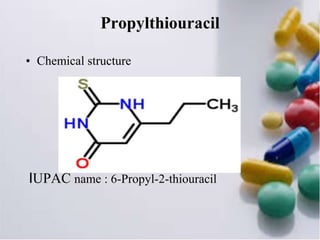
Thyroid hormone is produced by the thyroid gland and includes triiodothyronine (T3), tetraiodothyronine (T4), and calcitonin. T4 is the main hormone produced and helps regulate tissue growth. Antithyroid drugs like propylthiouracil and carbimazole are used to treat hyperthyroidism by inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversion of iodide to iodine and hormone production. Carbimazole is more potent and converts to methimazole which prevents hormone coupling and iodination. Both drugs can cause rashes, fever, and bone marrow suppression as adverse effects.