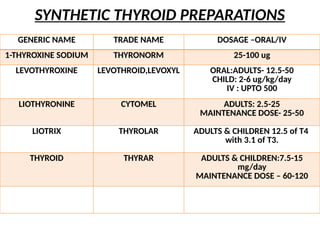
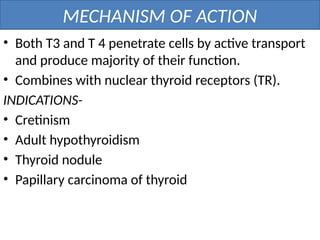
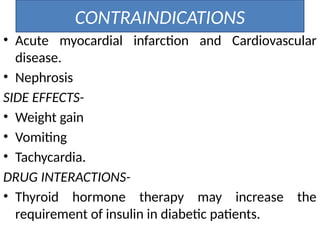
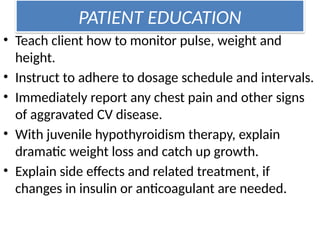
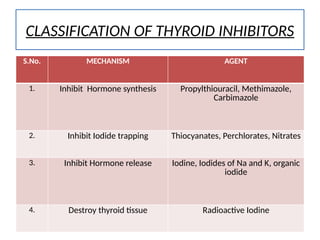
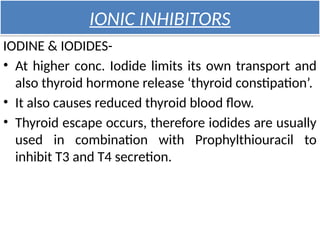
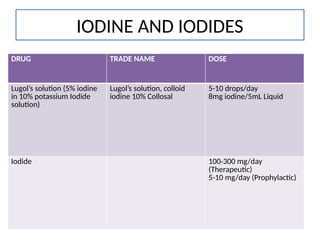
The document provides an overview of thyroid drugs, including their mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, and nursing responsibilities. It details both thyroid hormone preparations used for treating hypothyroid conditions and thyroid inhibitors for managing hyperthyroid conditions, particularly Graves' disease. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of patient education and monitoring for side effects associated with these medications.