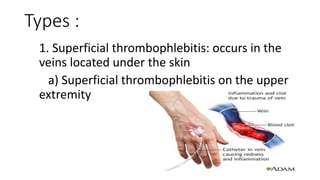
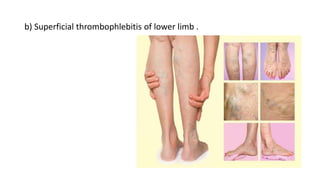
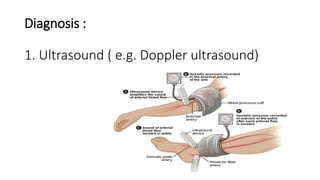
Thrombophlebitis is a circulatory condition caused by inflammation and blood clots in the veins. It can be superficial, affecting veins under the skin, or deep. Common causes include varicose veins, immobility, trauma, pregnancy, and cancer. Symptoms are swelling, redness, tenderness, and warmth around the affected vein. Diagnosis involves ultrasound, D-dimer blood tests, and imaging tests. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and preventing clots from worsening using blood thinners, anti-inflammatories, physiotherapy, and sometimes stents or surgery to remove clots.