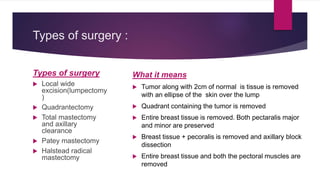
Mastectomy is the surgical removal of one or both breasts to treat breast cancer. There are several types of mastectomies that remove varying amounts of breast tissue. Complications can include lymphedema, nerve damage, hematoma, seroma, chronic pain, and infection. The document discusses the different types of mastectomies and breast surgery procedures, as well as indications for surgery, postoperative radiotherapy, complications, and incision types.