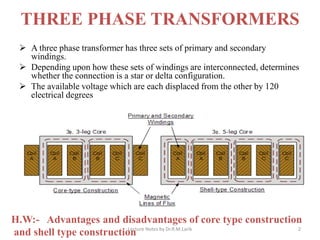
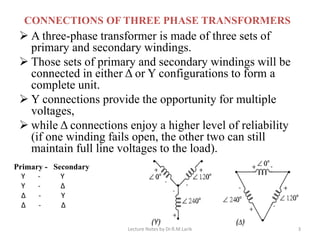
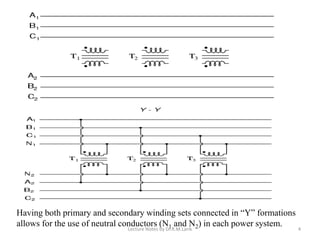
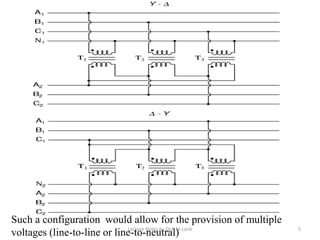
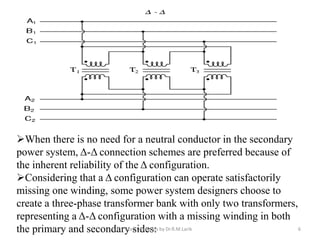
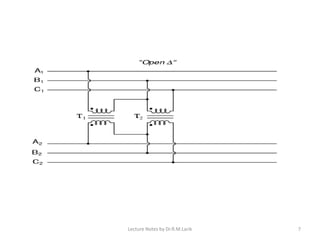
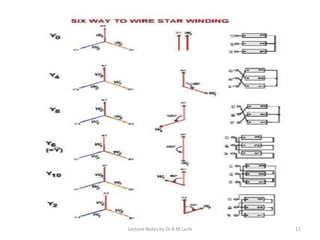
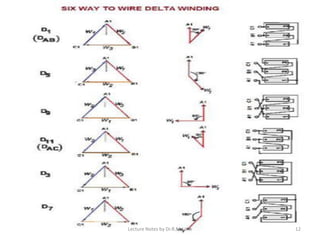
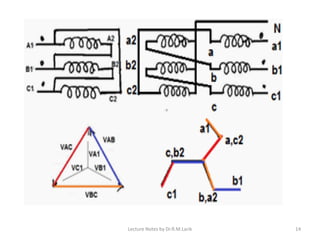
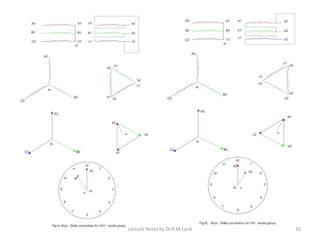
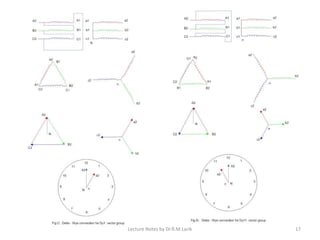
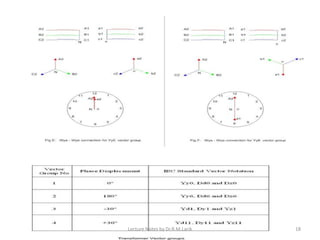
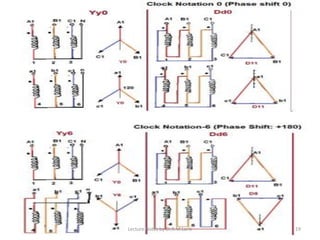
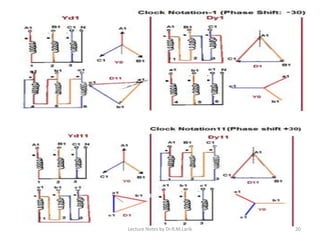
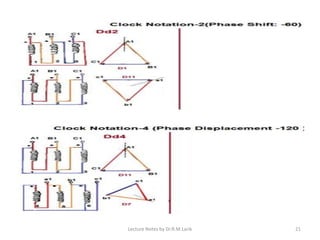
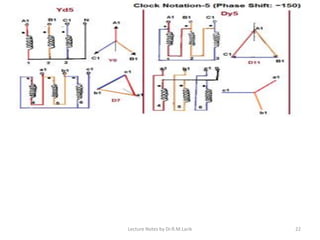
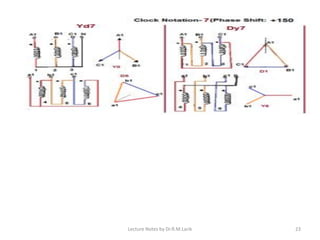
Three phase transformers have three sets of primary and secondary windings that can be connected in either a star or delta configuration. The vector group of a transformer indicates the phase difference between the primary and secondary windings, which is important when connecting multiple transformers in parallel. Vector groups use letters and numbers to denote the winding configuration and phase displacement between windings. Zigzag transformers contain six coils on three cores and can cancel certain harmonic currents.