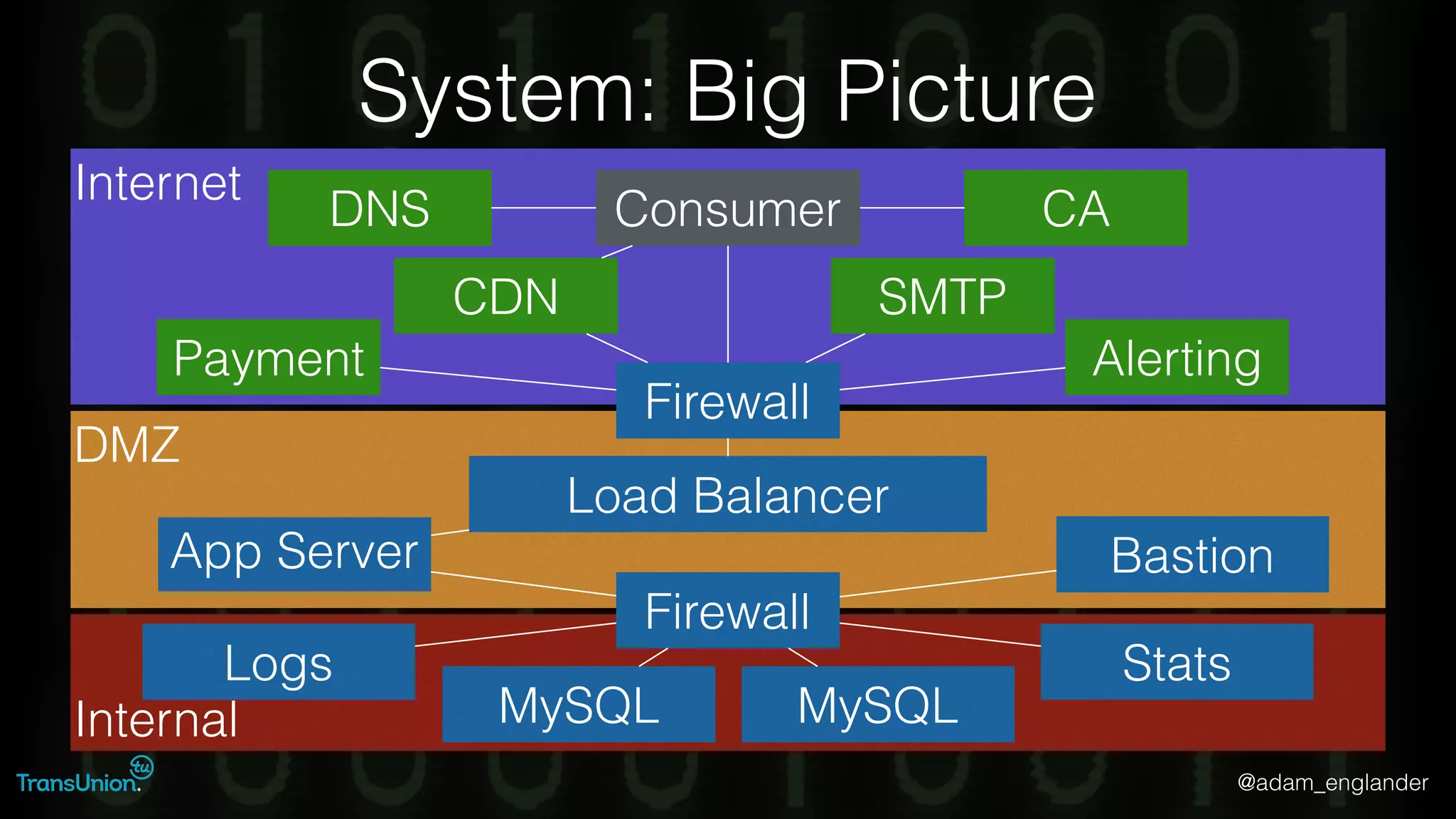
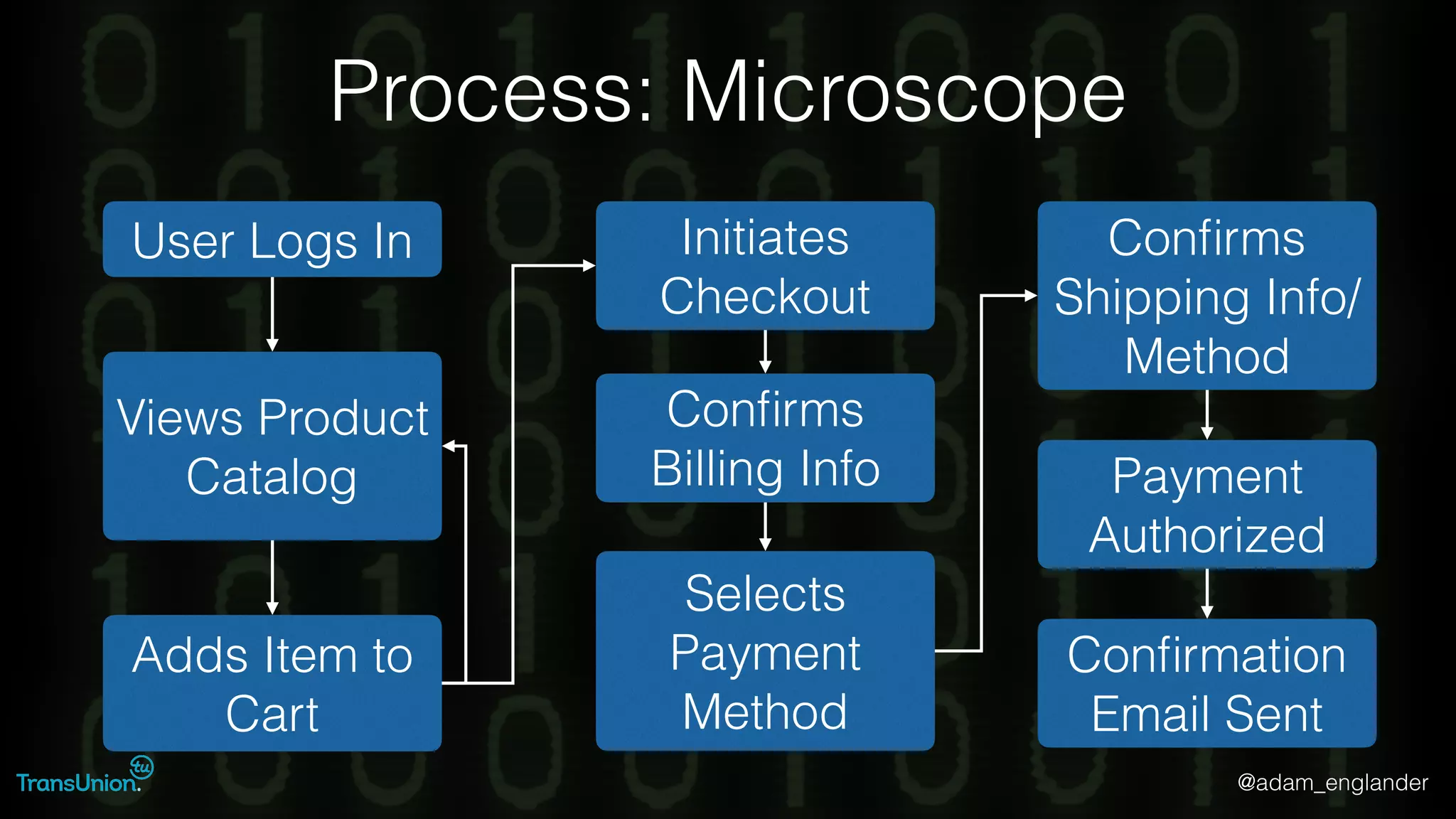
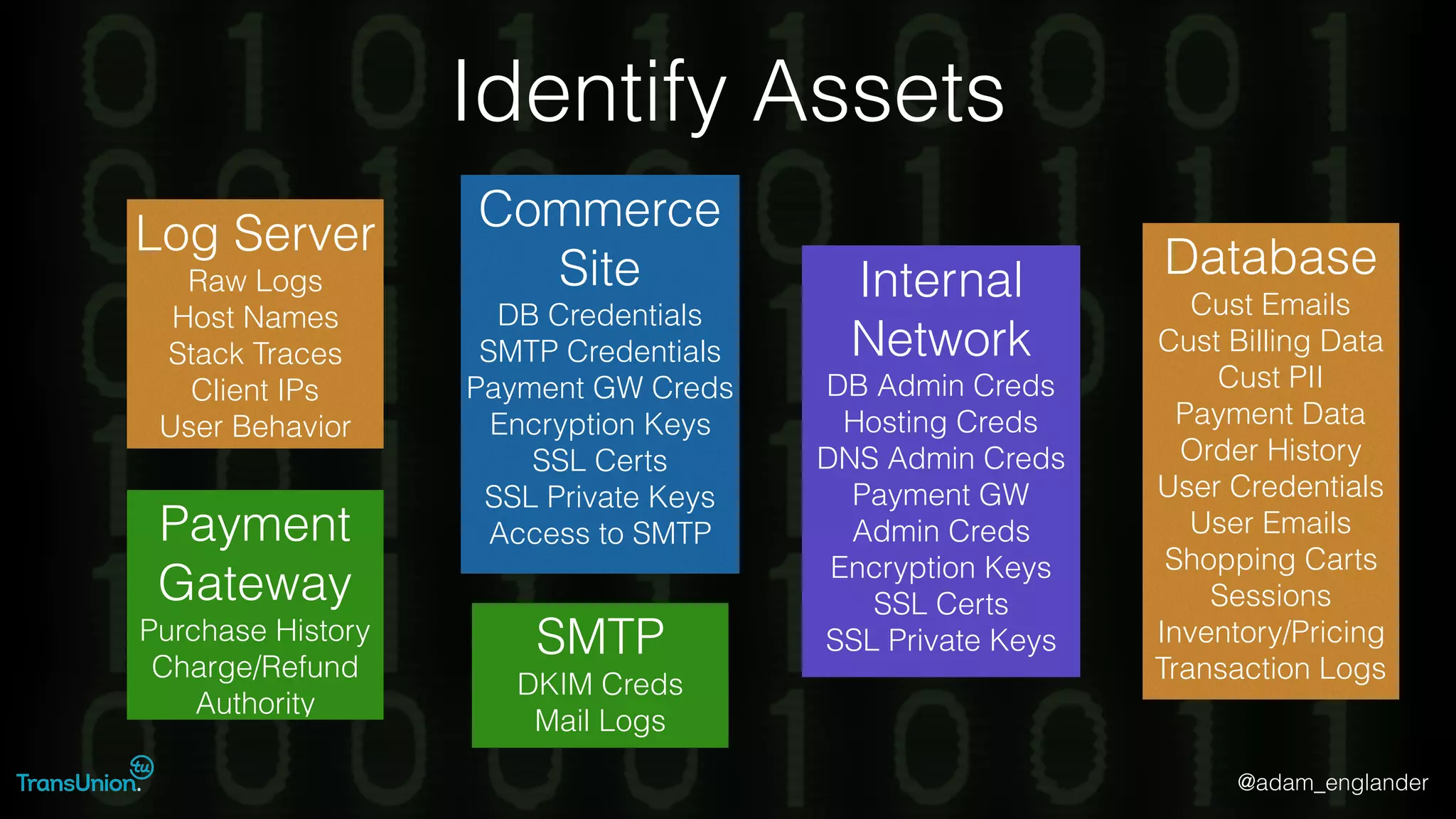
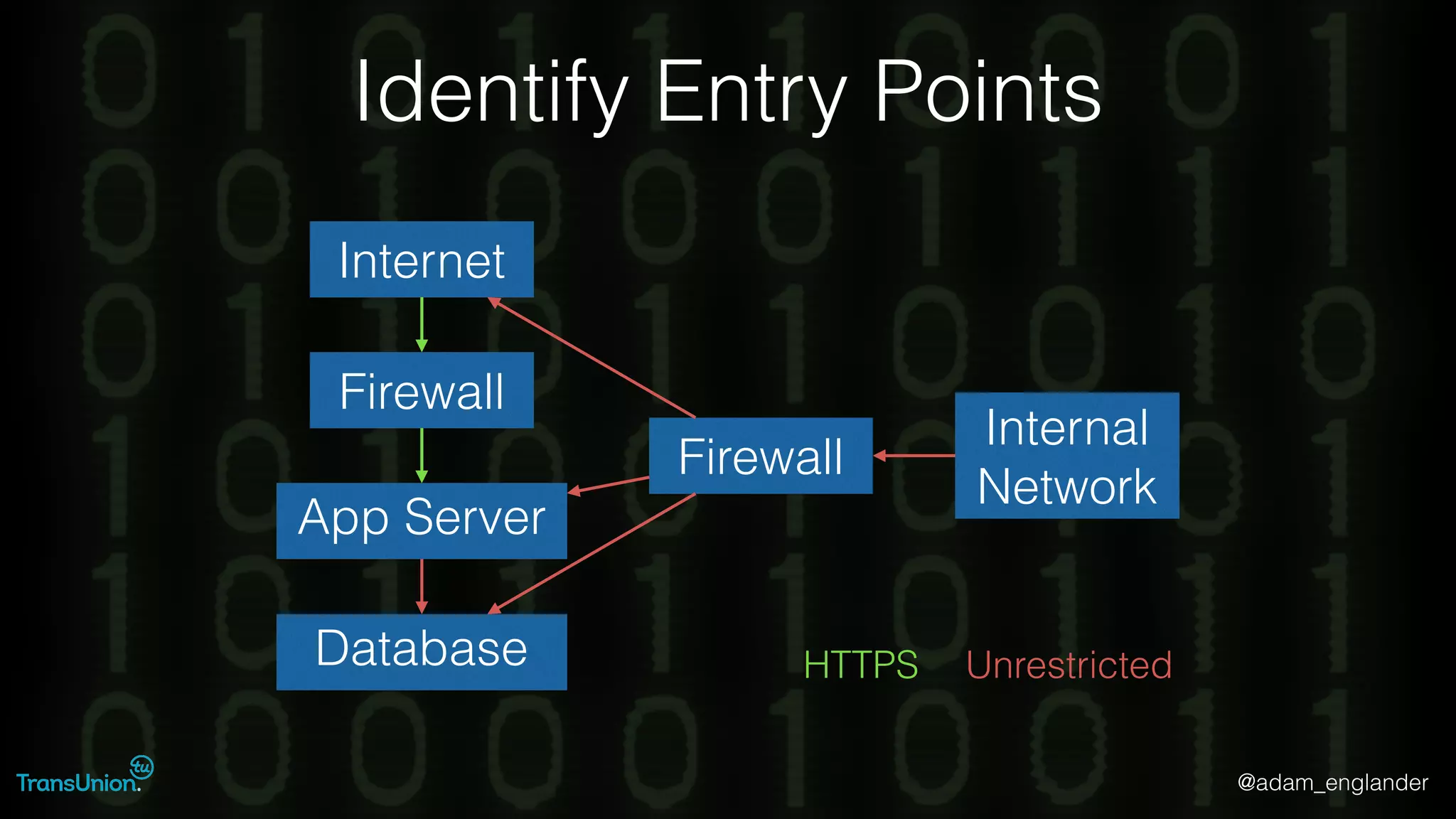
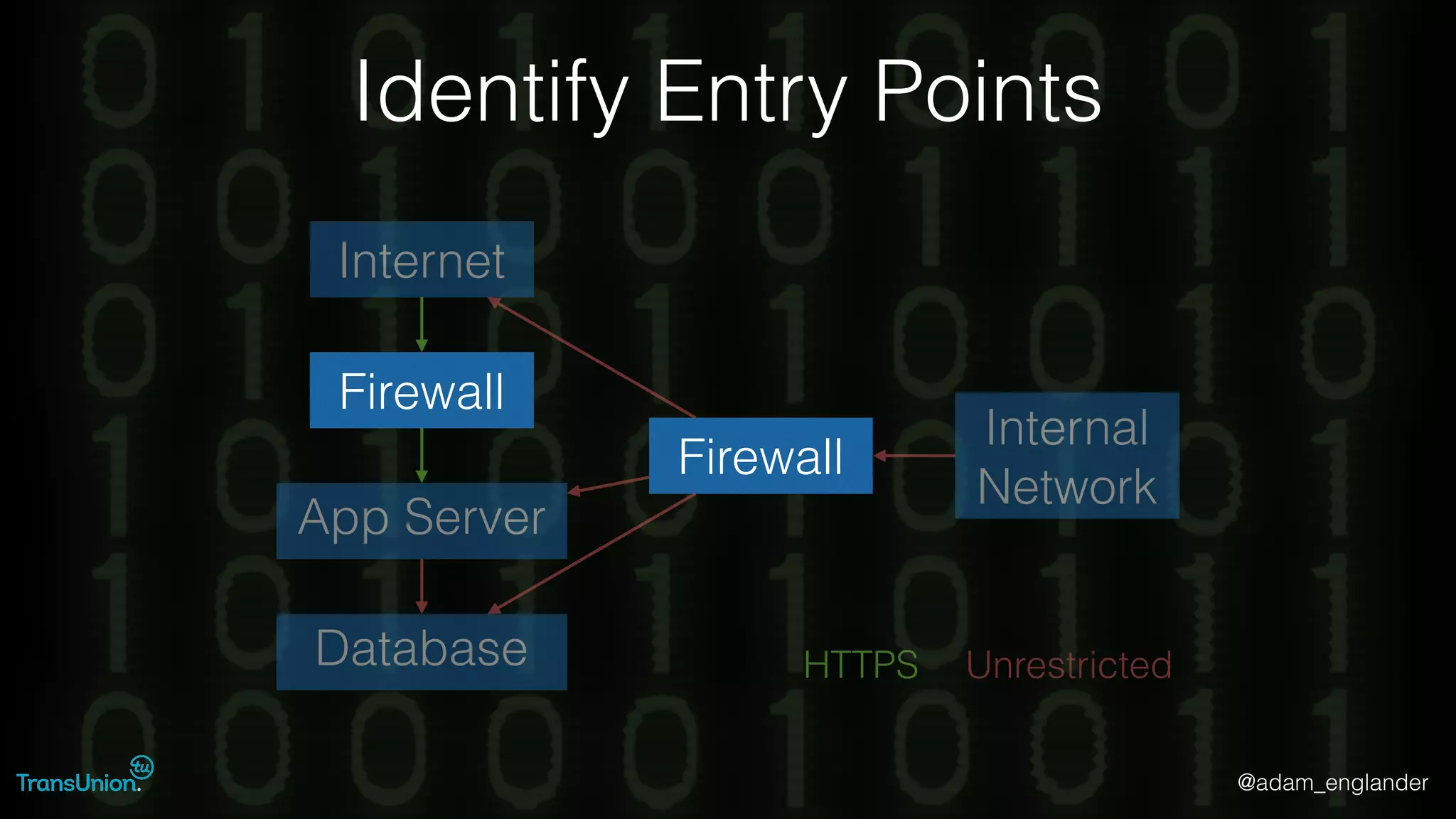
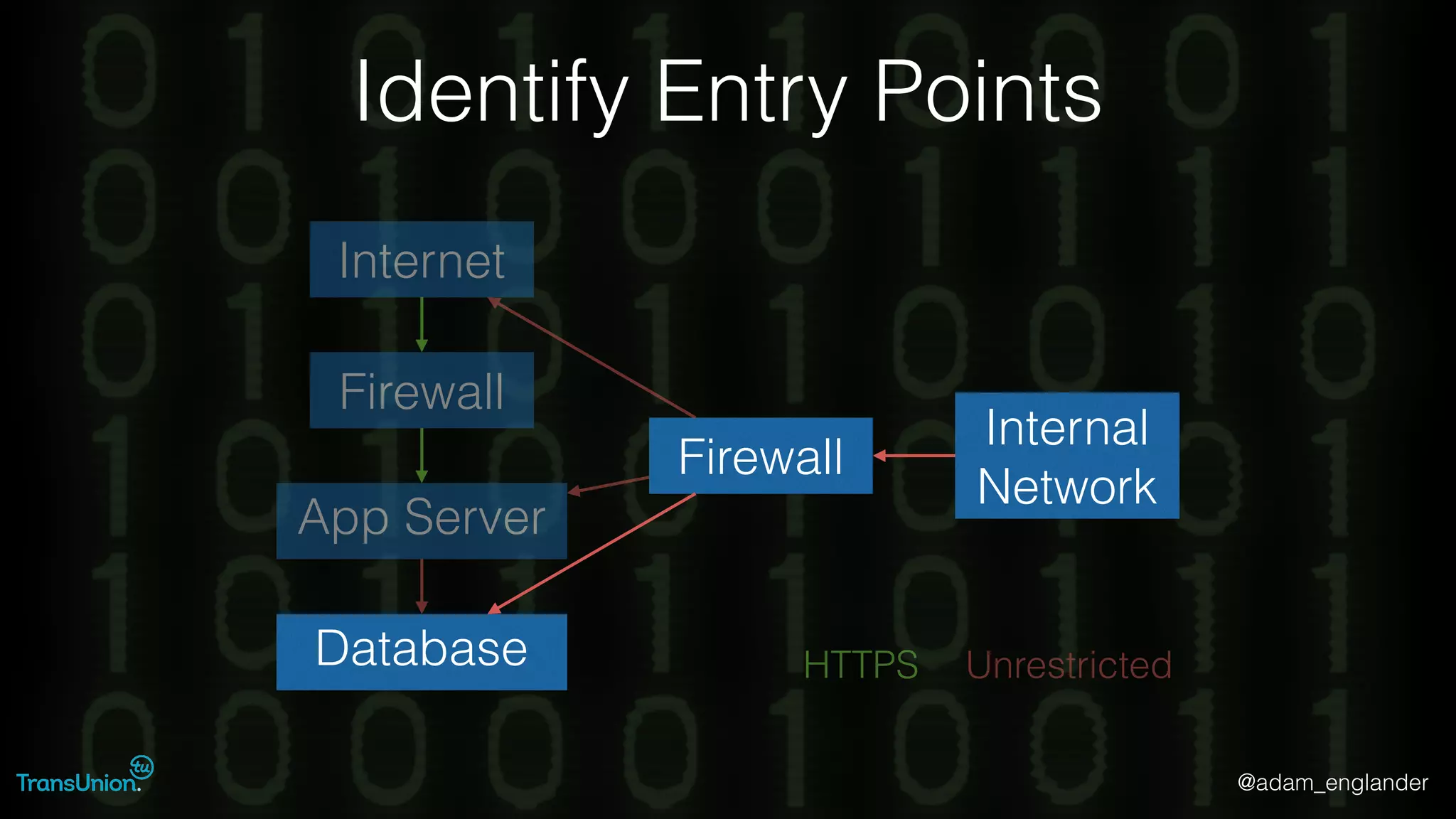
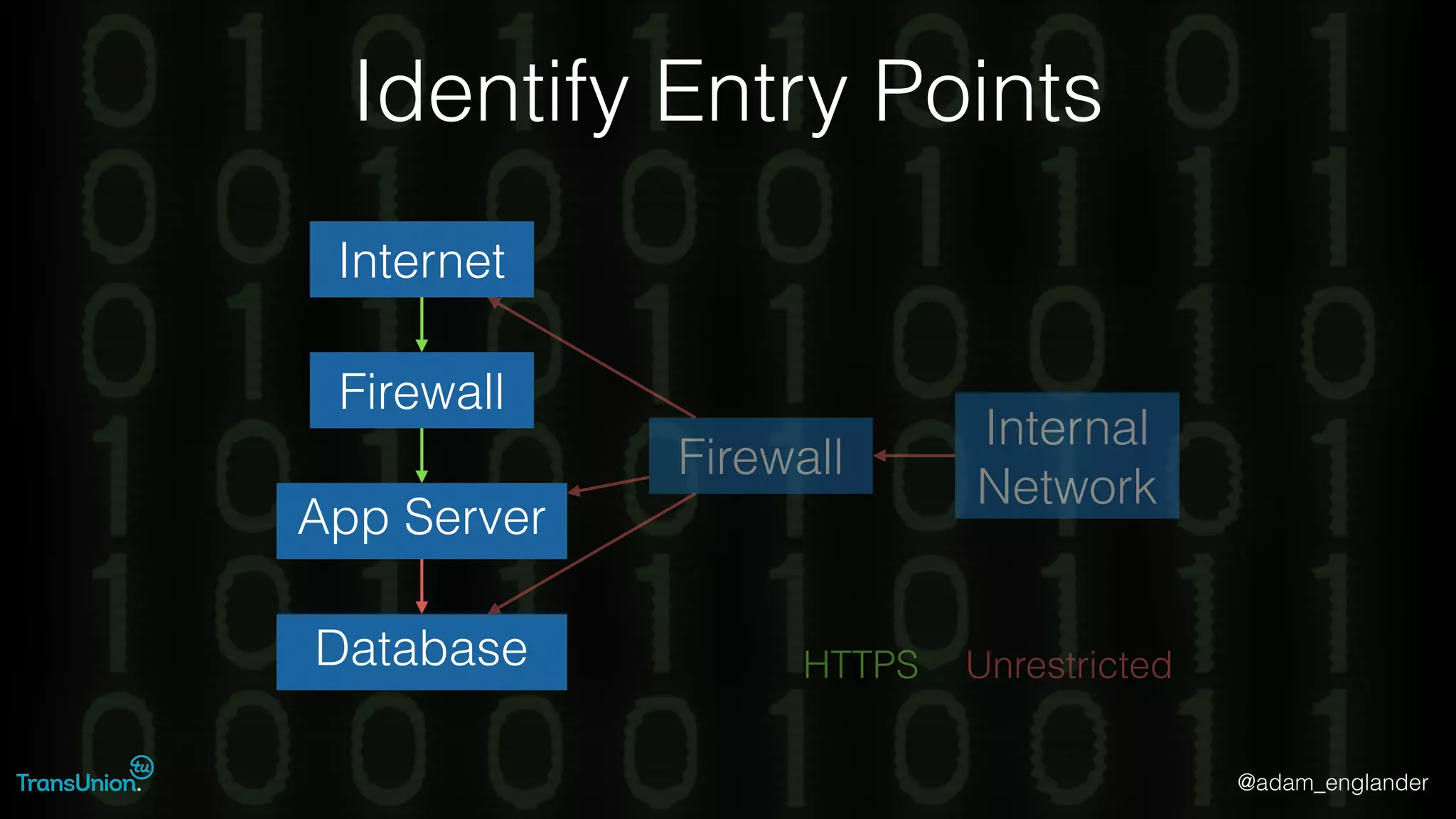
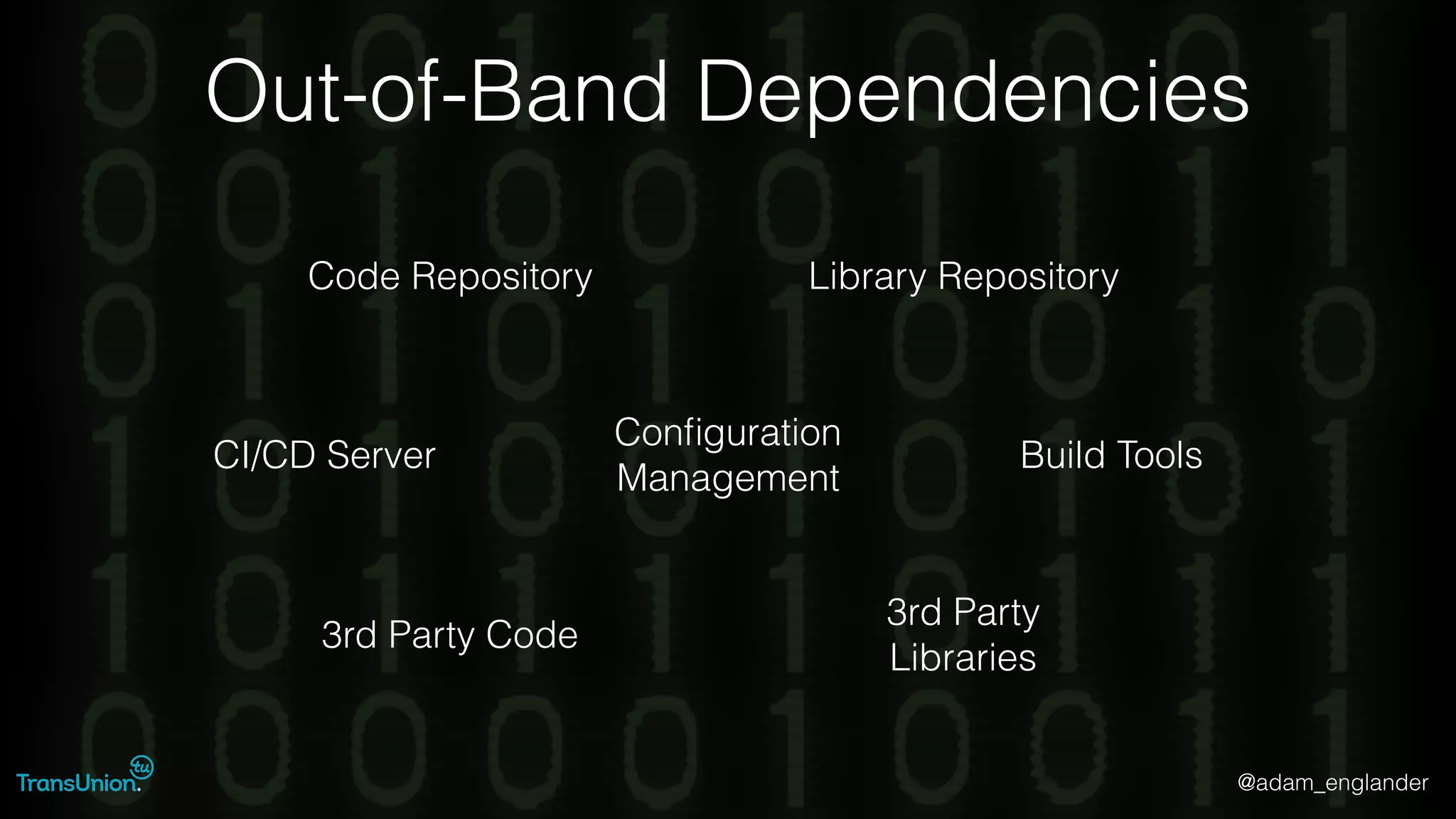
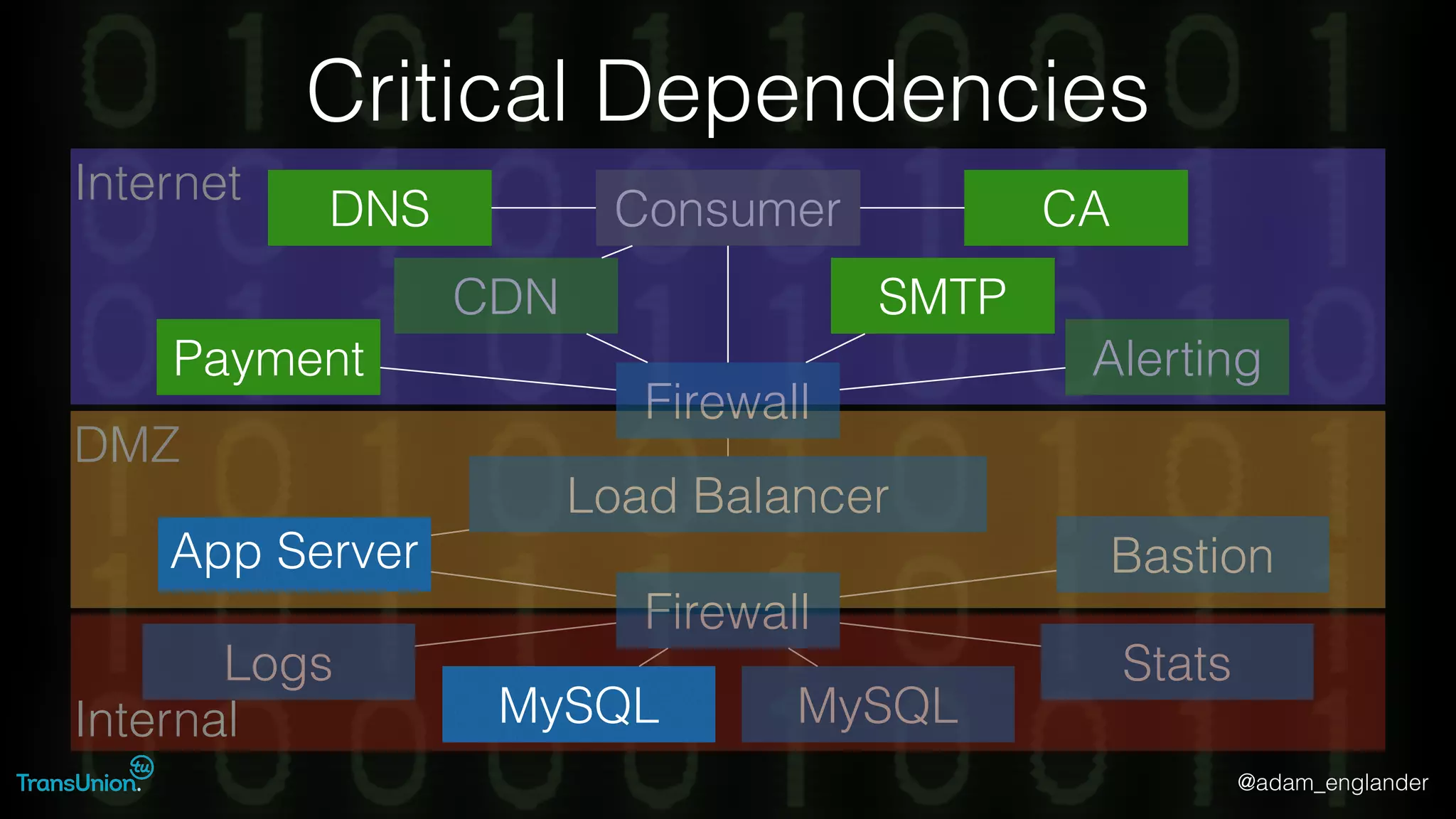
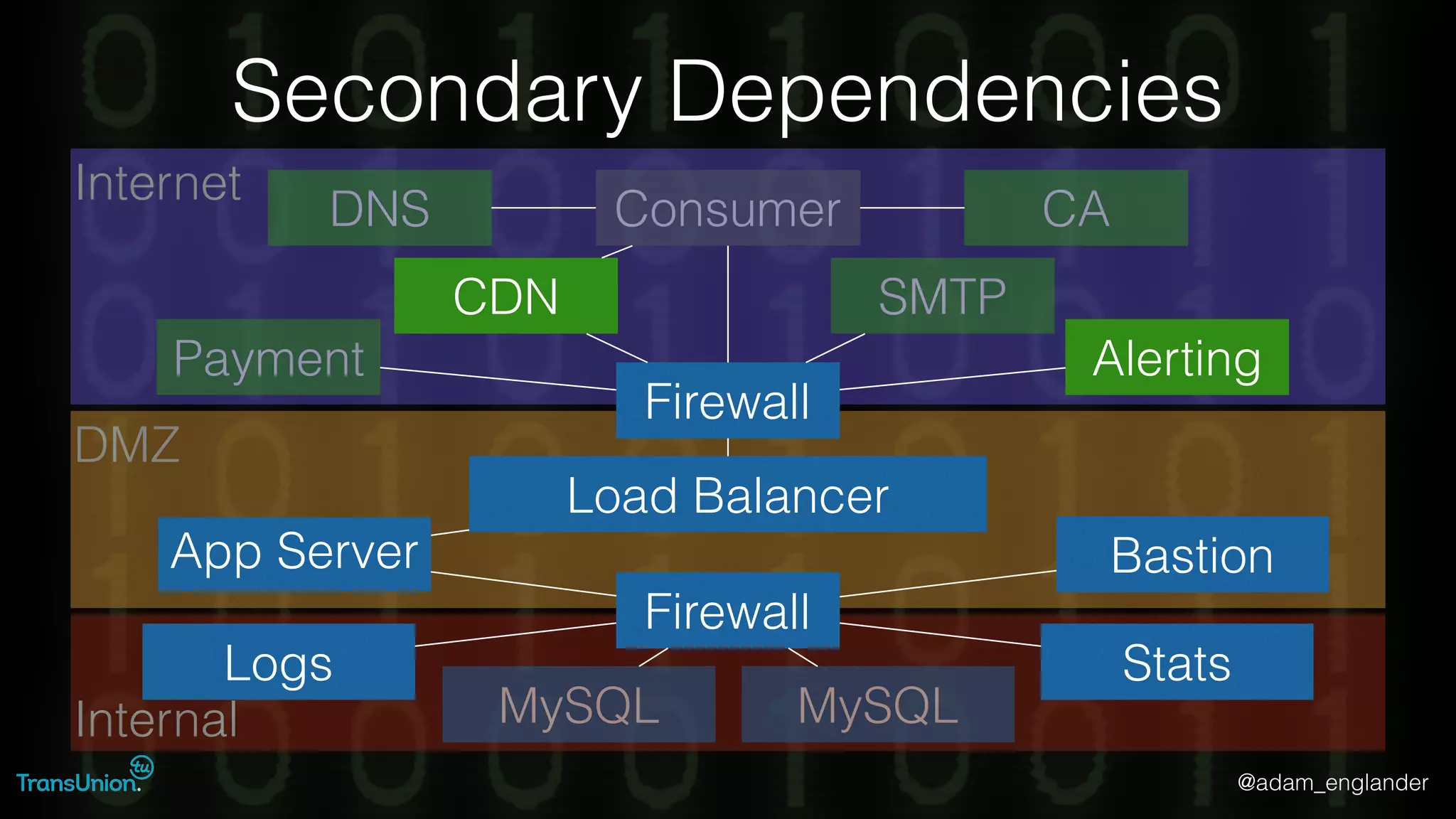
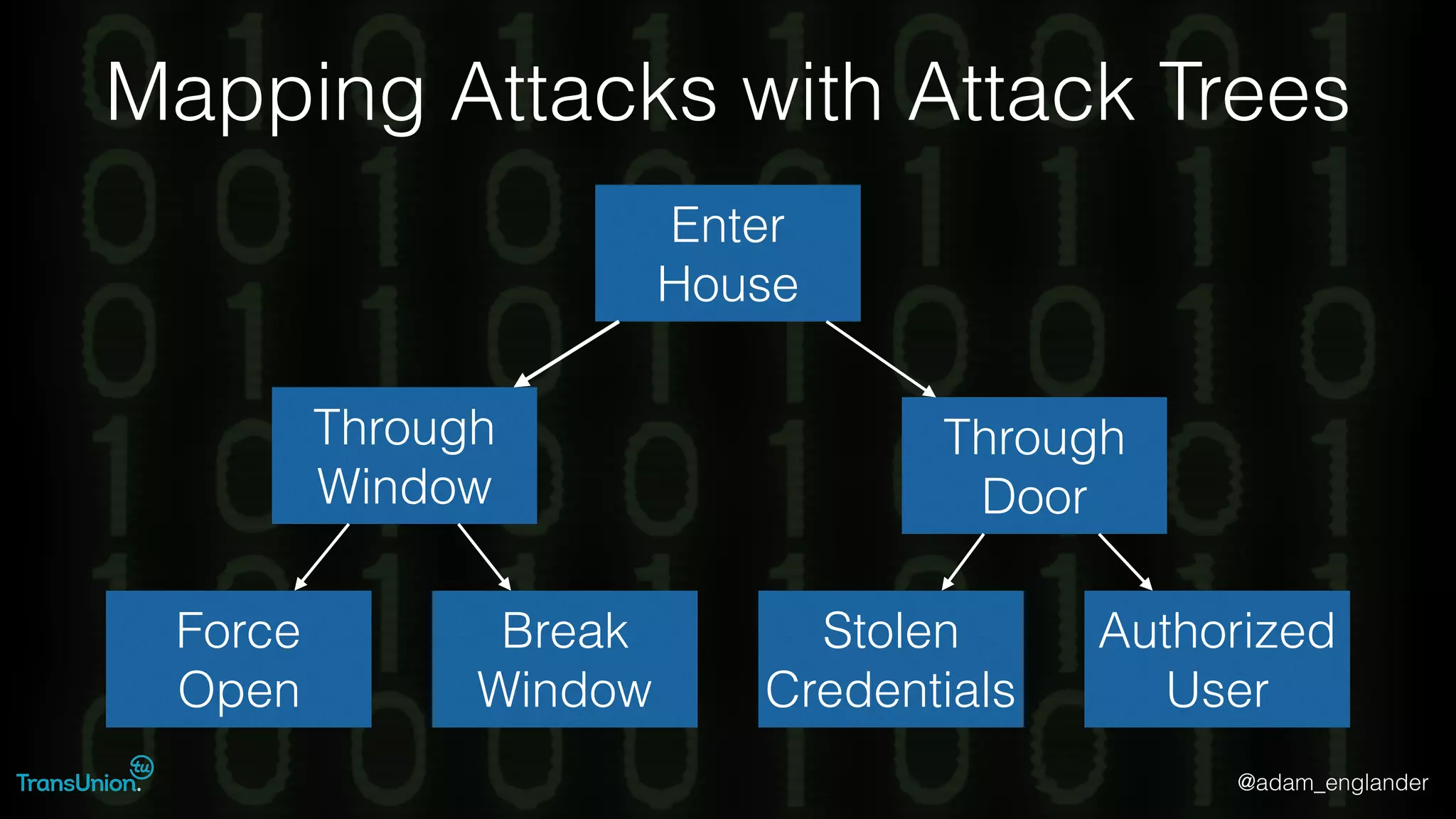
The document discusses threat modeling and provides an overview of the threat modeling process. It describes documenting assets and entry points, identifying threats using techniques like STRIDE and attack trees, assessing risk with DREAD, and resolving threats by mitigating them in stages from quick reductions to complete mitigation. An example threat of an insider attack on a database is analyzed in detail. The document concludes by recommending starting with the OWASP Top 10, incorporating threat modeling into the SDLC, and improving skills through resources like books and games.