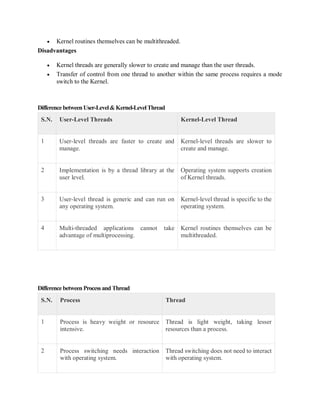
A thread is a flow of execution through a process's code that maintains its own program counter, registers, and stack. Threads allow for parallel execution within a process to improve performance. There are two types of threads: user-level threads managed by a thread library and kernel-level threads managed by the operating system kernel. User-level threads are faster to create but cannot take advantage of multiprocessing, while kernel-level threads can utilize multiple processors but are slower to create and manage.