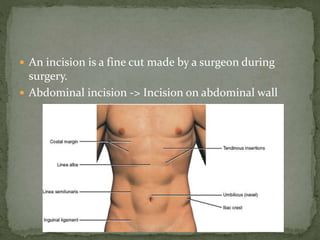
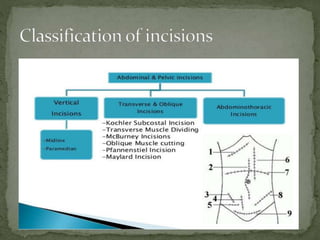
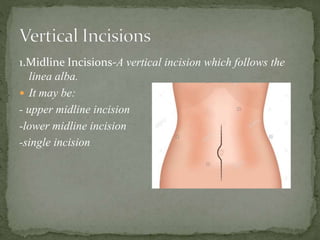
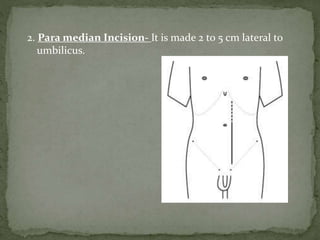
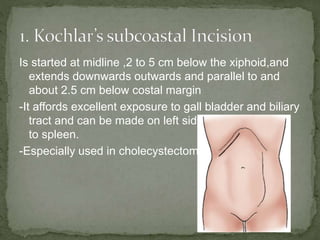
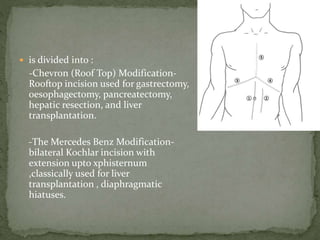
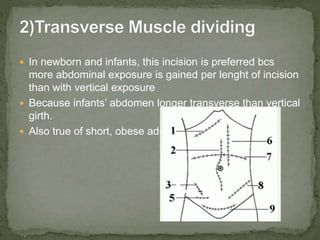
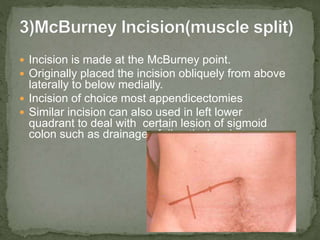
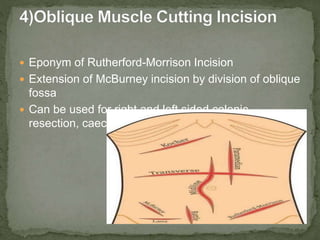
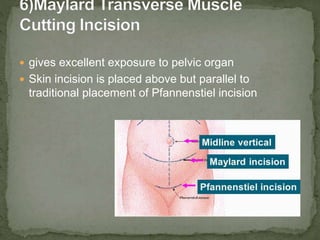
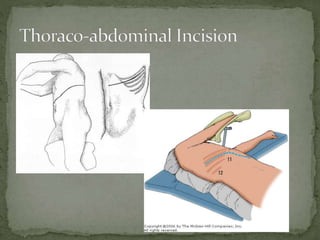
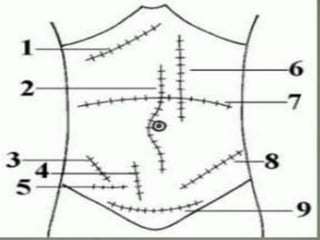
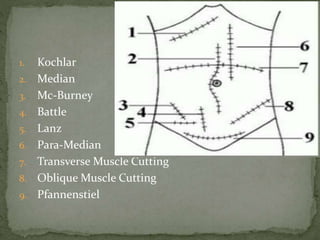
An incision is a cut made by a surgeon during surgery. This document describes and compares various types of abdominal incisions including their advantages and disadvantages. Midline incisions provide good access but are cosmetically disapproved. Para-median incisions have weaker muscle repair but access lateral structures. Transverse incisions have the best cosmetic results but take more time. McBurney incisions are best for appendicectomies while Pfannenstiel incisions are commonly used in gynecological and obstetric surgeries.