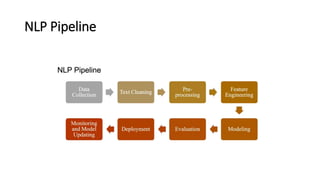
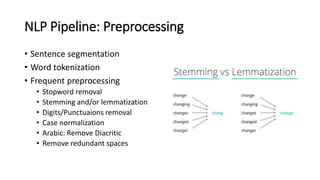
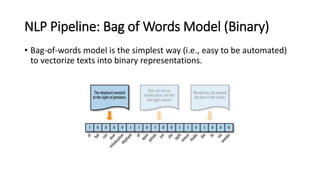
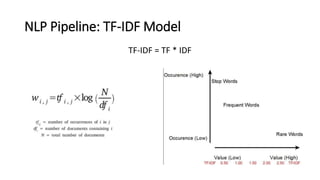
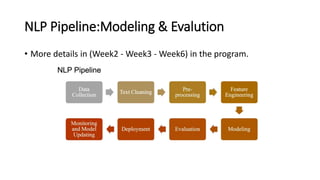
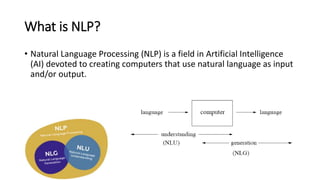
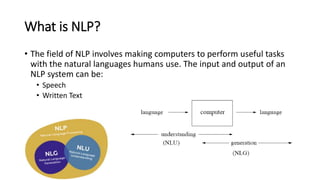
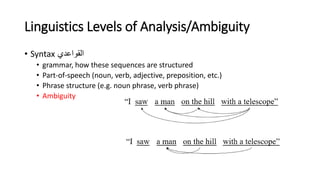
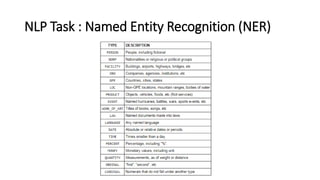
The document provides an introduction to natural language processing (NLP). It defines NLP as a field of artificial intelligence devoted to creating computers that can use natural language as input and output. Some key NLP applications mentioned include data analysis of user-generated content, conversational agents, translation, classification, information retrieval, and summarization. The document also discusses various linguistic levels of analysis like phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics that involve ambiguity challenges. Common NLP tasks like part-of-speech tagging, named entity recognition, parsing, and information extraction are described. Finally, the document outlines the typical steps in an NLP pipeline including data collection, text cleaning, preprocessing, feature engineering, modeling and evaluation.










![NLP Task : Parsing and dependency parsing
• Shallow (or Partial) parsing identifies the (base) syntactic phases in a
sentence.
• After NEs are identified, dependency parsing is often applied to
extract the syntactic/dependency relations between the NEs.
[NP He] [v saw] [NP the big dog]
[PER Bill Gates] founded [ORG Microsoft].
found
Bill Gates Microsoft
nsubj dobj
Dependency Relations
nsubj(Bill Gates, found)
dobj(found, Microsoft)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtonlp-gazaskygeeks-210911185232/85/Introduction-to-natural-language-processing-NLP-16-320.jpg)