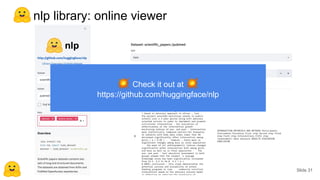
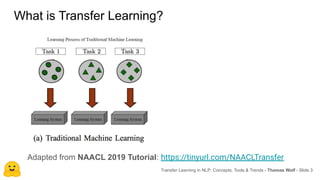
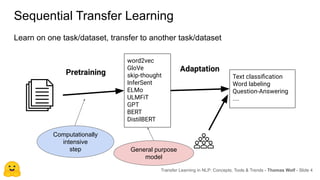
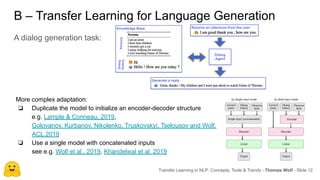
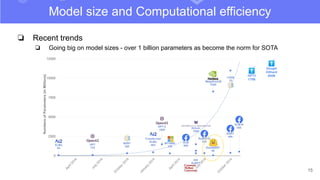
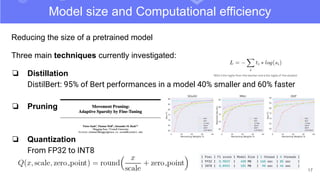
The document discusses transfer learning in natural language processing (NLP), emphasizing the concepts, tools, and trends in the field. It highlights the advantages of pretraining models and their adaptation for specific tasks, illustrating workflow, efficiency, and challenges such as model size and generalization issues. Additionally, the document outlines the initiatives of Hugging Face in democratizing NLP through the development of open-source libraries and tools.







![The generalization problem:
❏ Models are brittle: fail when text is modified, even with meaning preserved
❏ Models are spurious: memorize artifacts and biases instead of truly learning
Brittle Spurious
Robin Jia and Percy Liang, “Adversarial Examples for Evaluating Reading Comprehension
Systems,” ArXiv:1707.07328 [Cs], July 23, 2017, http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.07328
R. Thomas McCoy, Junghyun Min, and Tal Linzen, “BERTs of a Feather Do Not Generalize Together: Large Variability in Generalization across Models with Similar
Test Set Performance,” ArXiv:1911.02969 [Cs], November 7, 2019, http://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02969.
18
The inductive bias question](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fwdays2020-transferlearningandhuggingface-200828074212/85/Thomas-Wolf-An-Introduction-to-Transfer-Learning-and-Hugging-Face-18-320.jpg)