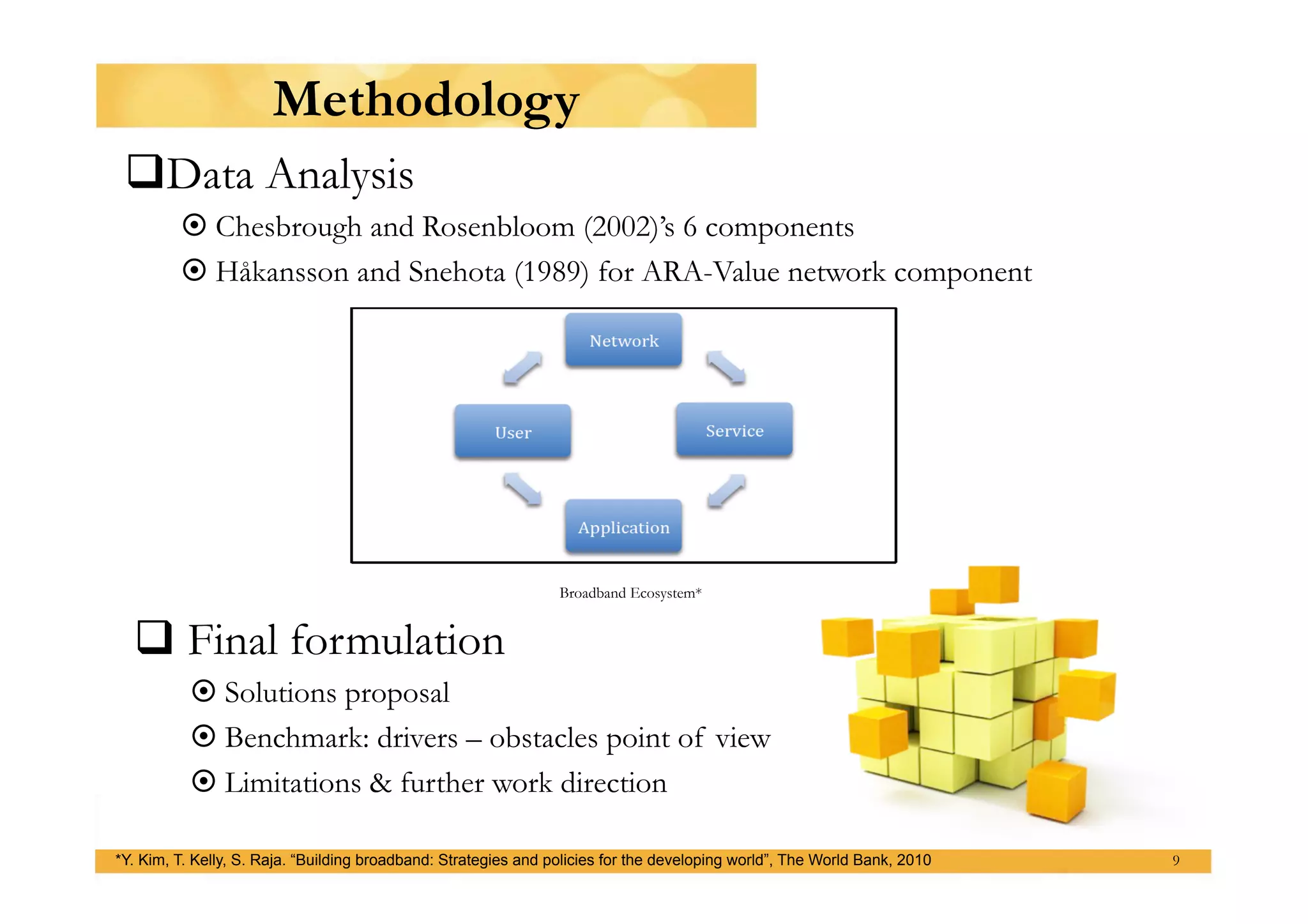
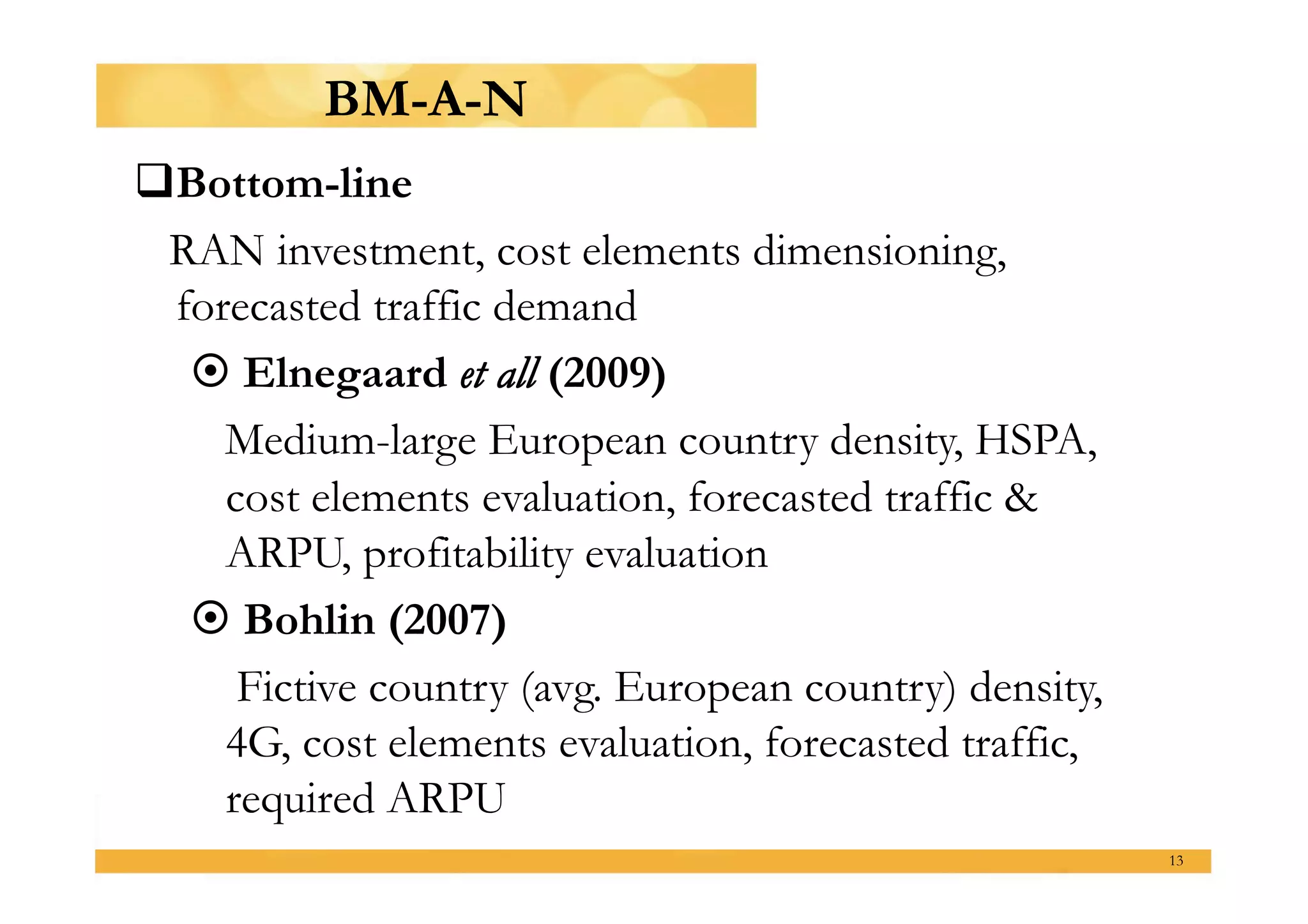
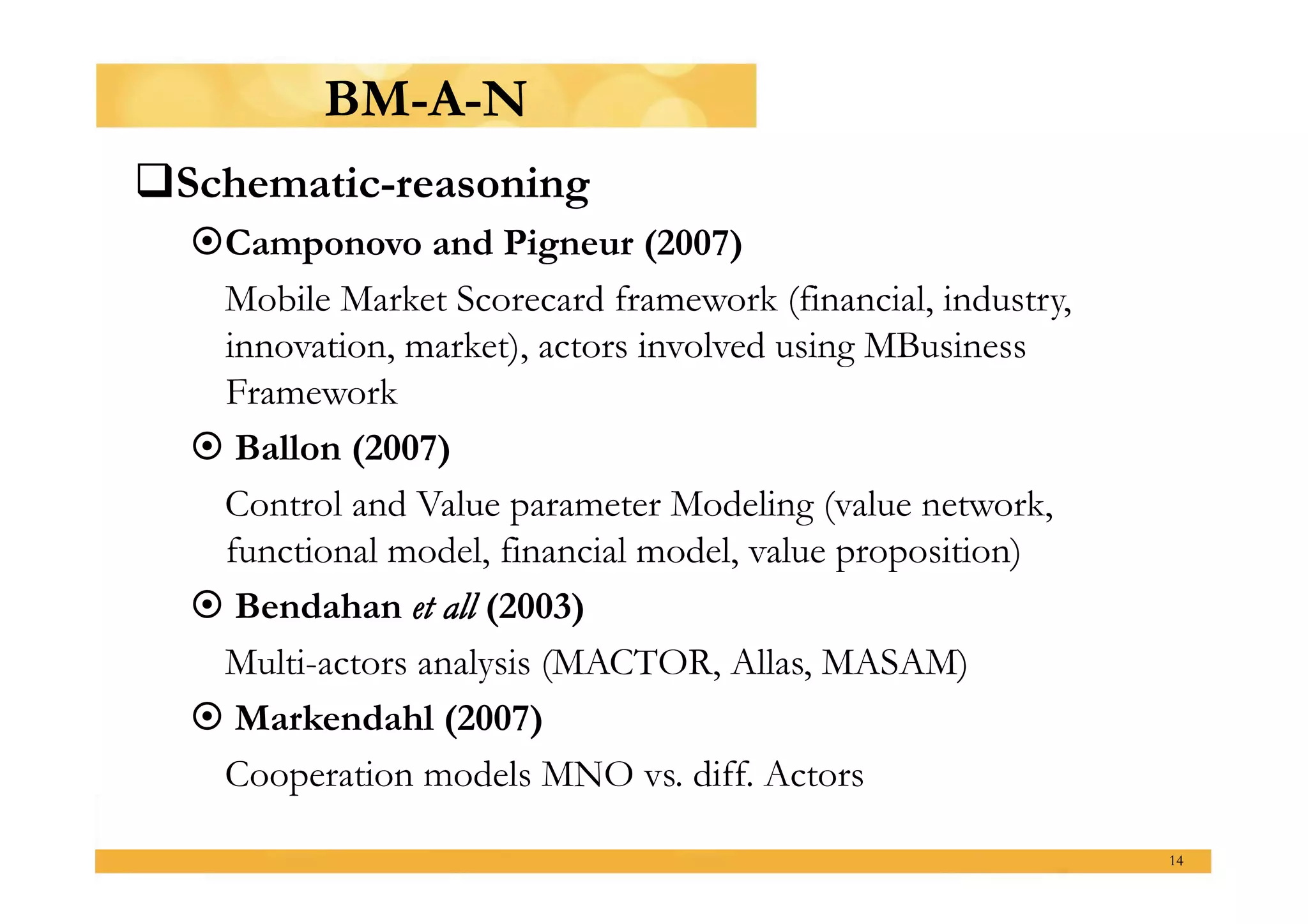
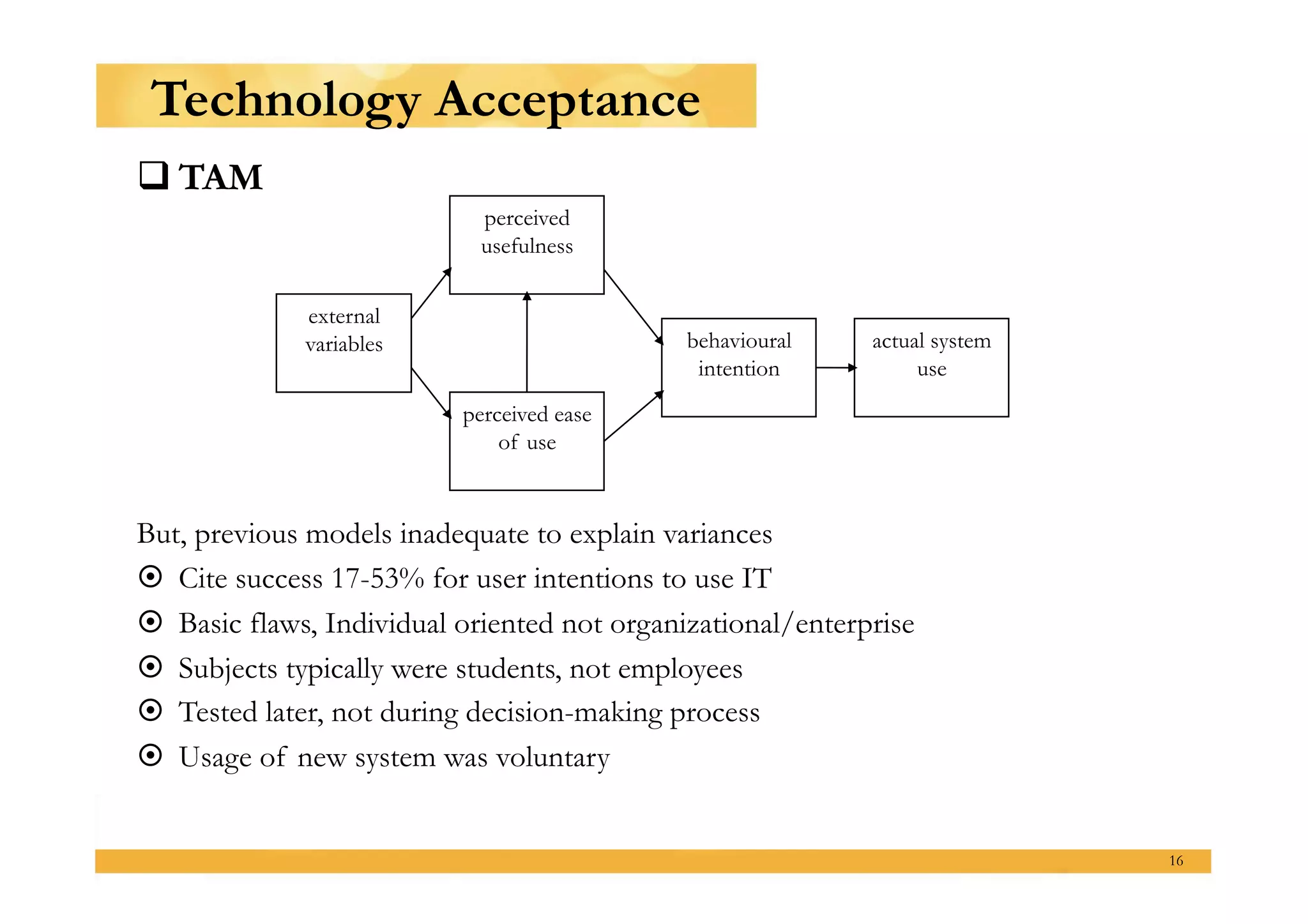
This presentation outlines a master's thesis proposal on developing business models for profitable mobile broadband media services in Indonesia. The proposal discusses background on shifting usage patterns and expectations for mobile broadband. It defines the problem of making these media services sustainable businesses while addressing common and unique market challenges in Indonesia. The methodology will use a mixed qualitative and quantitative approach including literature review, data collection from experts and users, and analysis of the broadband ecosystem and value networks. The expected results are identification of strategies by assessing existing business models and Indonesia's telecom landscape, understanding the market by analyzing user characteristics, and providing recommendations to feasibility test solutions and highlight suitable options.