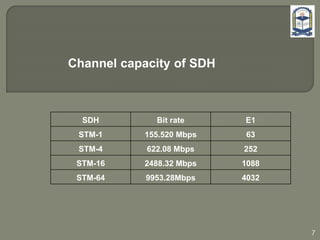
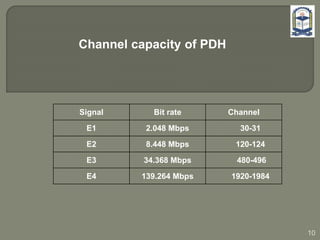
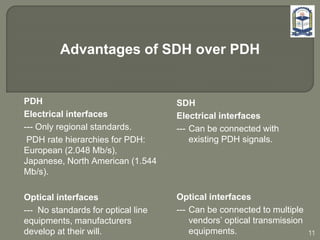
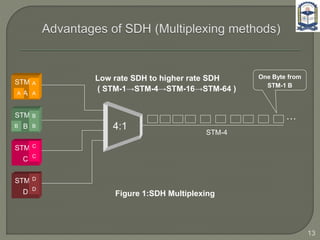
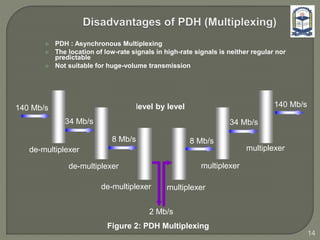
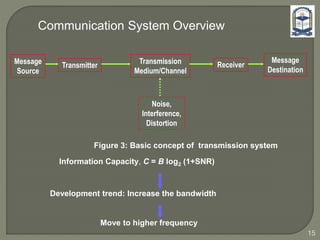
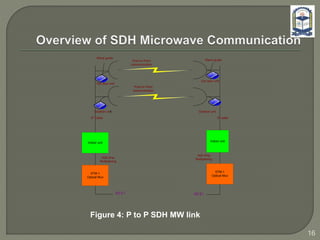
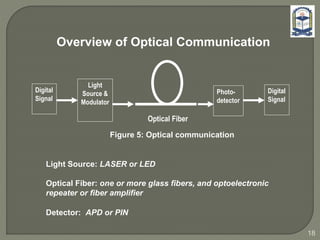
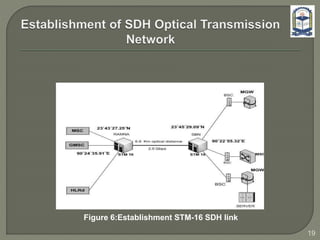
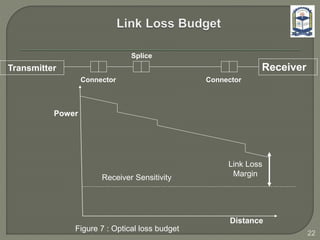
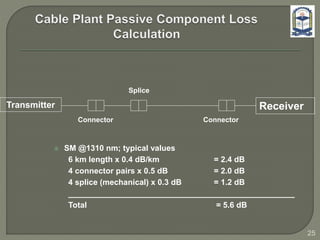
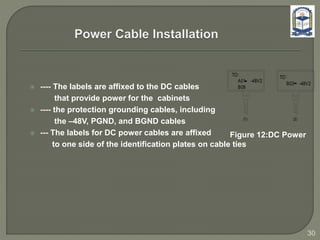
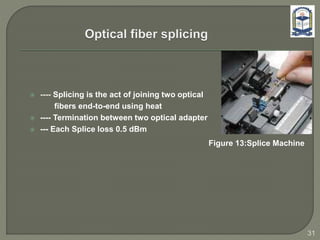
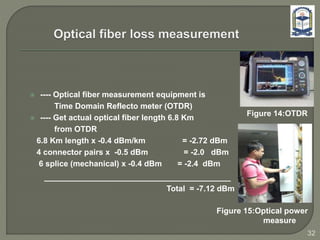
The document discusses the installation and configuration of an STM-16 synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) transmission link between Ramna and SBN sites. Key steps included installing single-mode fiber, optical multiplexer equipment, electrical interfaces and cross-connects. Testing validated the optical power levels, fiber continuity and service commissioning over the 2.5 Gbps link. Minor issues were addressed during installation and the STM-16 SDH connection was completed successfully.