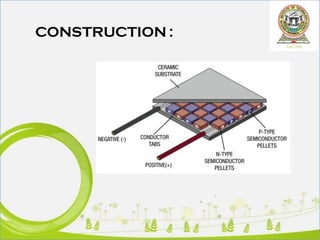
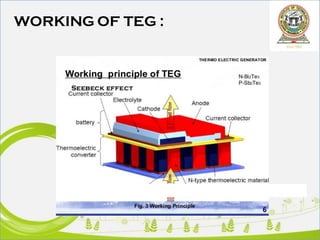
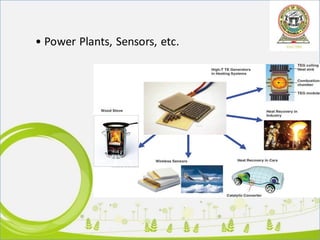
This document discusses thermoelectric generators (TEGs). It introduces TEGs and their importance as a renewable energy source that can convert wasted heat into electricity. It describes the basic construction and working of TEGs, and lists some of their applications such as in automobiles and power plants. The document outlines key advantages of TEGs like their long operational life, lack of moving parts, and ability to generate power from waste heat 24/7. It also notes limitations including low efficiency and lack of industry adoption. Finally, it predicts growth in the TEG market and potential future applications utilizing nano-technology.