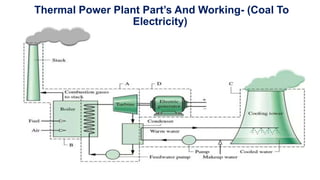
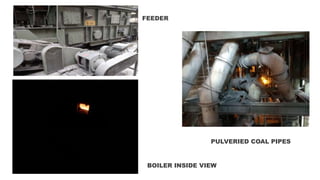
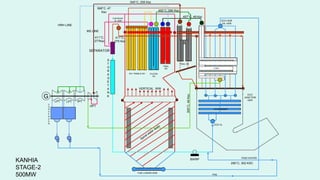
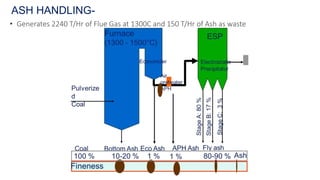
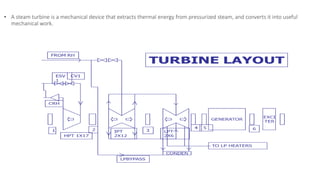
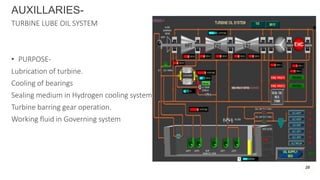
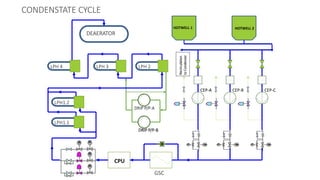
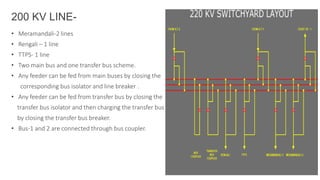
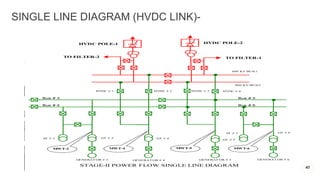
NTPC Kanhia is a 3,010 MW coal-fired power plant located in Talcher, Odisha. It has 6 units of 500 MW each. The plant uses coal from local mines to generate electricity which is supplied to the eastern and southern grids. It has various systems like the coal handling plant, boilers, turbines, generators, condensers and switchyard to generate and supply power efficiently. NTPC aims to further expand renewable energy capacity at the site.