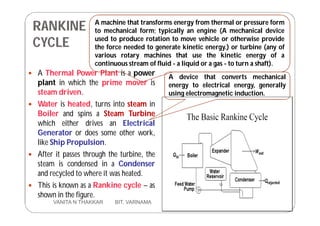
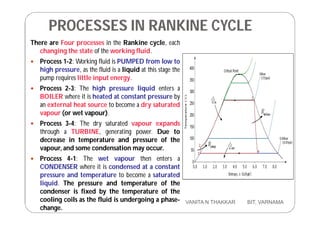
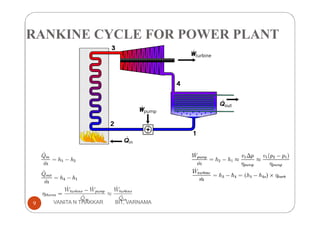
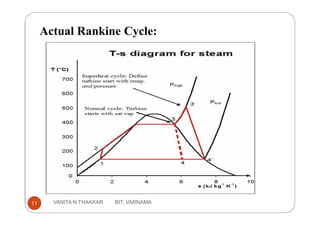
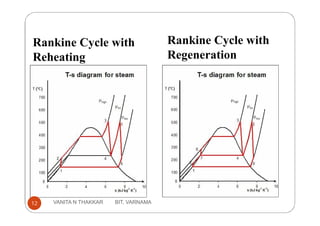
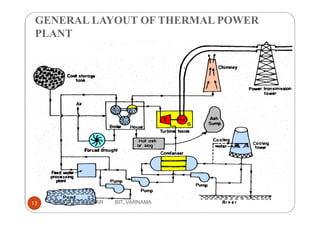
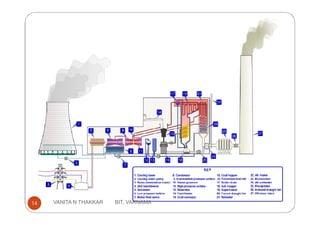
Thermal power plants generate electricity by converting heat energy, often from burning fossil fuels, into mechanical energy using a heat engine to power an electric generator. The Rankine cycle is the most common thermodynamic cycle used in thermal power plants. It involves heating water to create steam to power a turbine, which spins a generator to produce electricity, before condensing the steam back into water to repeat the cycle. Key components include a boiler, turbine, condenser and pumps. Site selection factors for thermal power plants include availability of fuel, water, land area and transportation infrastructure.