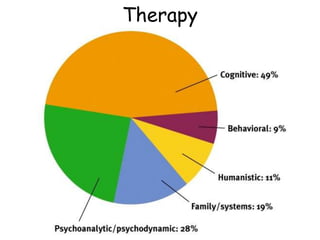
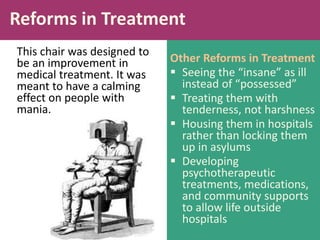
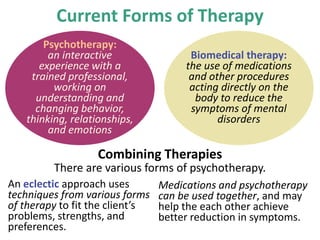
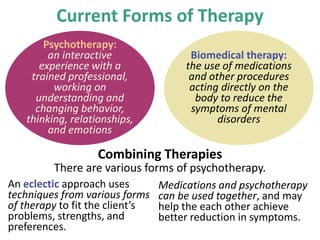
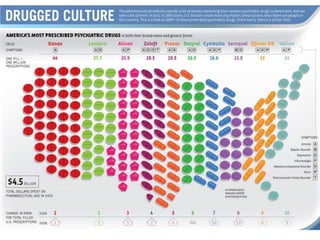
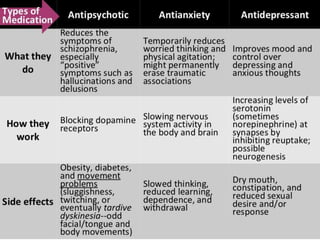
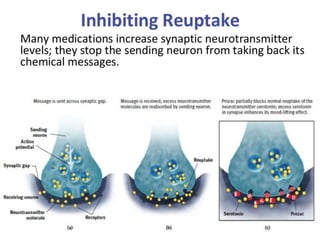
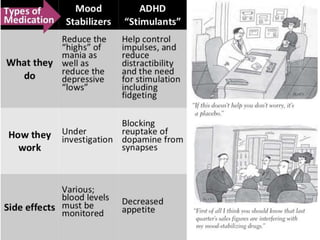
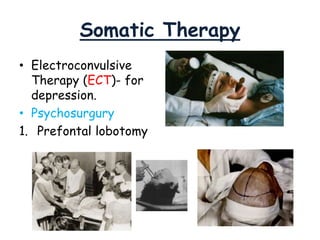
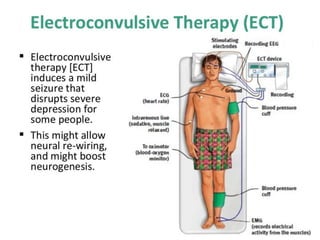
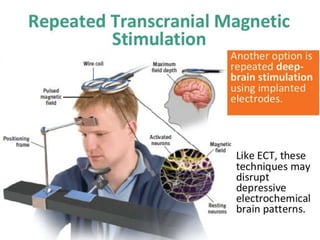
Therapy methods have evolved over time from institutionalization to community-based treatment. There are various forms of psychotherapy including psychoanalysis, humanistic, behavior, and cognitive therapies. Psychotherapy involves interaction with a trained professional to understand and change behavior, thinking, relationships, and emotions. Current therapies also include biomedical approaches using medications and procedures, as well as combining therapies to fit each client's specific needs.