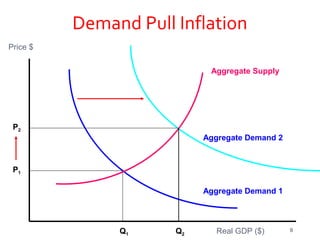
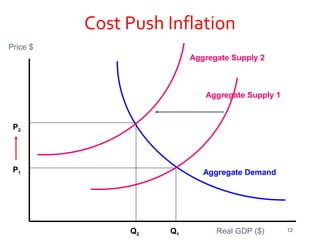
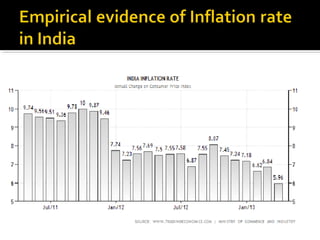
This document discusses different aspects of inflation including definitions, types (demand-pull and cost-push), causes, effects, and measures to control inflation. It defines inflation as a rise in the general price level and notes that it occurs when money supply grows faster than the rate of production of goods and services. The two main types of inflation are demand-pull, which is due to excess demand, and cost-push, which is due to increases in production costs. Fiscal, monetary, and general policy measures can be used to control inflation.