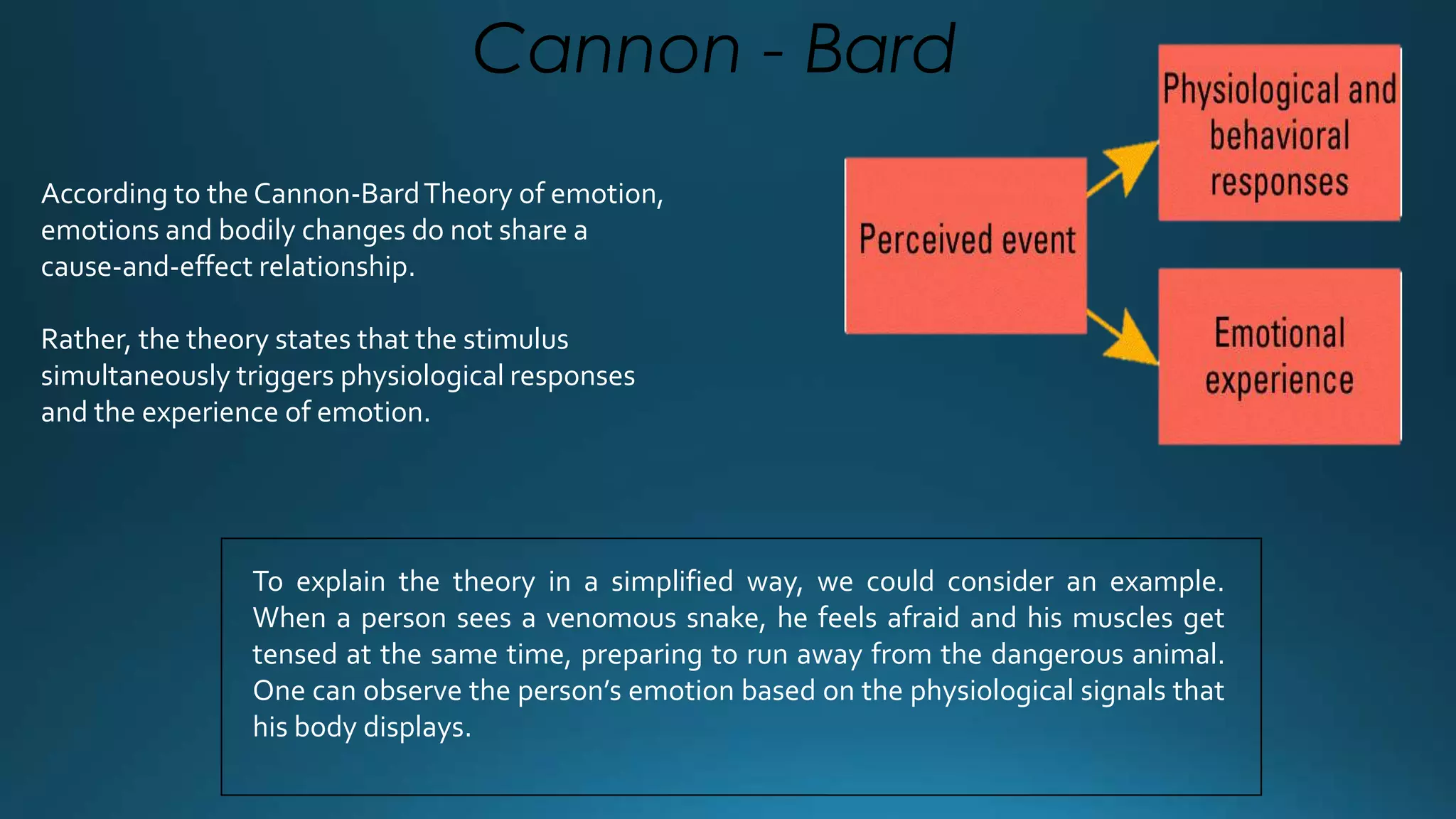
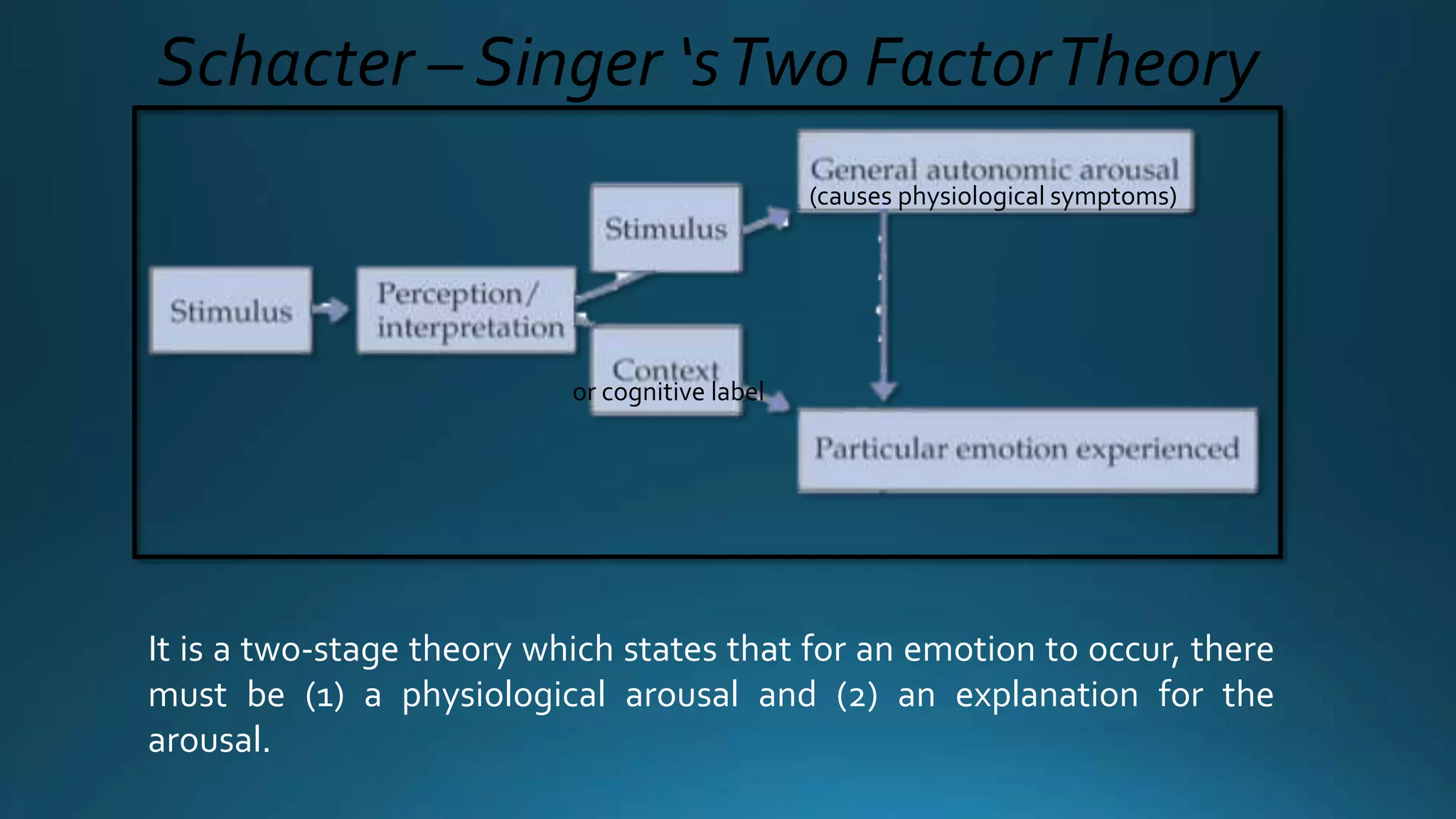
Emotion is a strong feeling influenced by circumstances, mood, and relationships, consisting of physical reactions and conscious experiences. Theories of emotion include the James-Lange theory, which posits that physiological changes precede emotional experience, and the Cannon-Bard theory, which suggests simultaneous emotional and physiological responses. The Schachter-Singer theory adds a cognitive element, requiring both arousal and an interpretation of the arousal for emotion to occur.