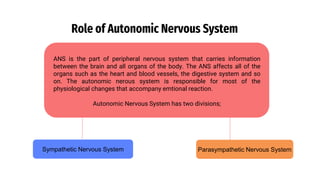
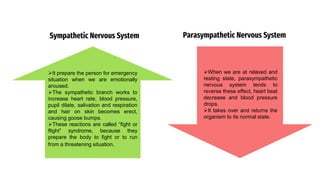
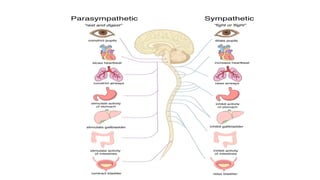
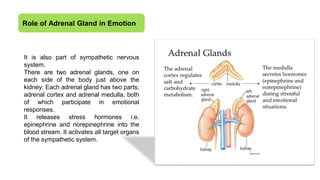
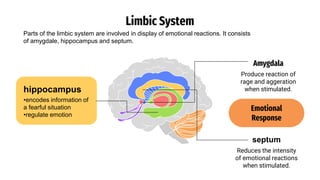
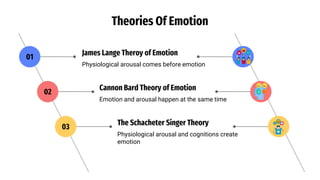
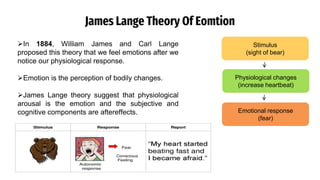
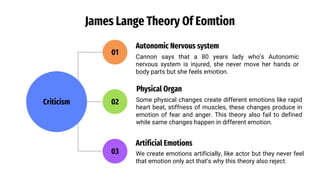
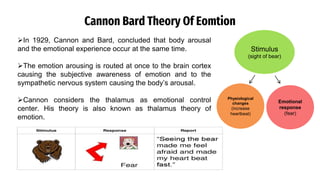
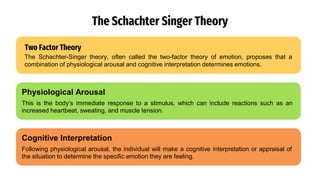
The document provides an overview of emotions, explaining their physiological, behavioral, and cognitive components, as well as the role of systems like the autonomic nervous system and the limbic system in emotional responses. It discusses several theories of emotion, including the James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Schachter-Singer theories, each offering different perspectives on the relationship between physiological arousal and emotional experience. Additionally, the document highlights the expression of emotions through verbal and non-verbal communication, emphasizing the universality of certain facial expressions associated with basic emotions.