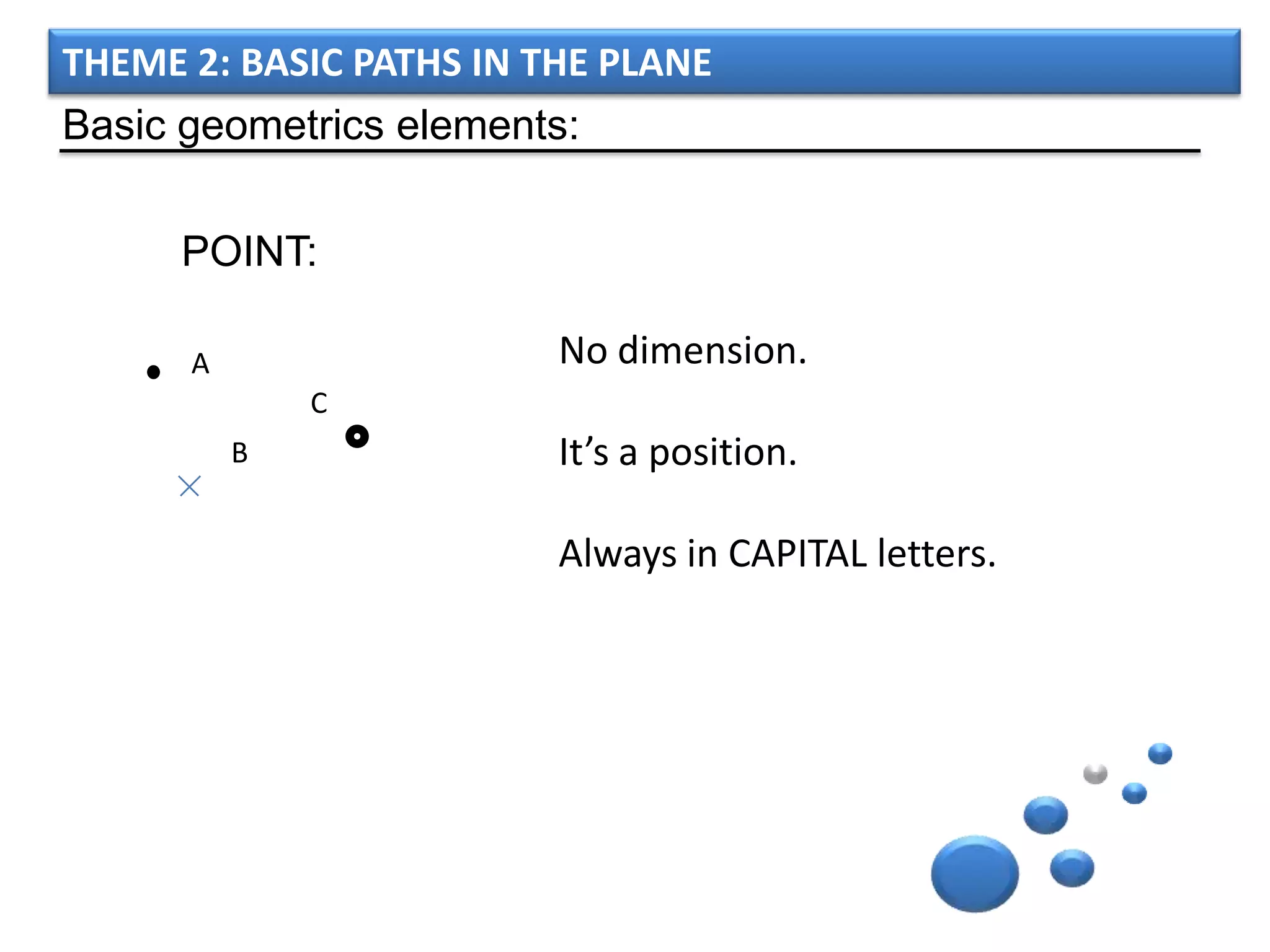
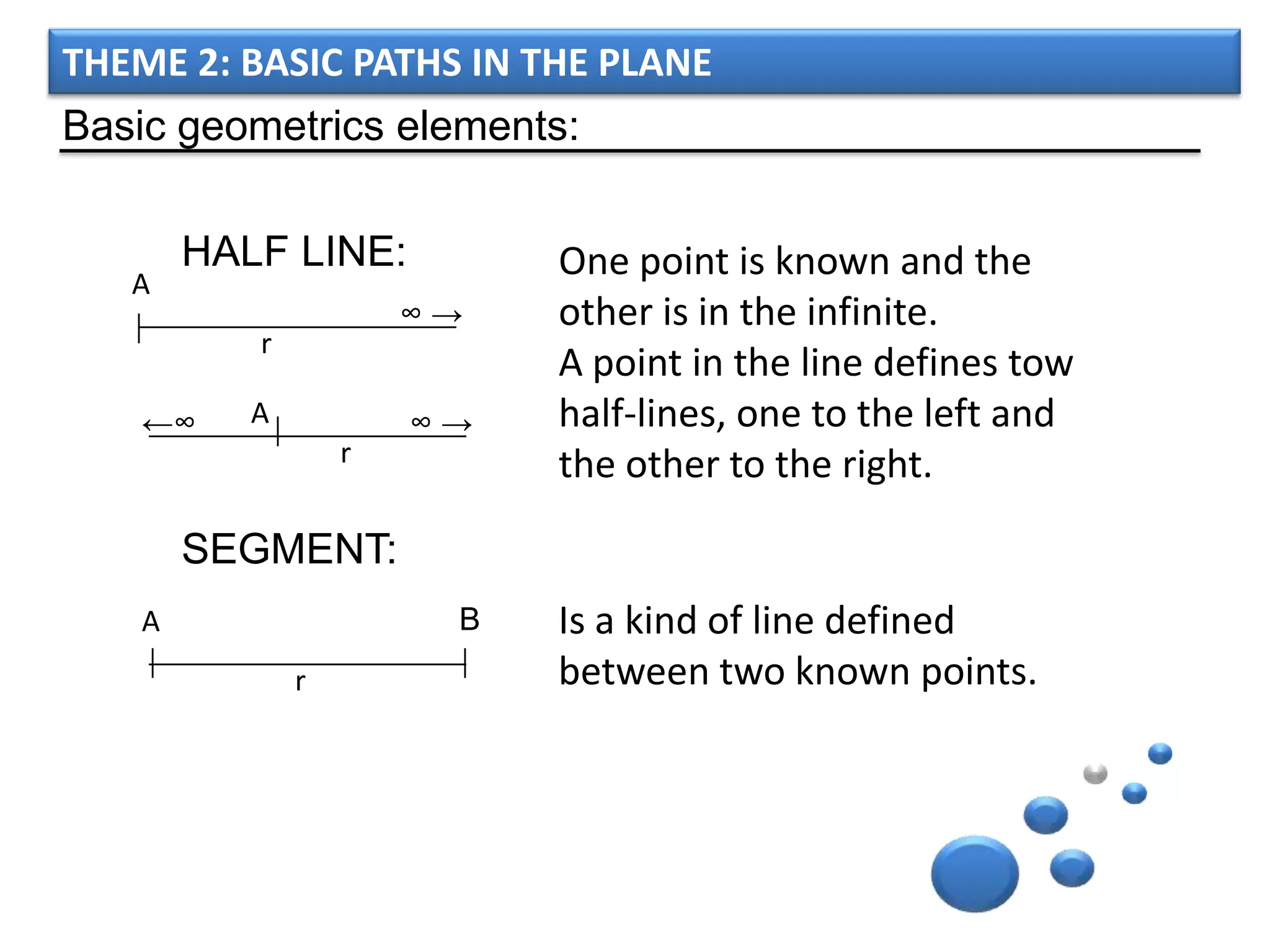
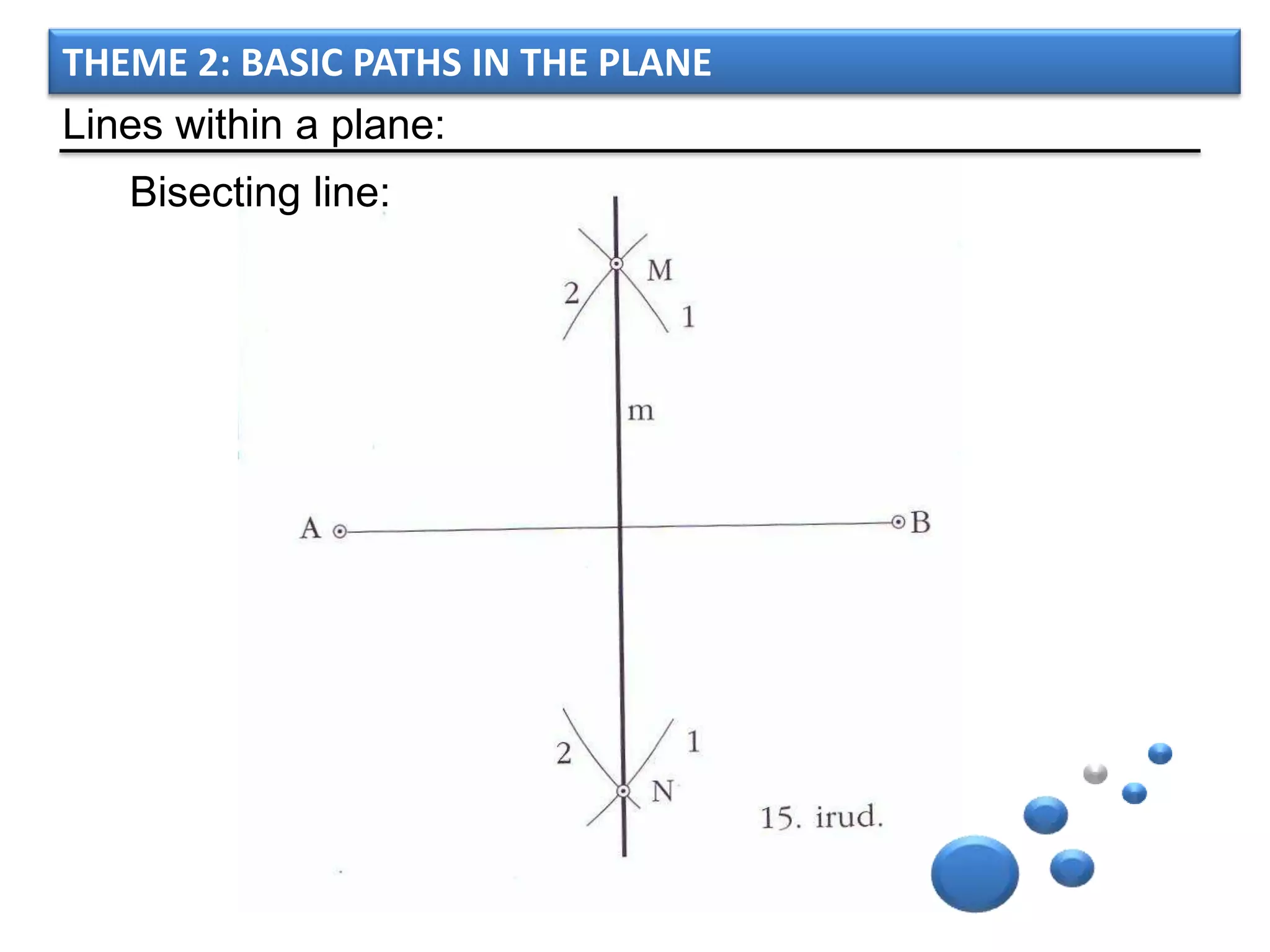
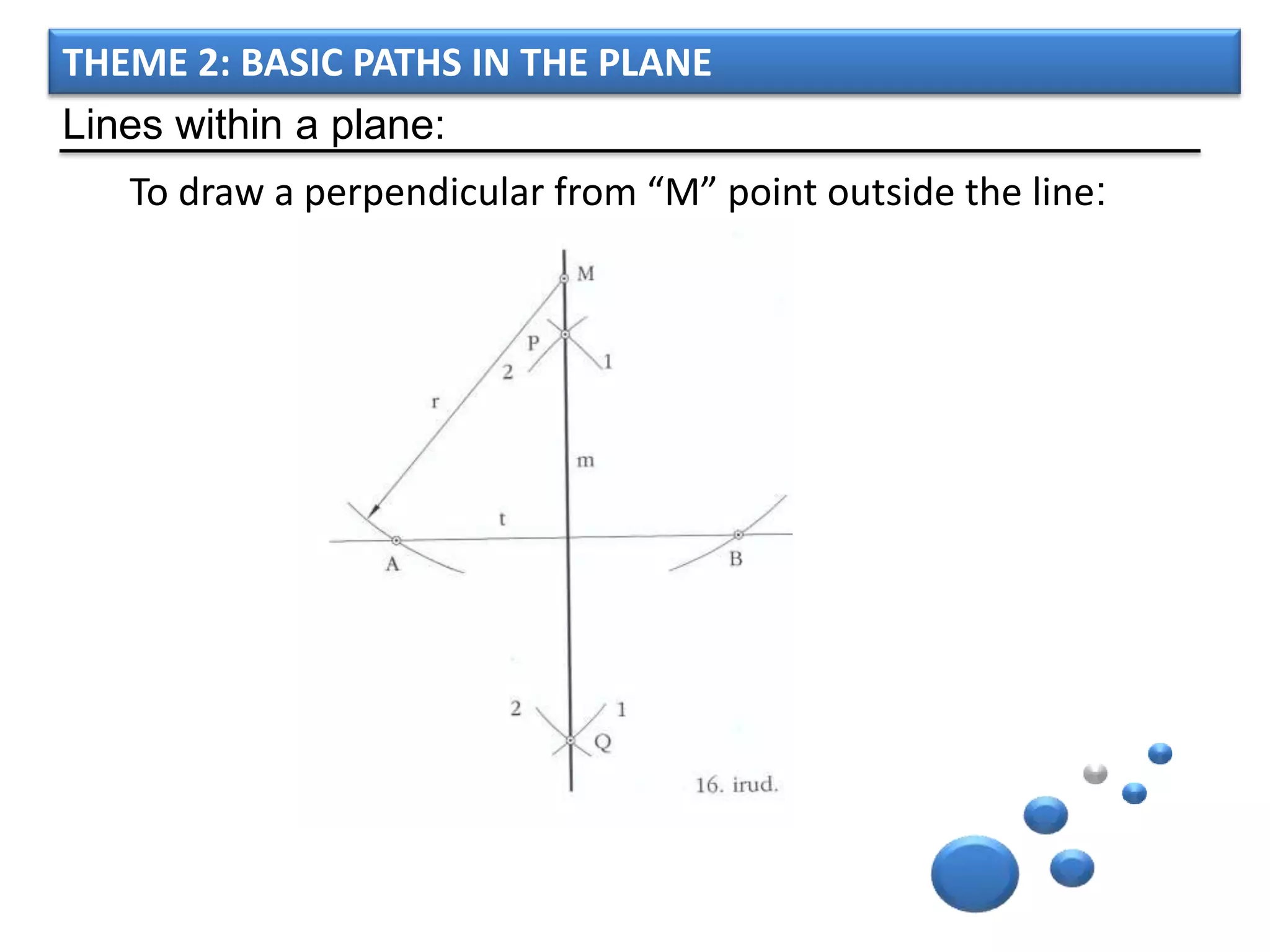
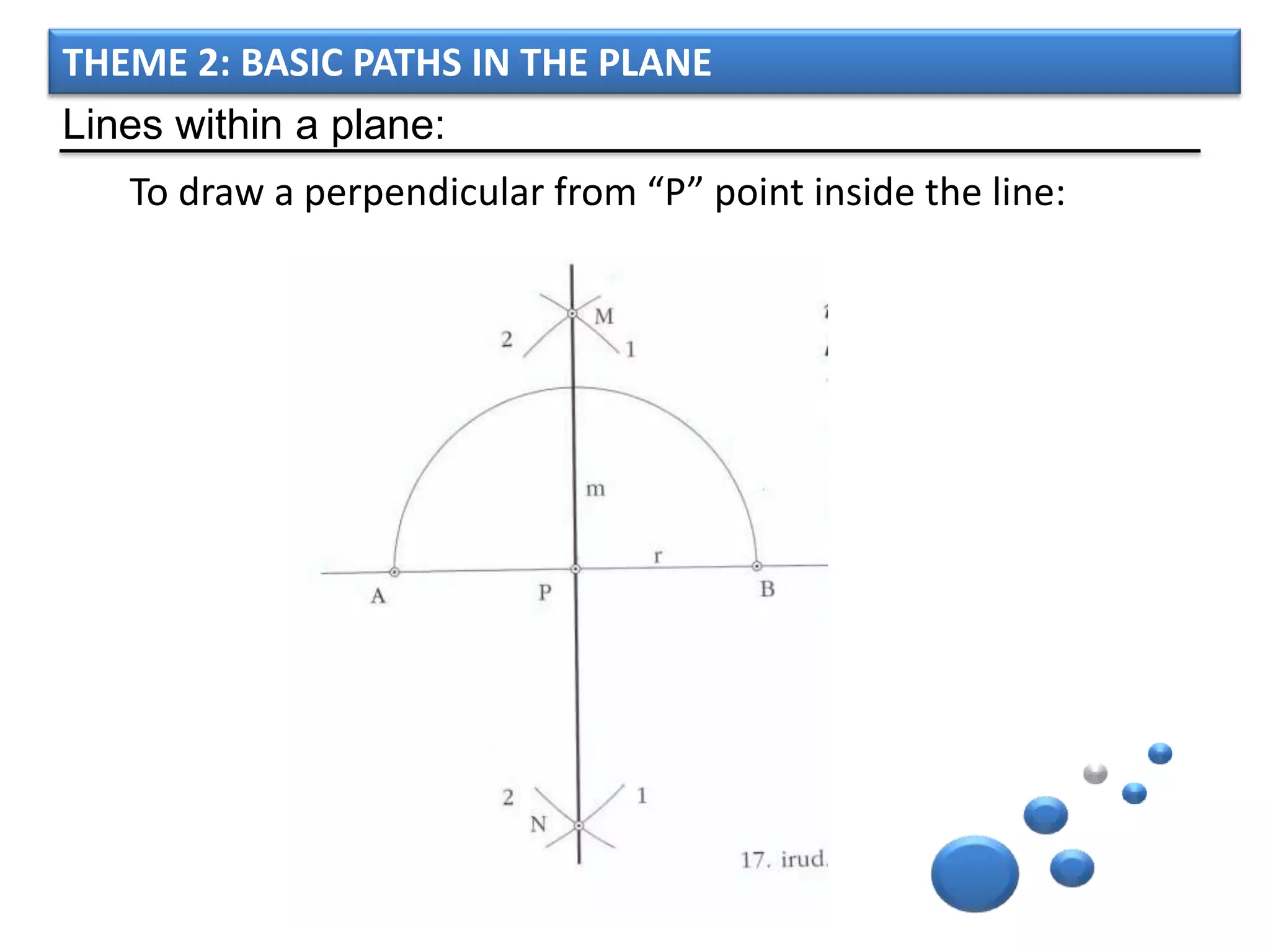
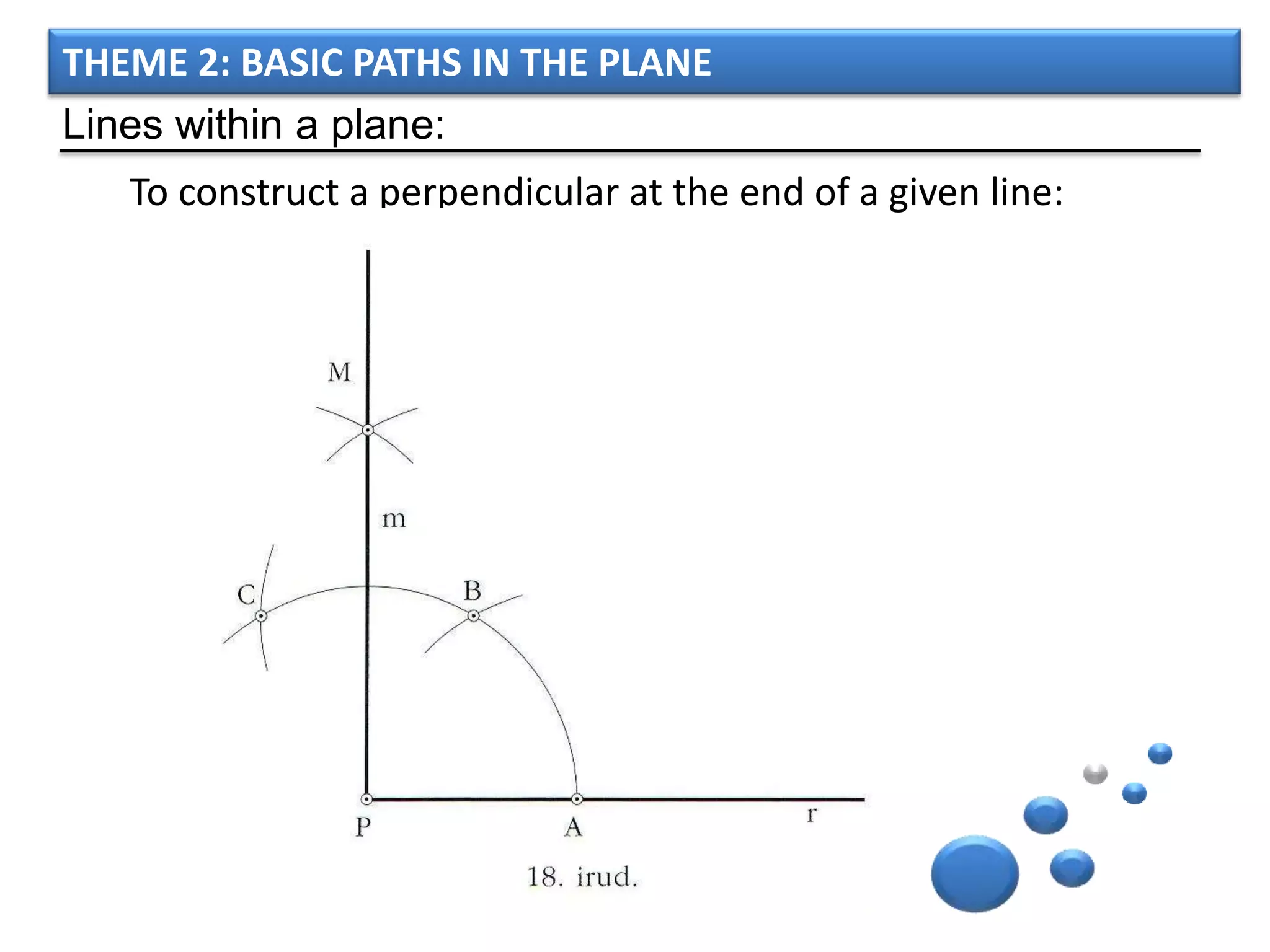
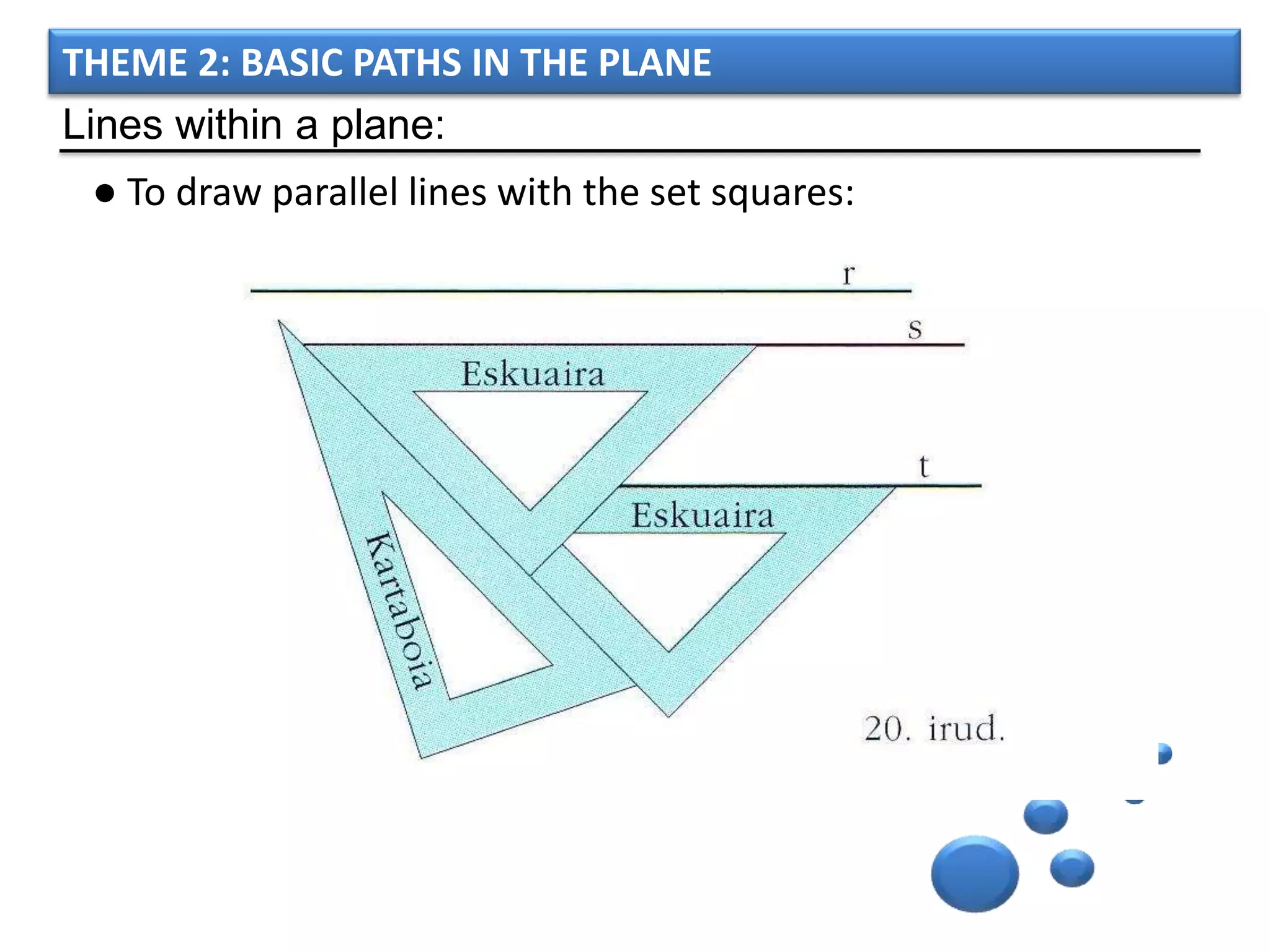
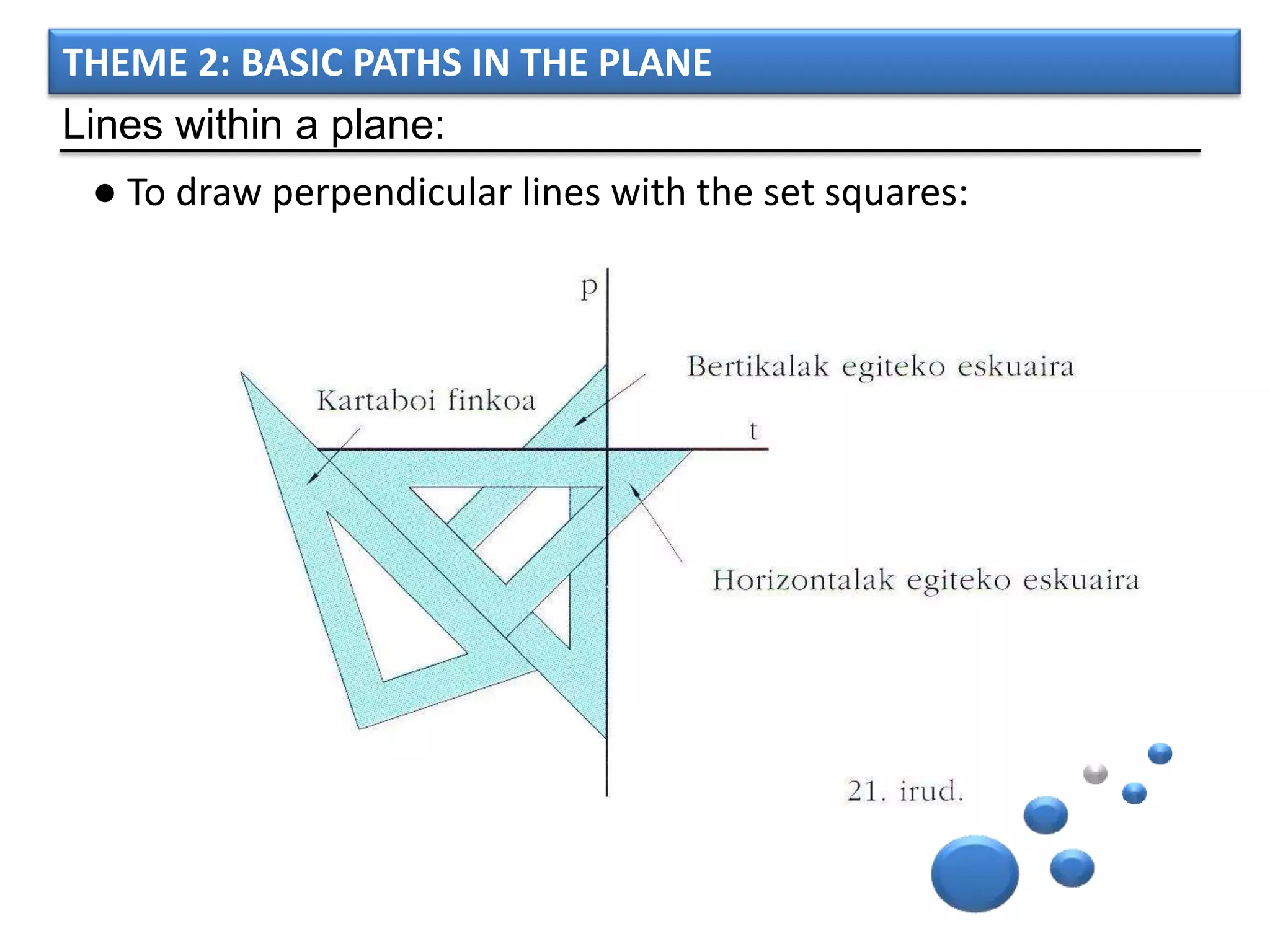
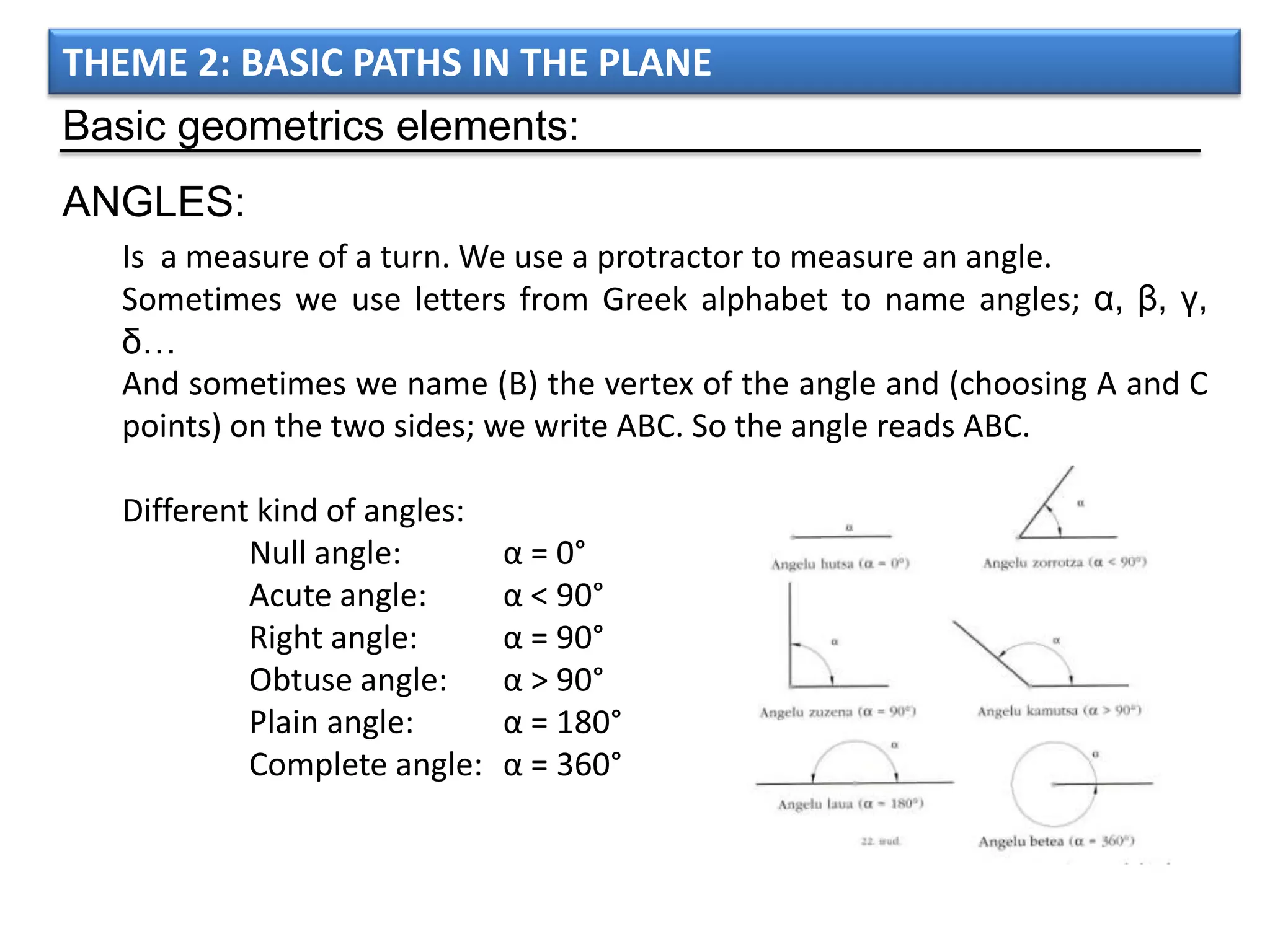
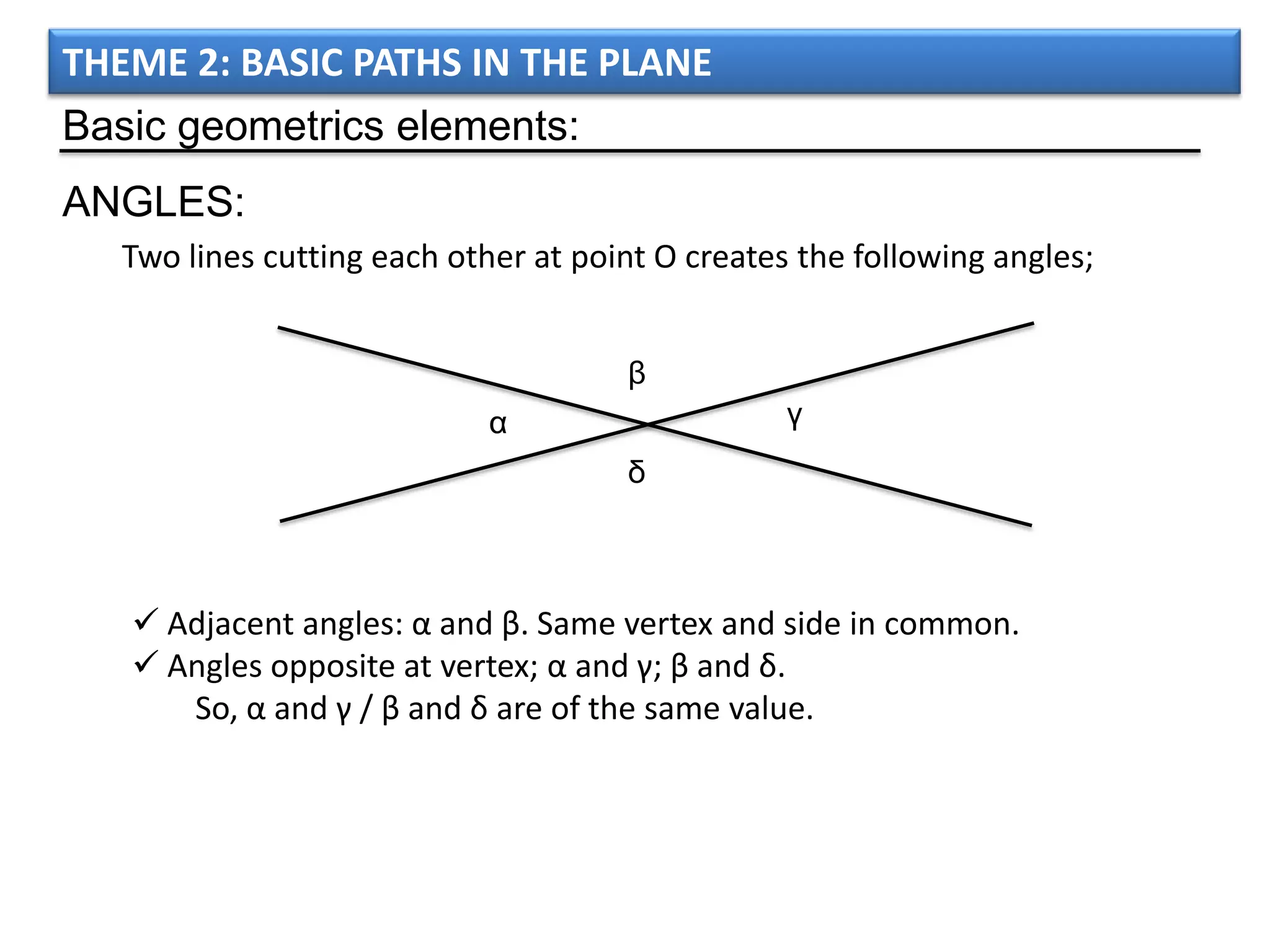
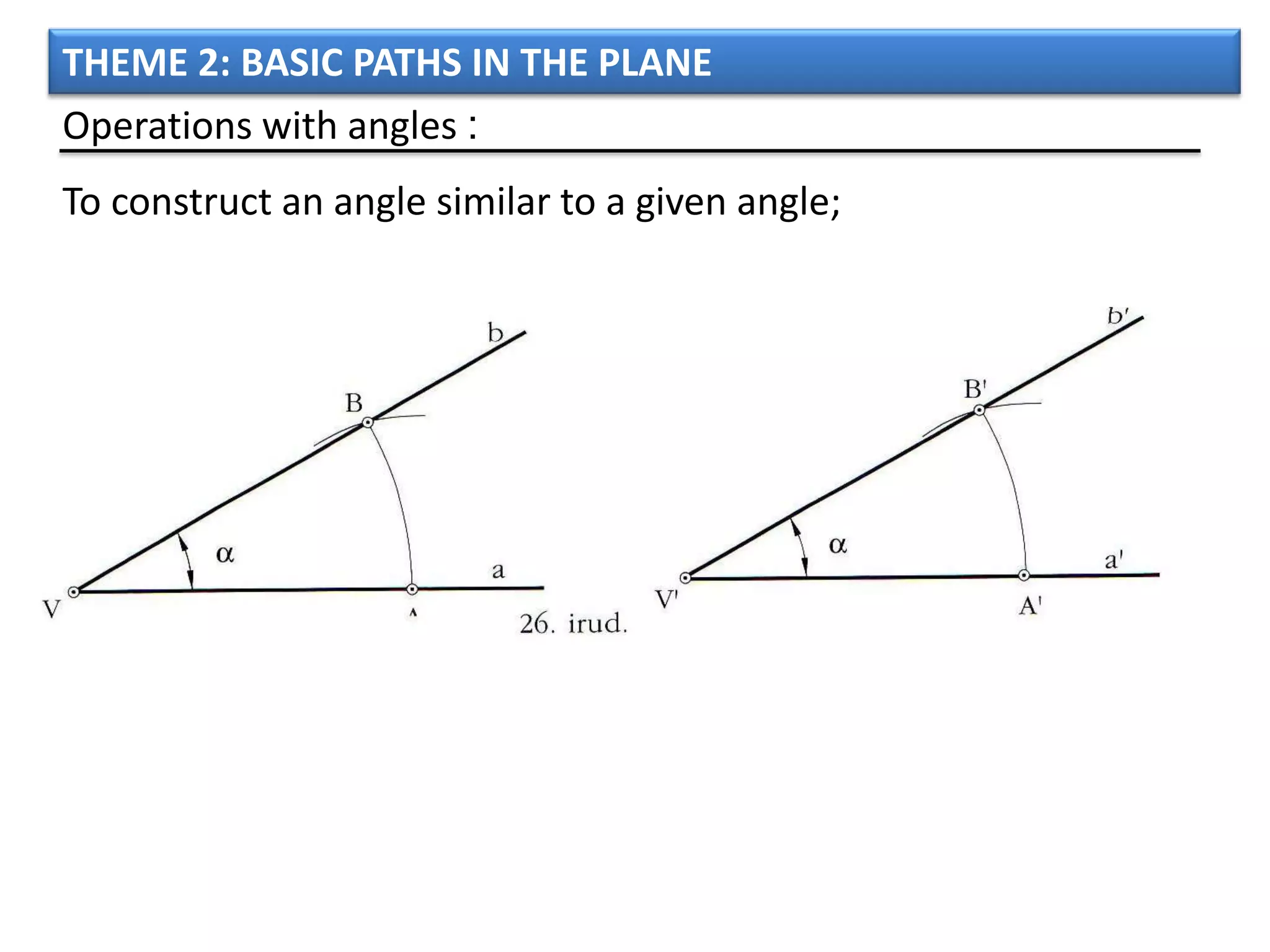
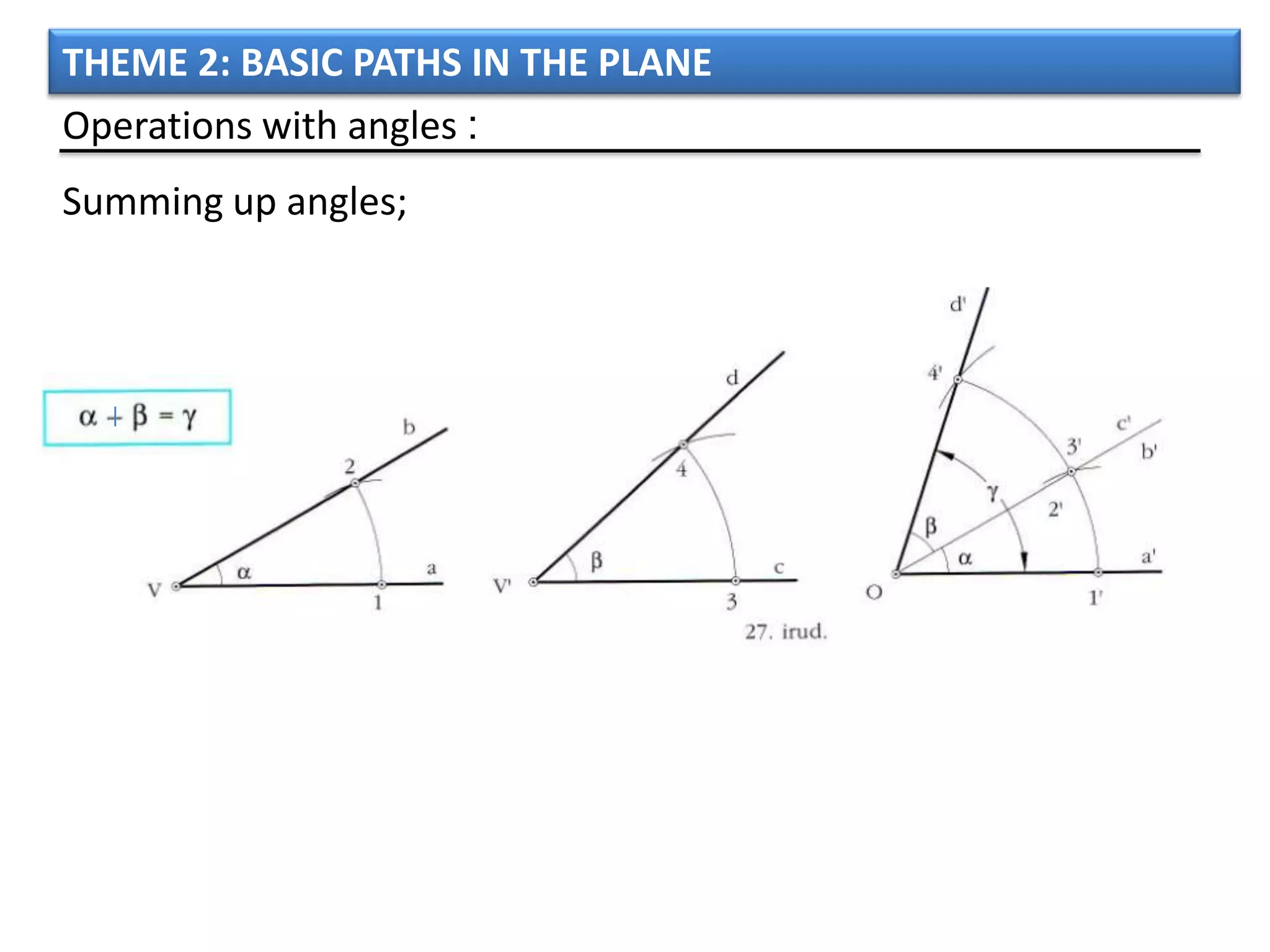
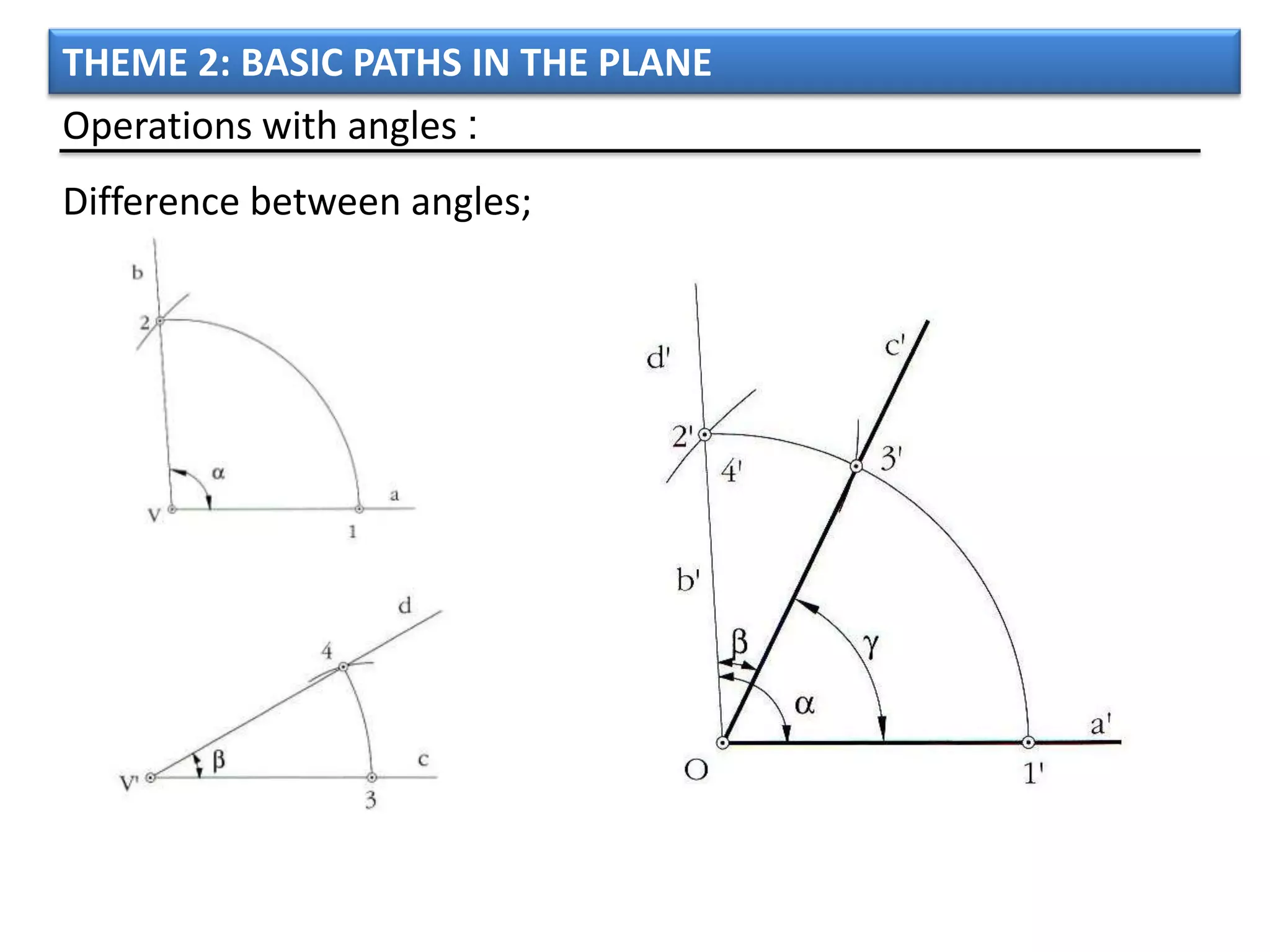
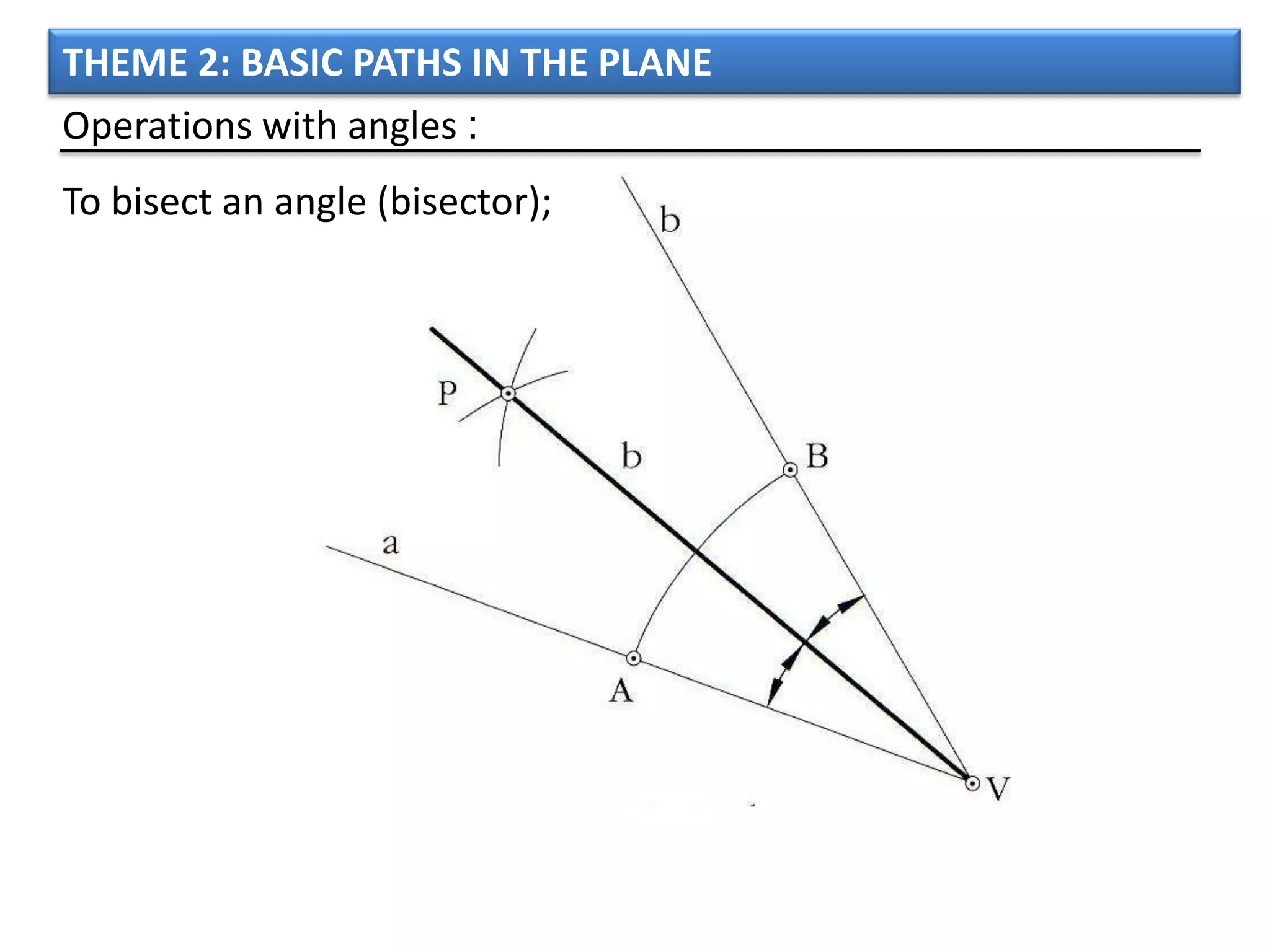
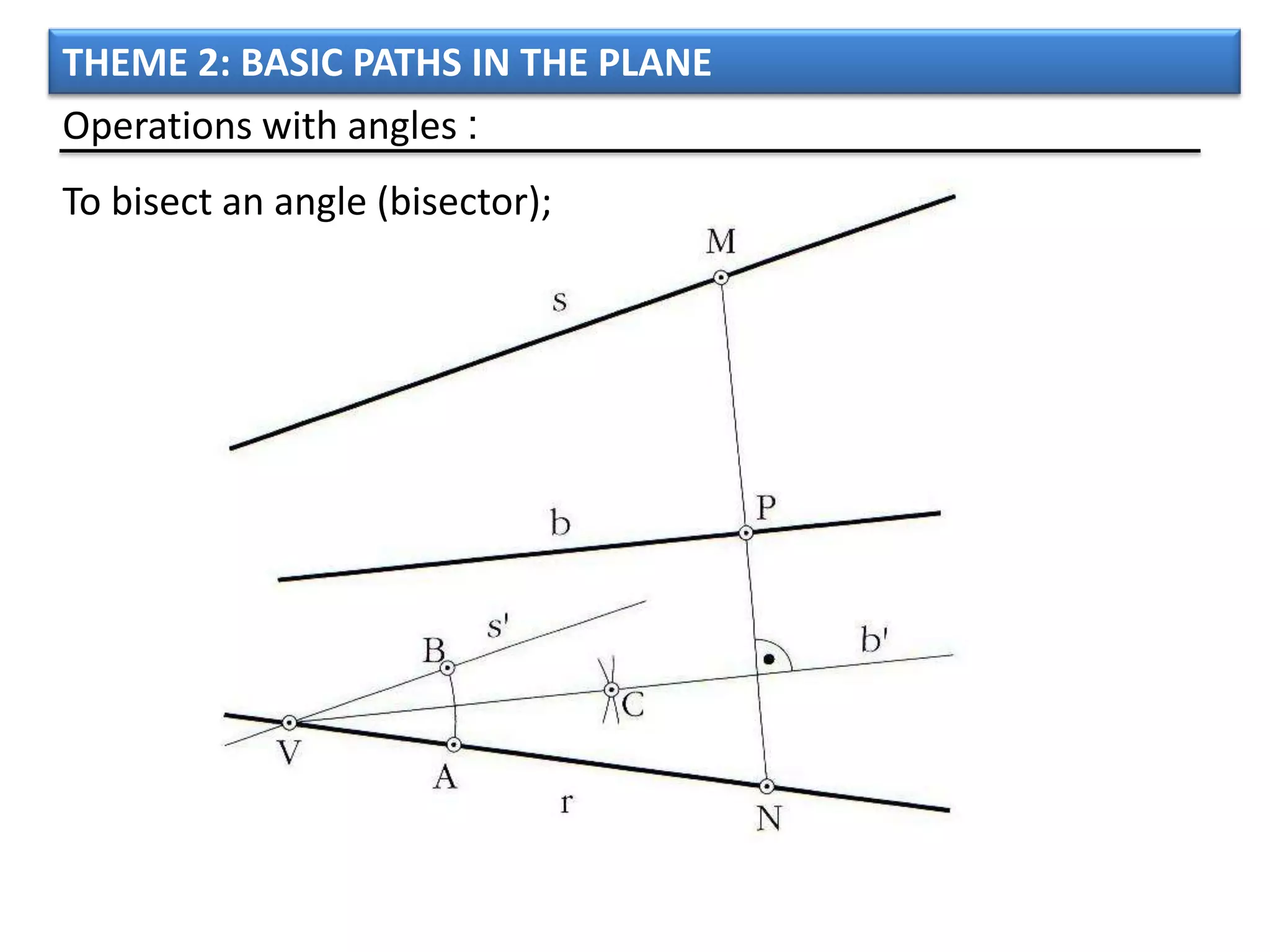
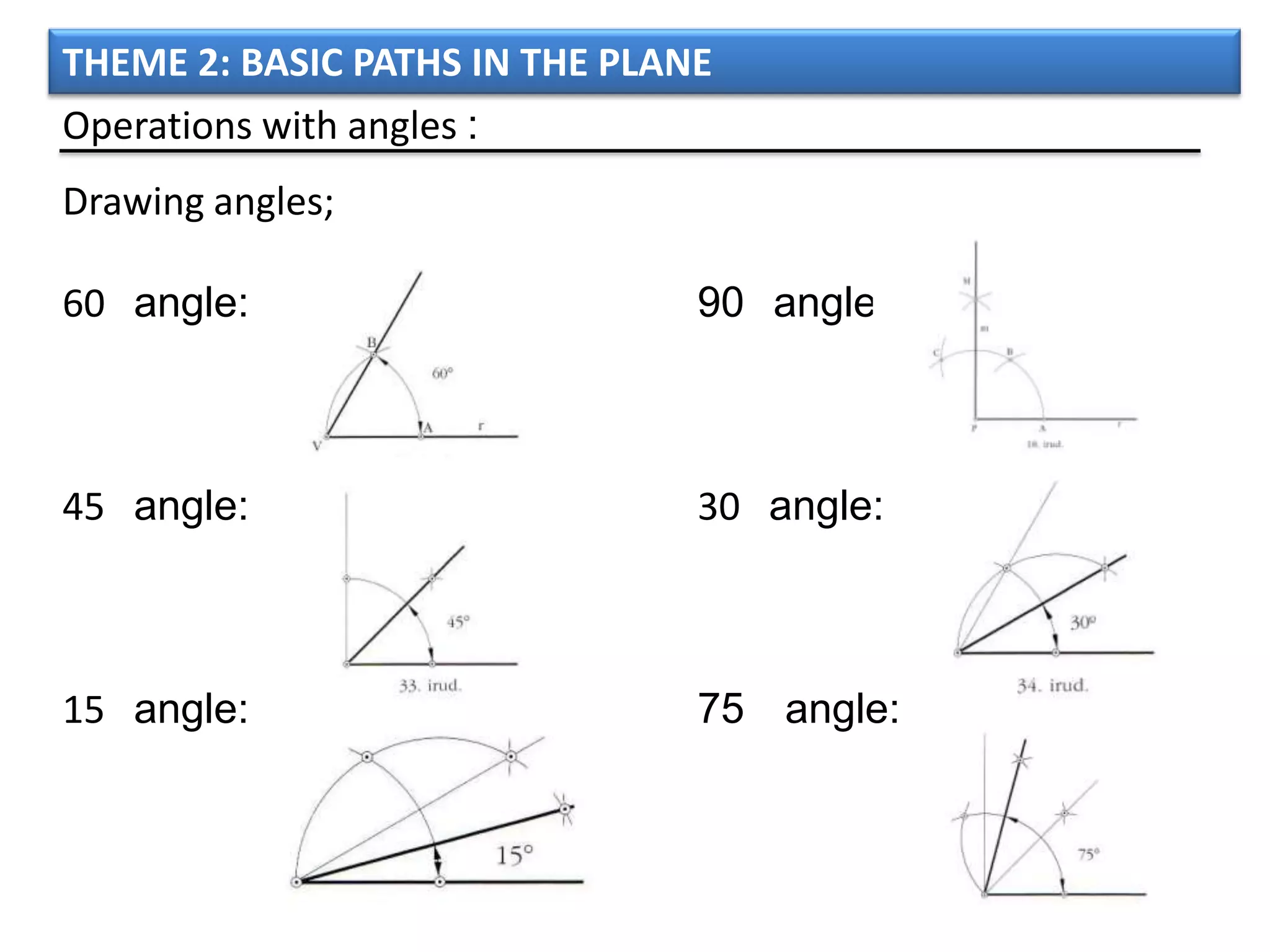
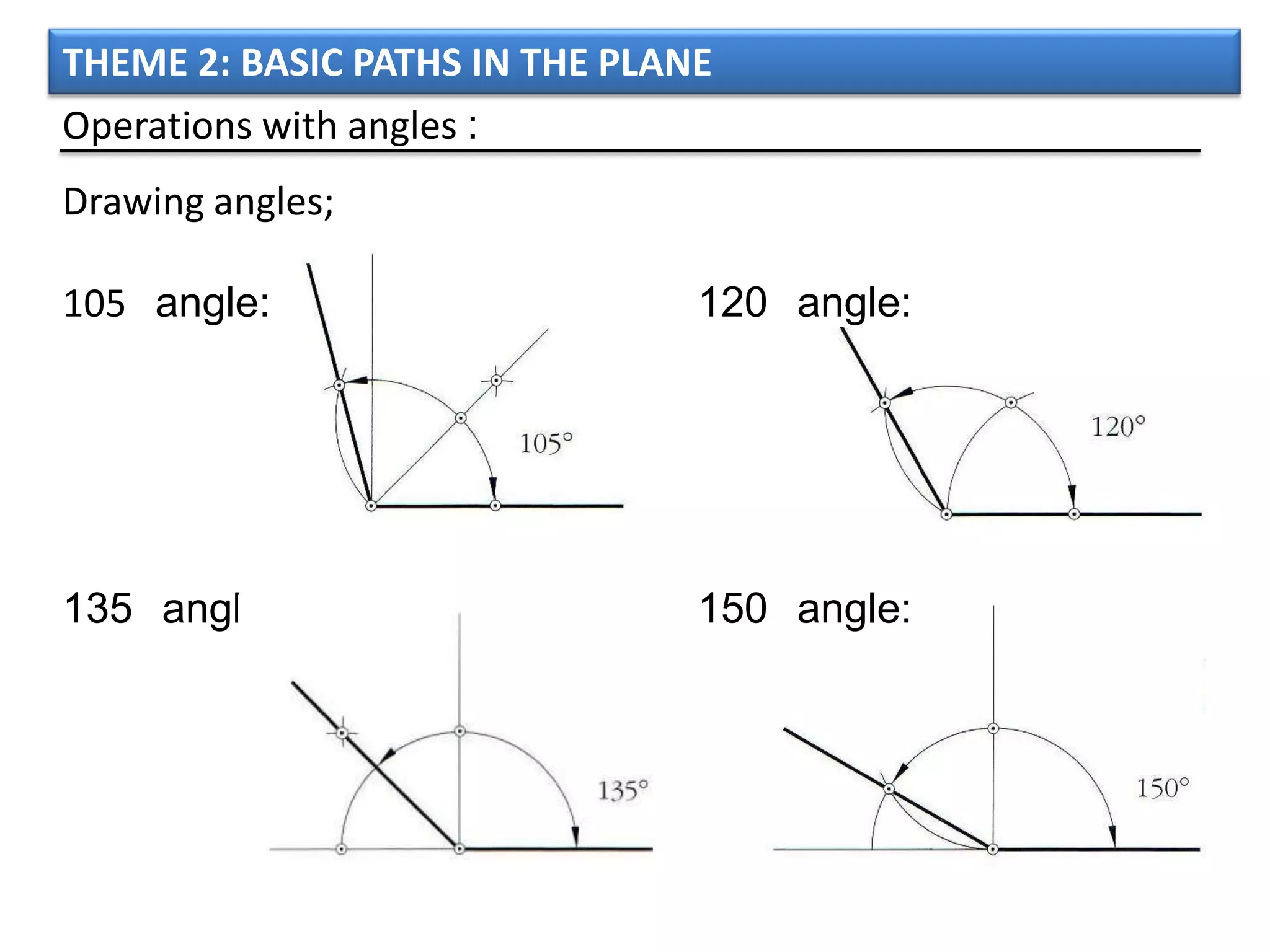
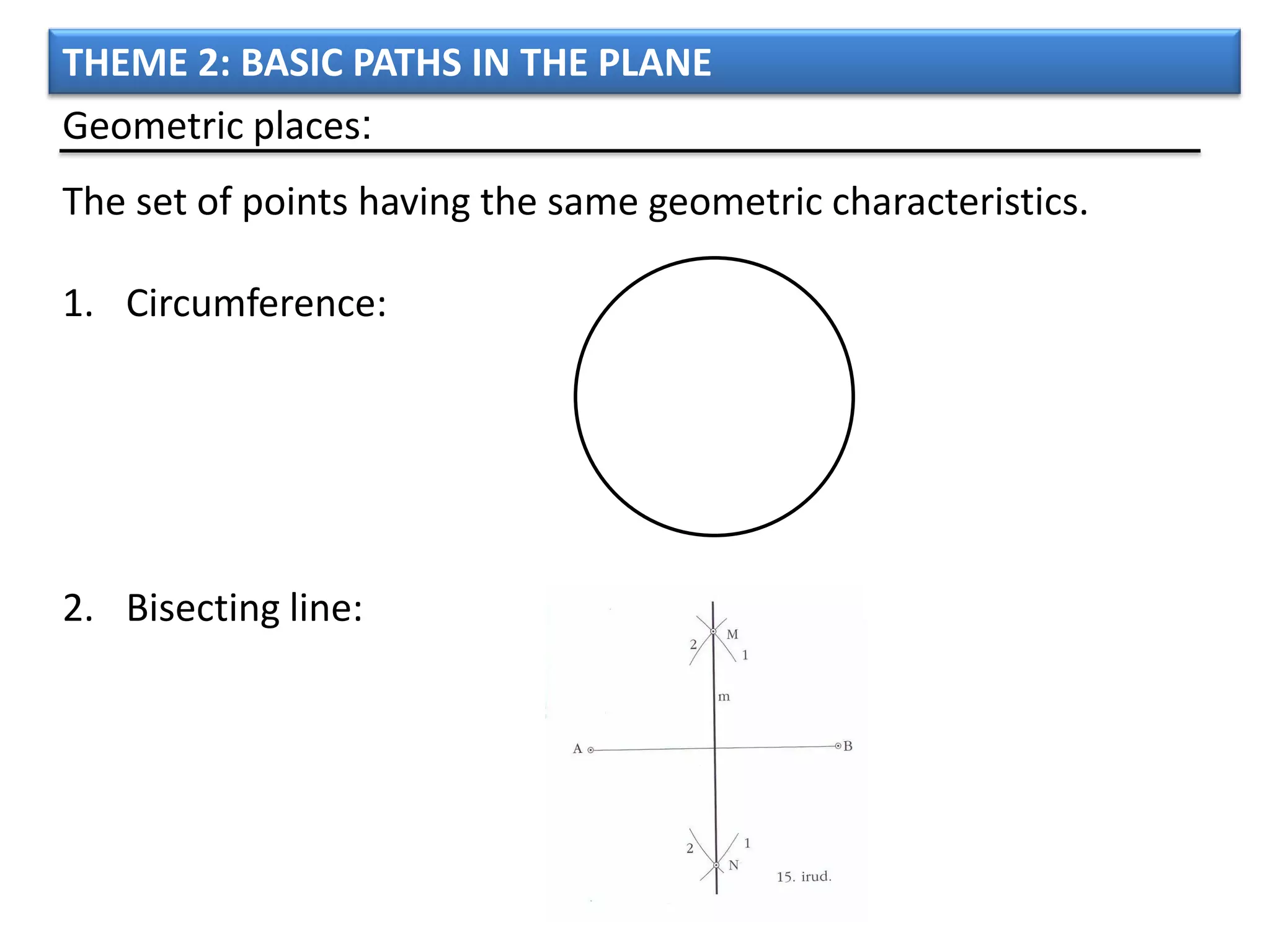
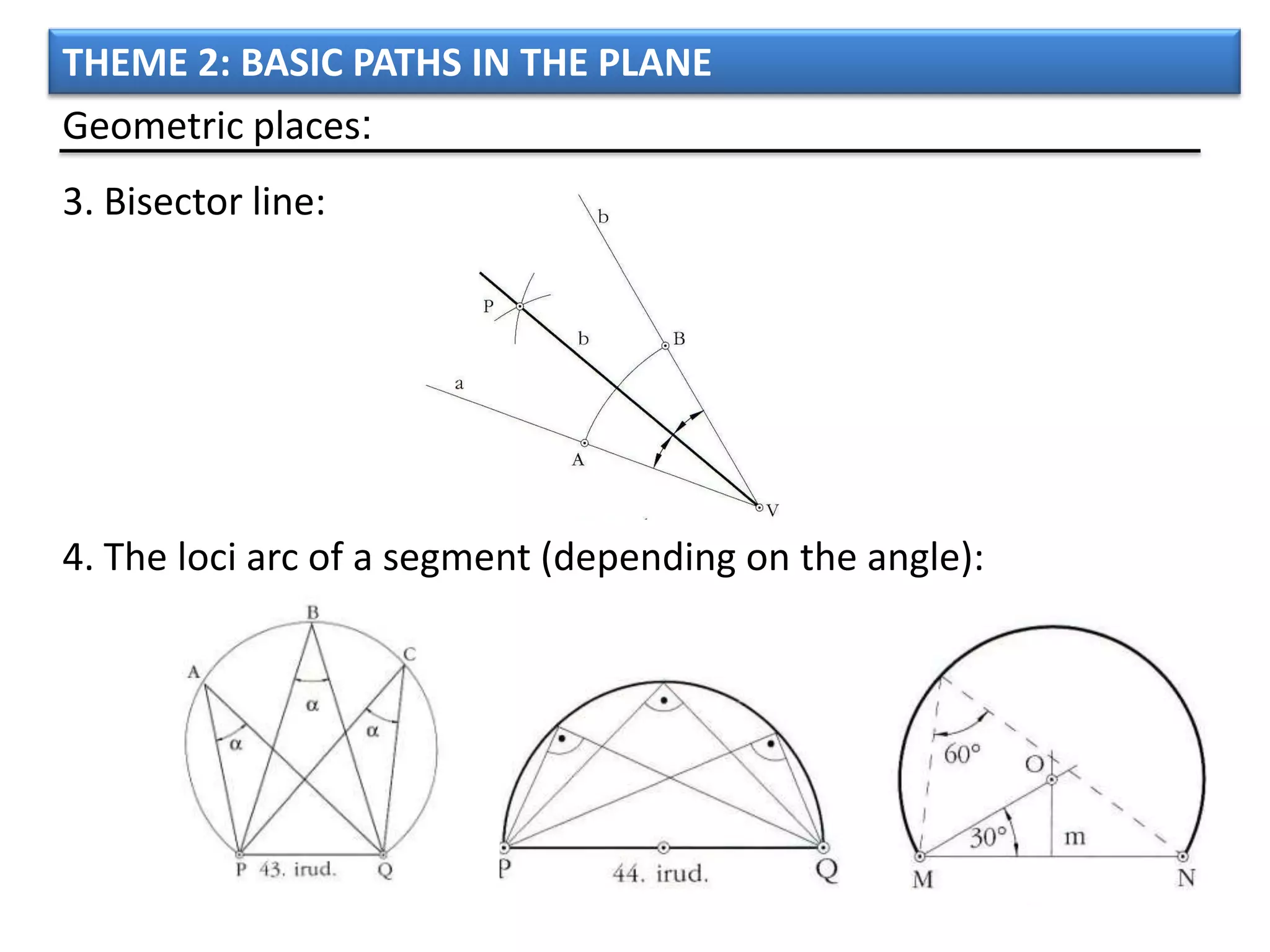
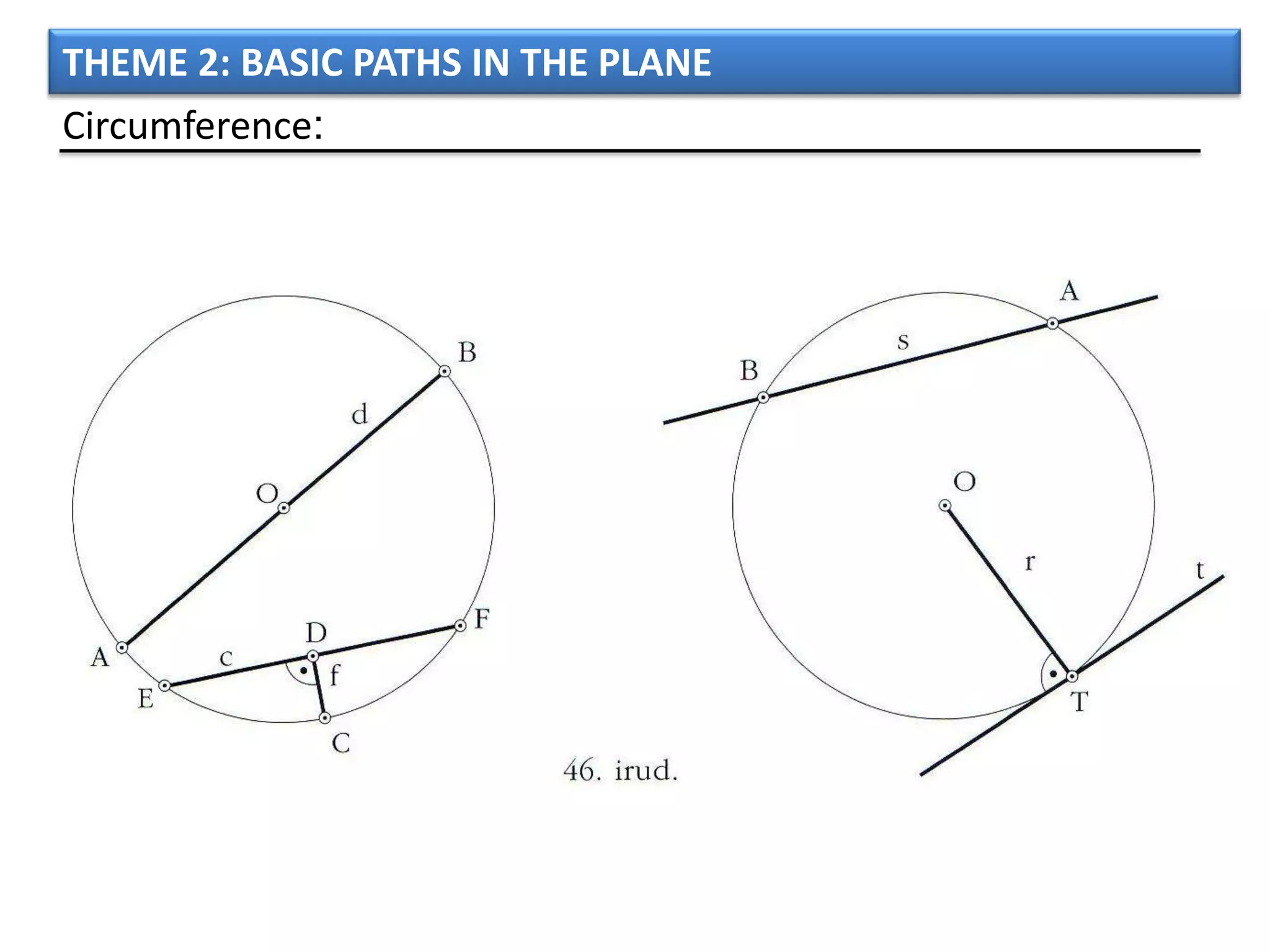
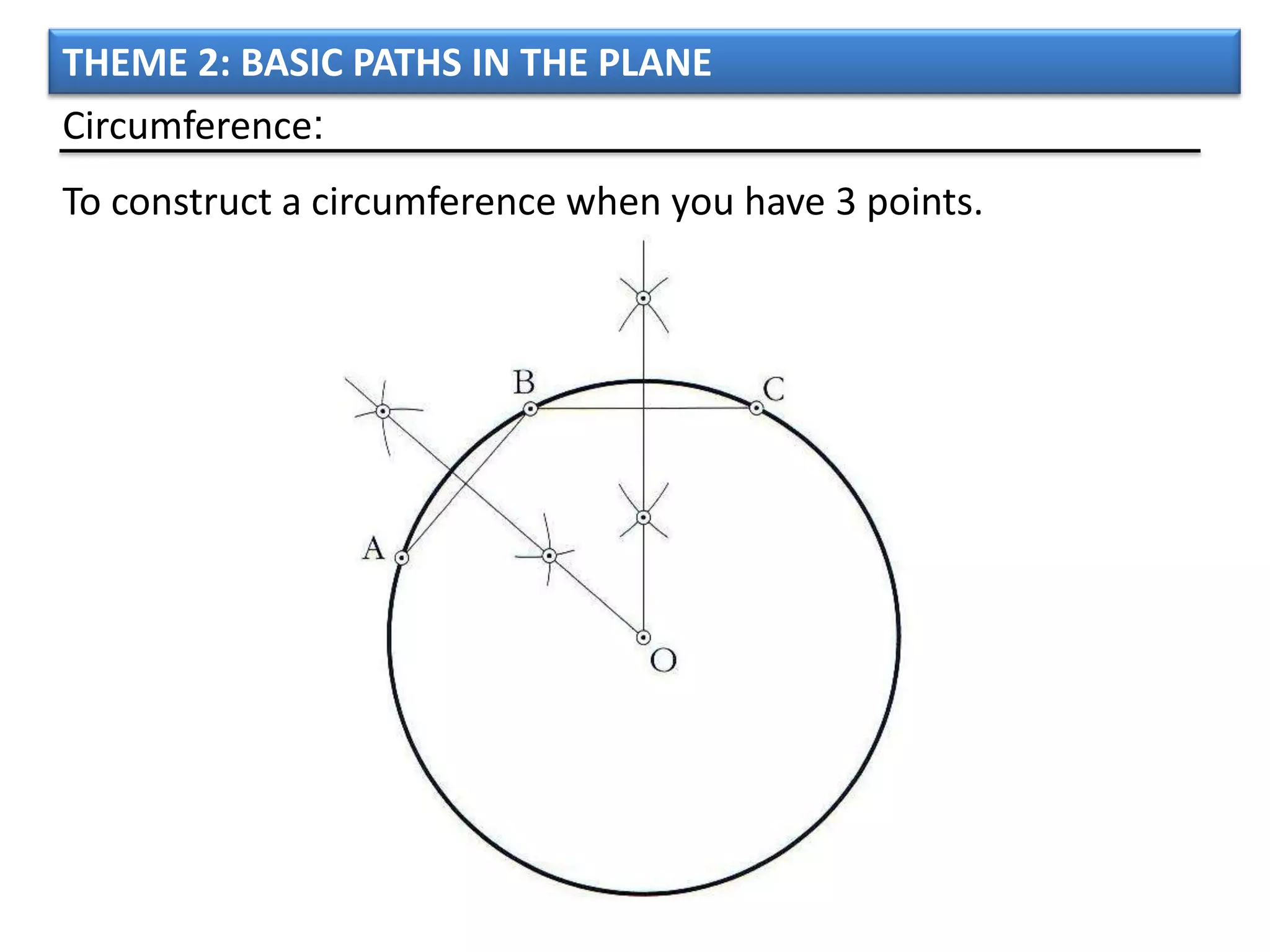
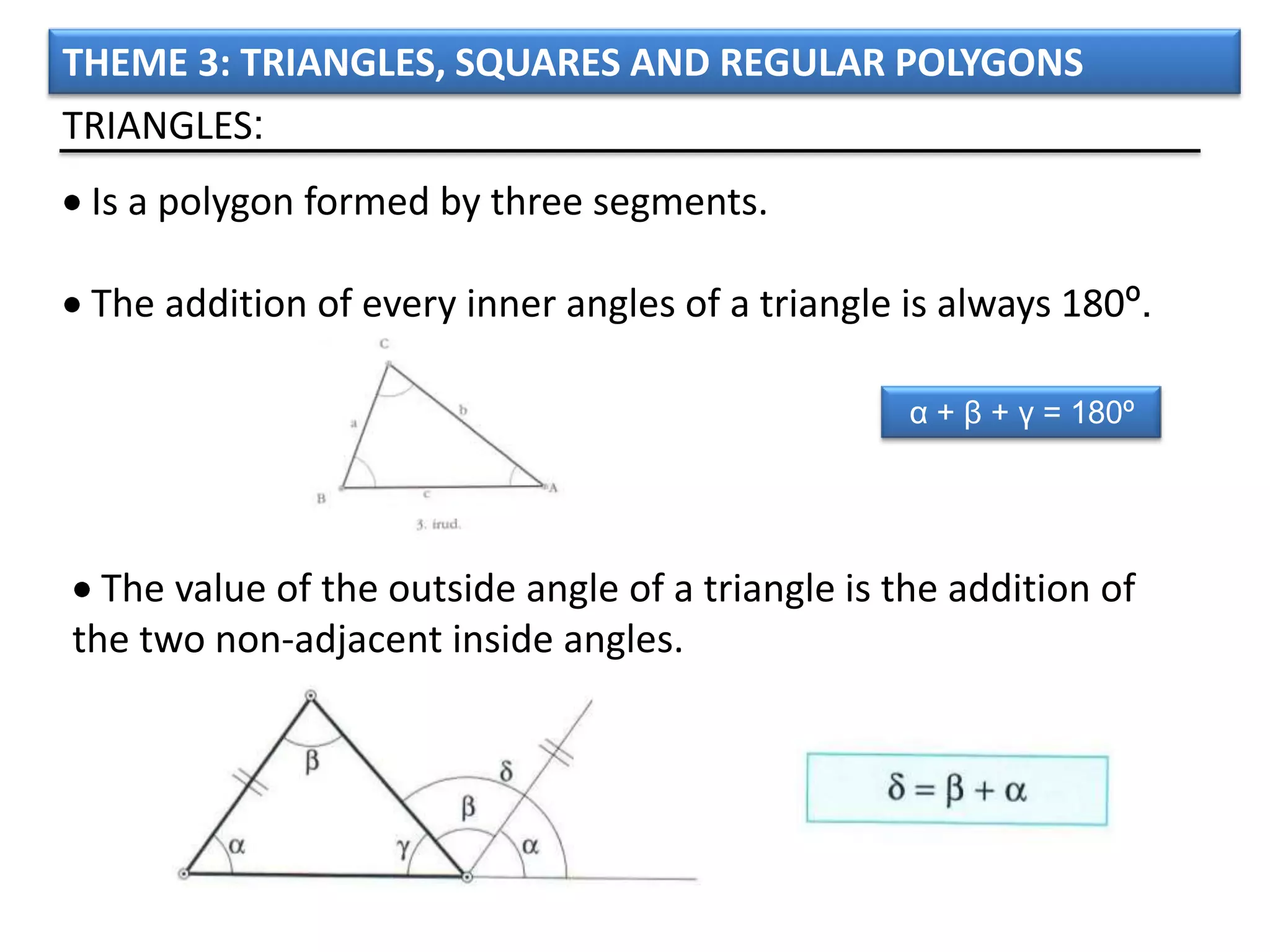
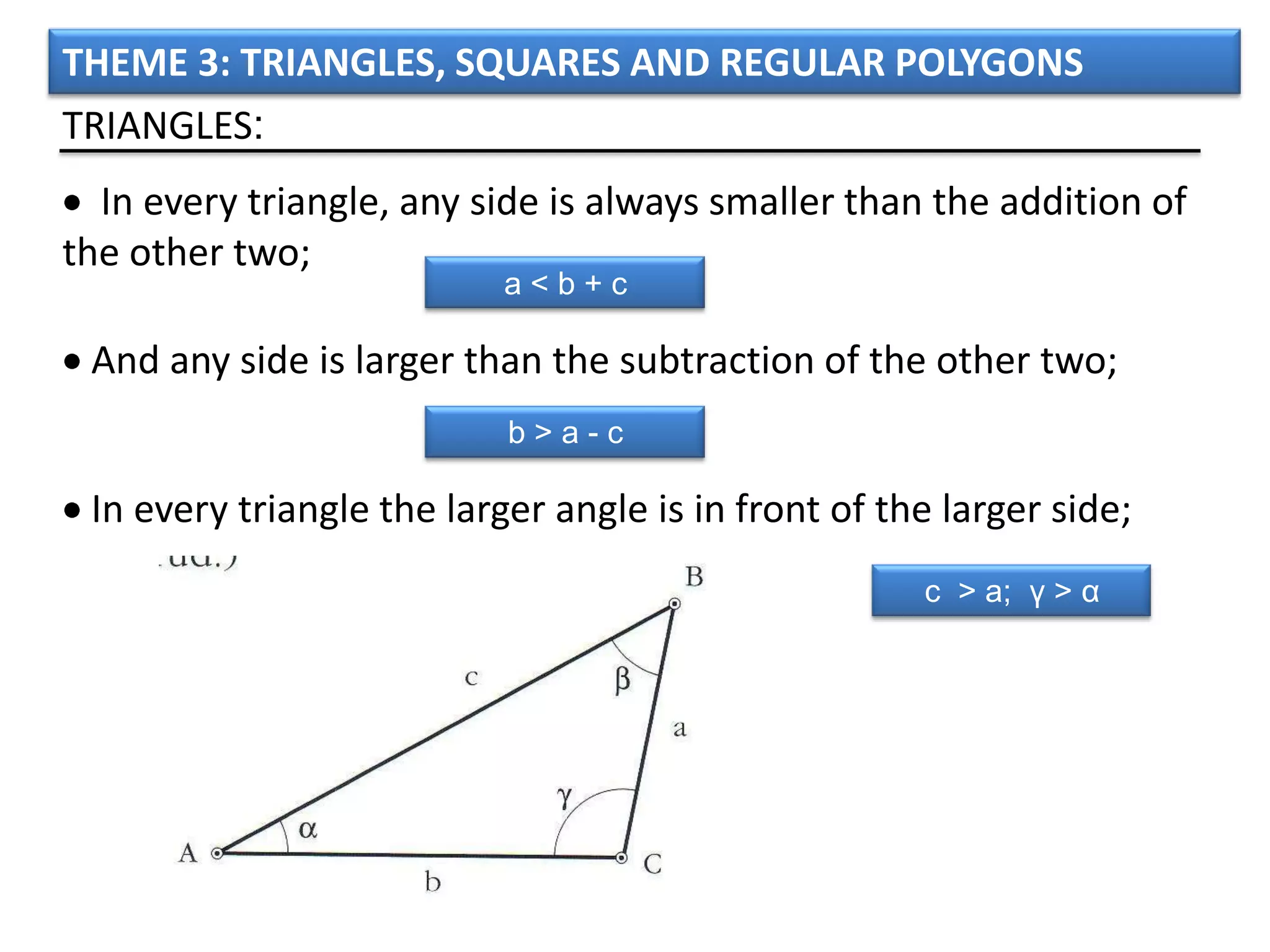
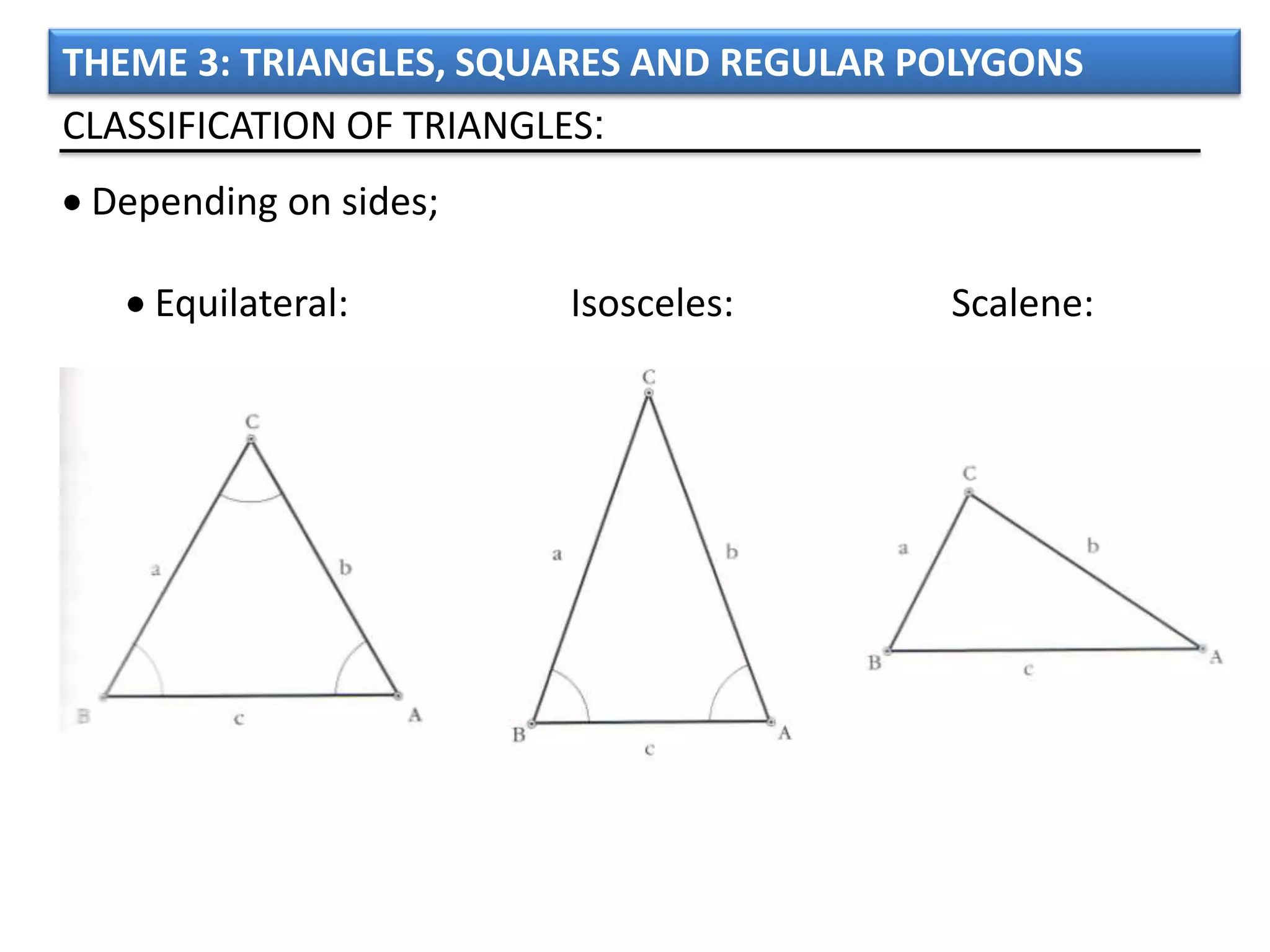
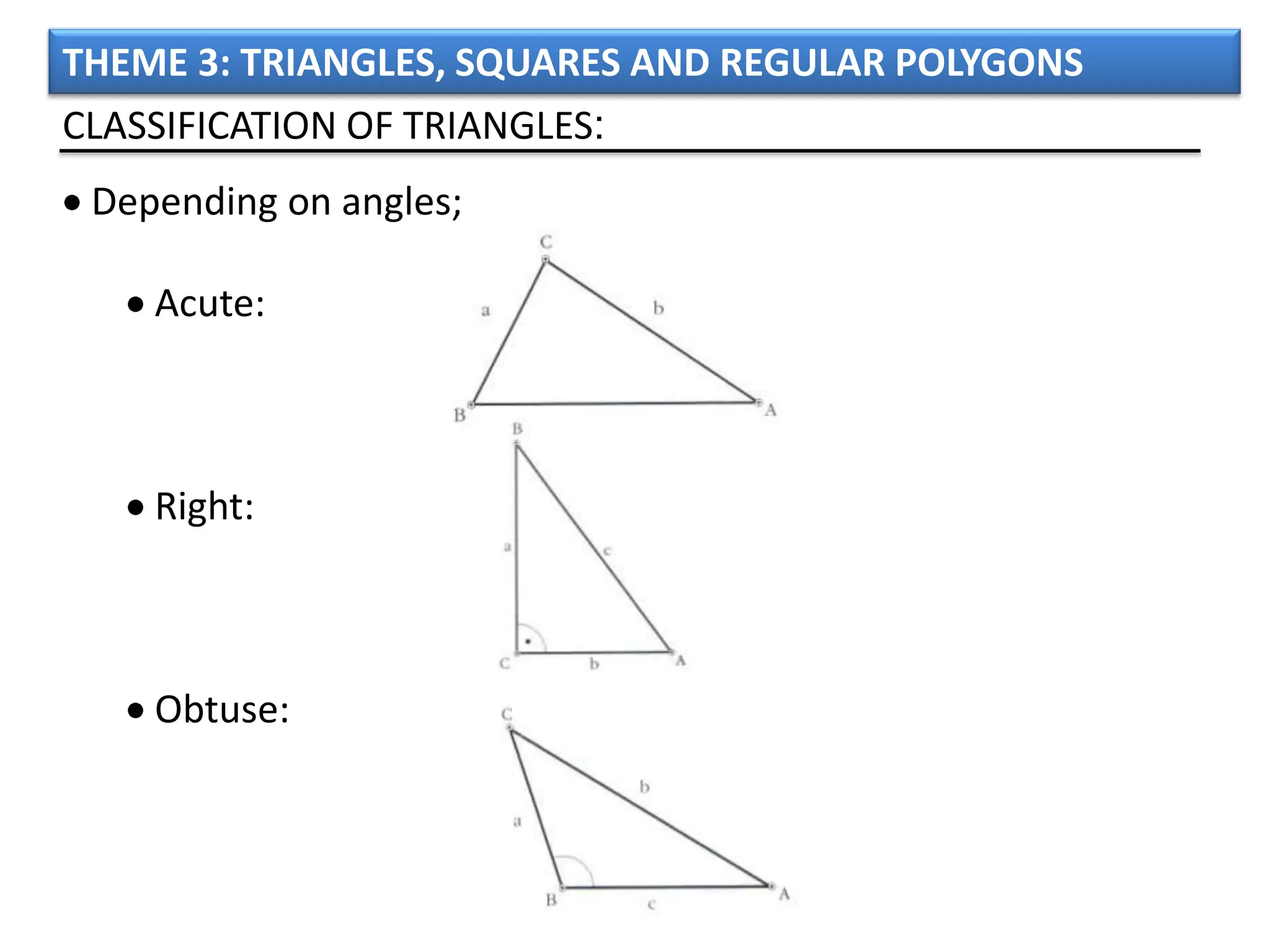
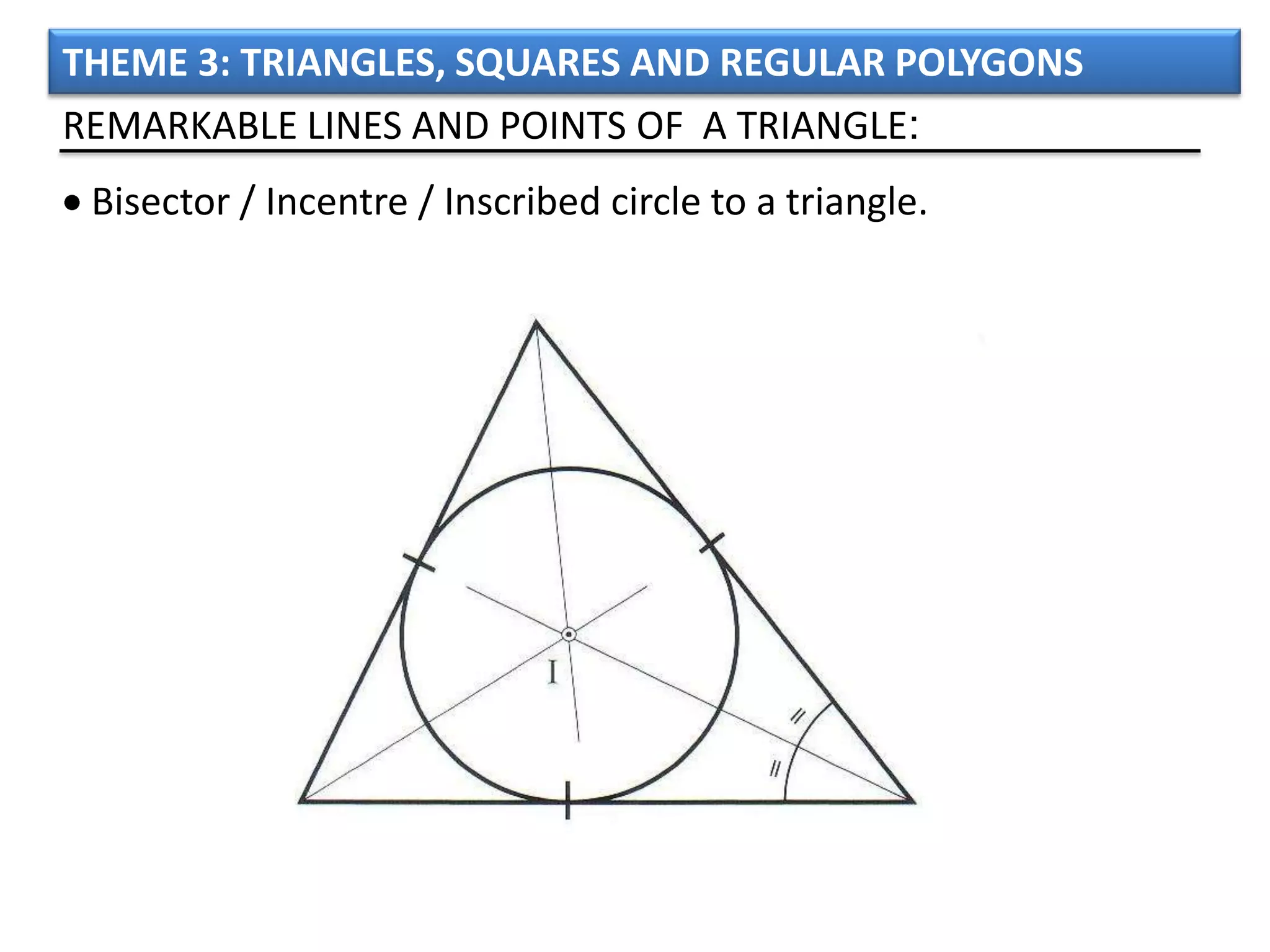
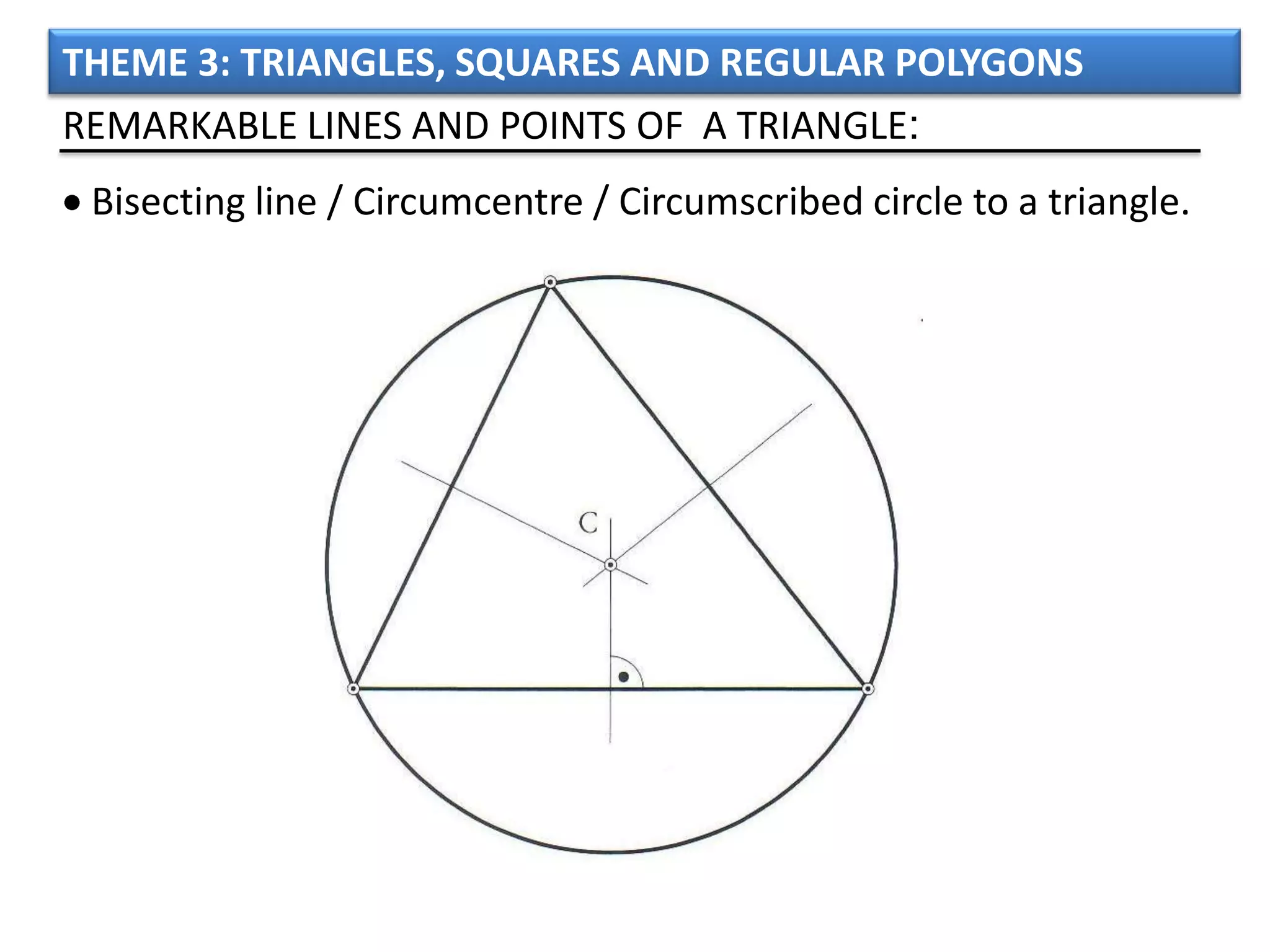
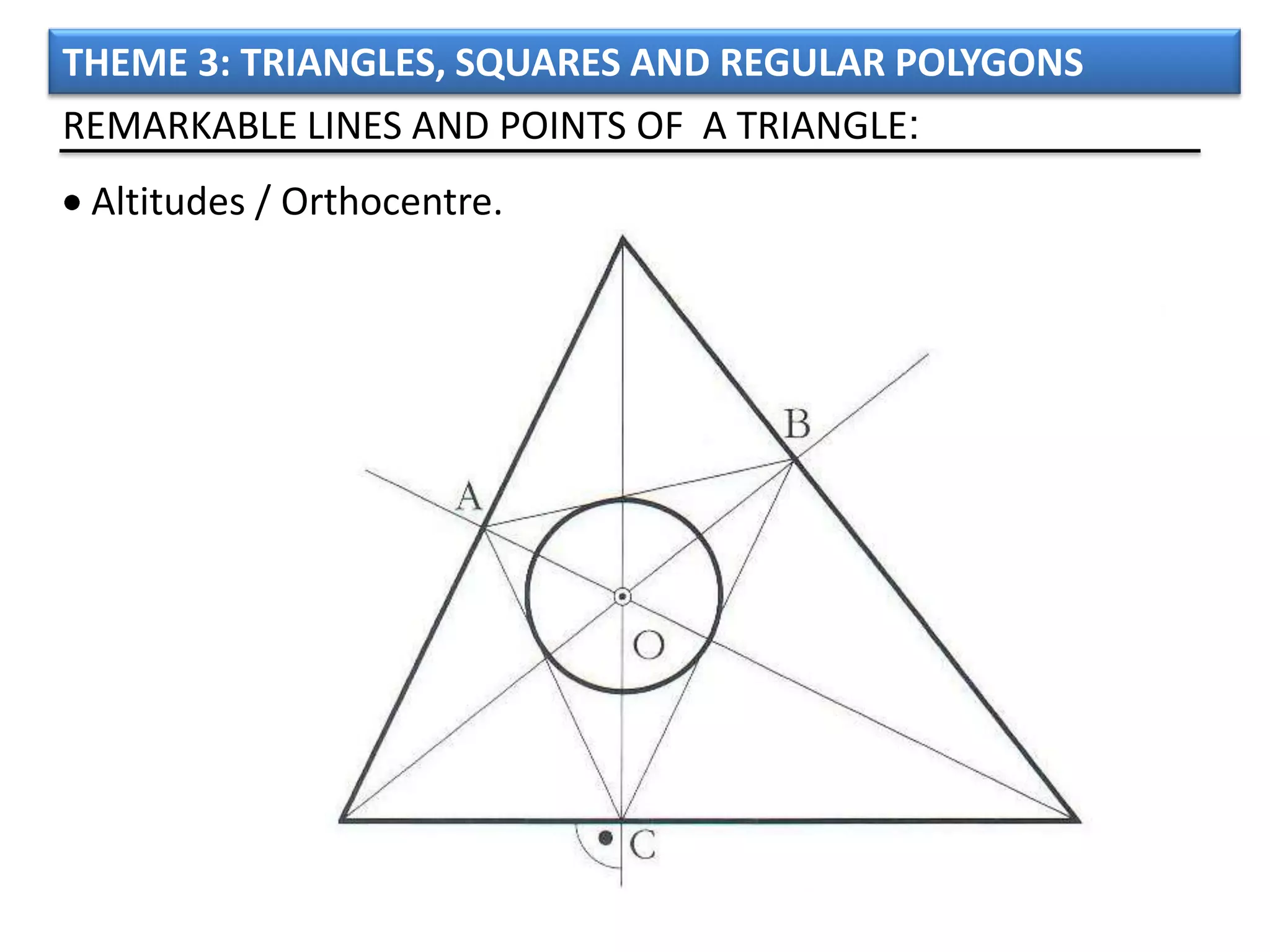
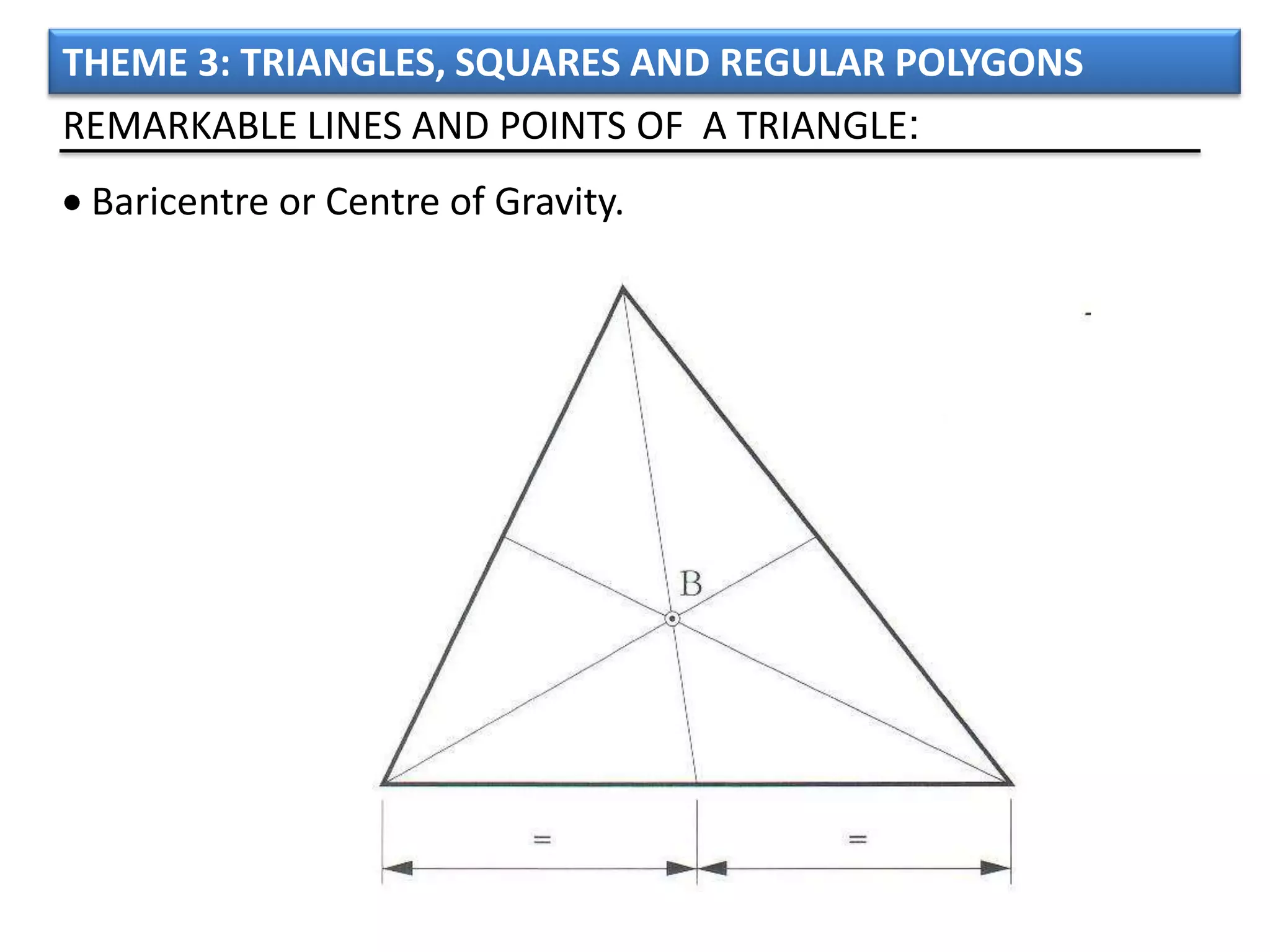
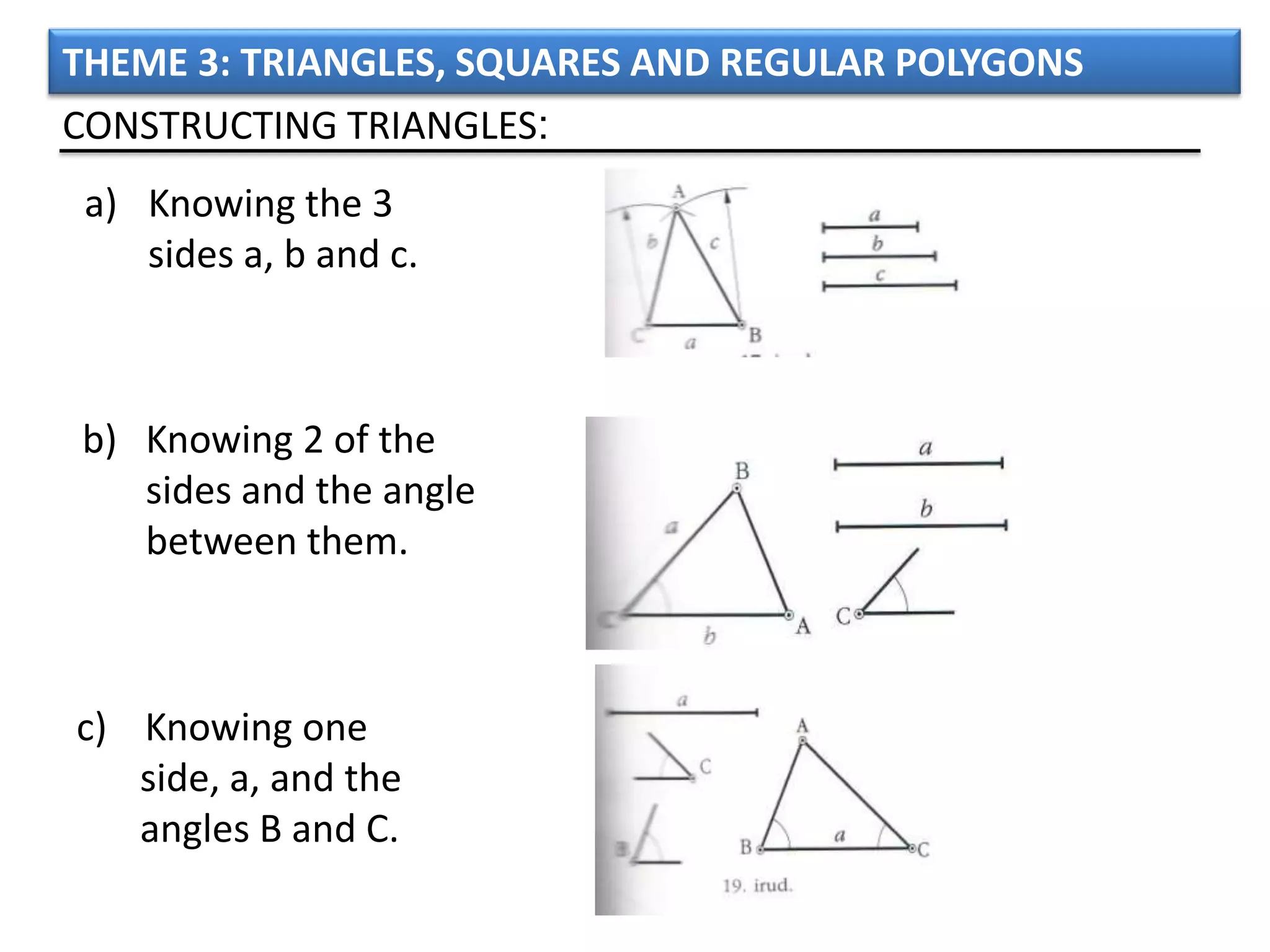
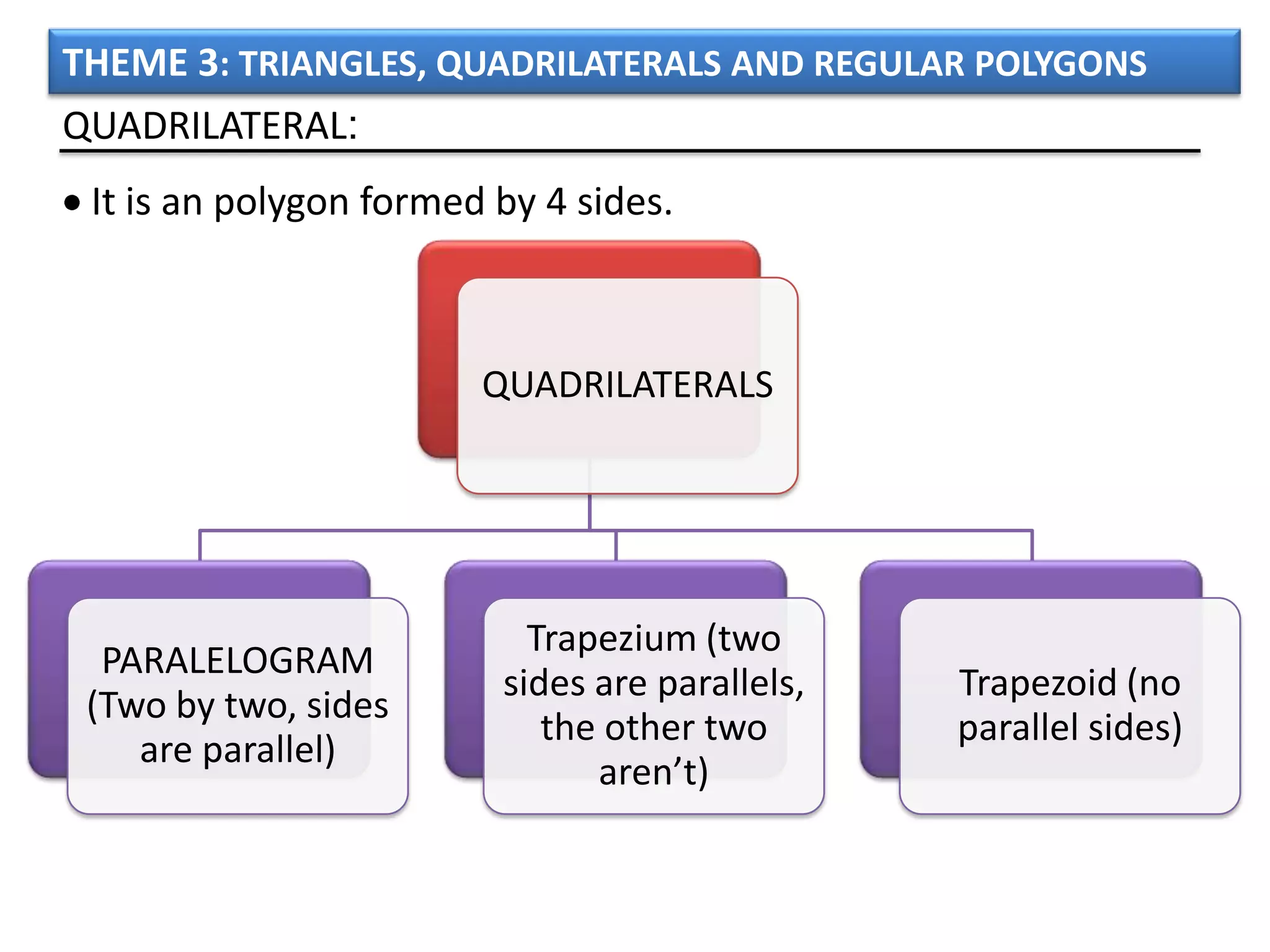
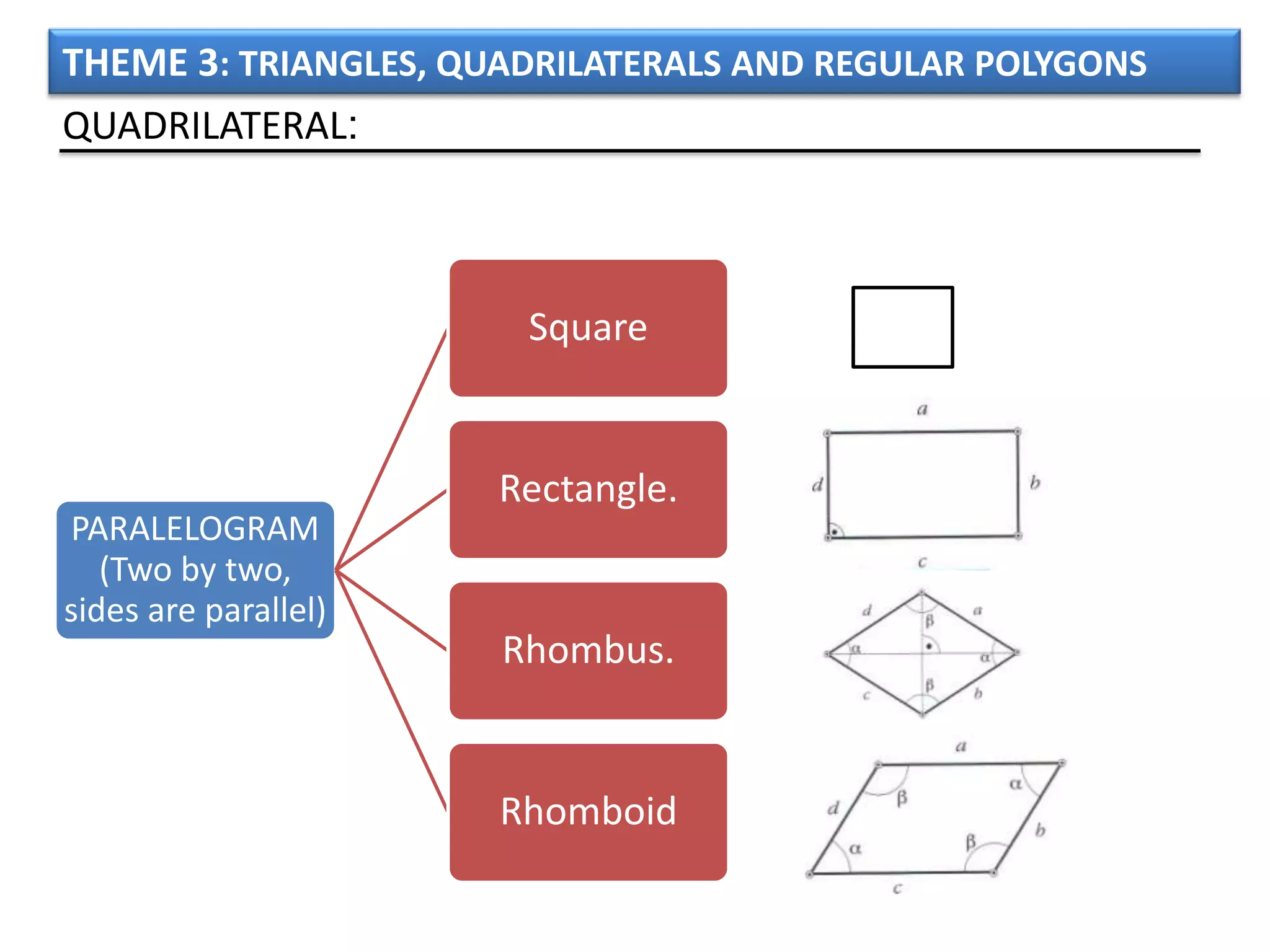
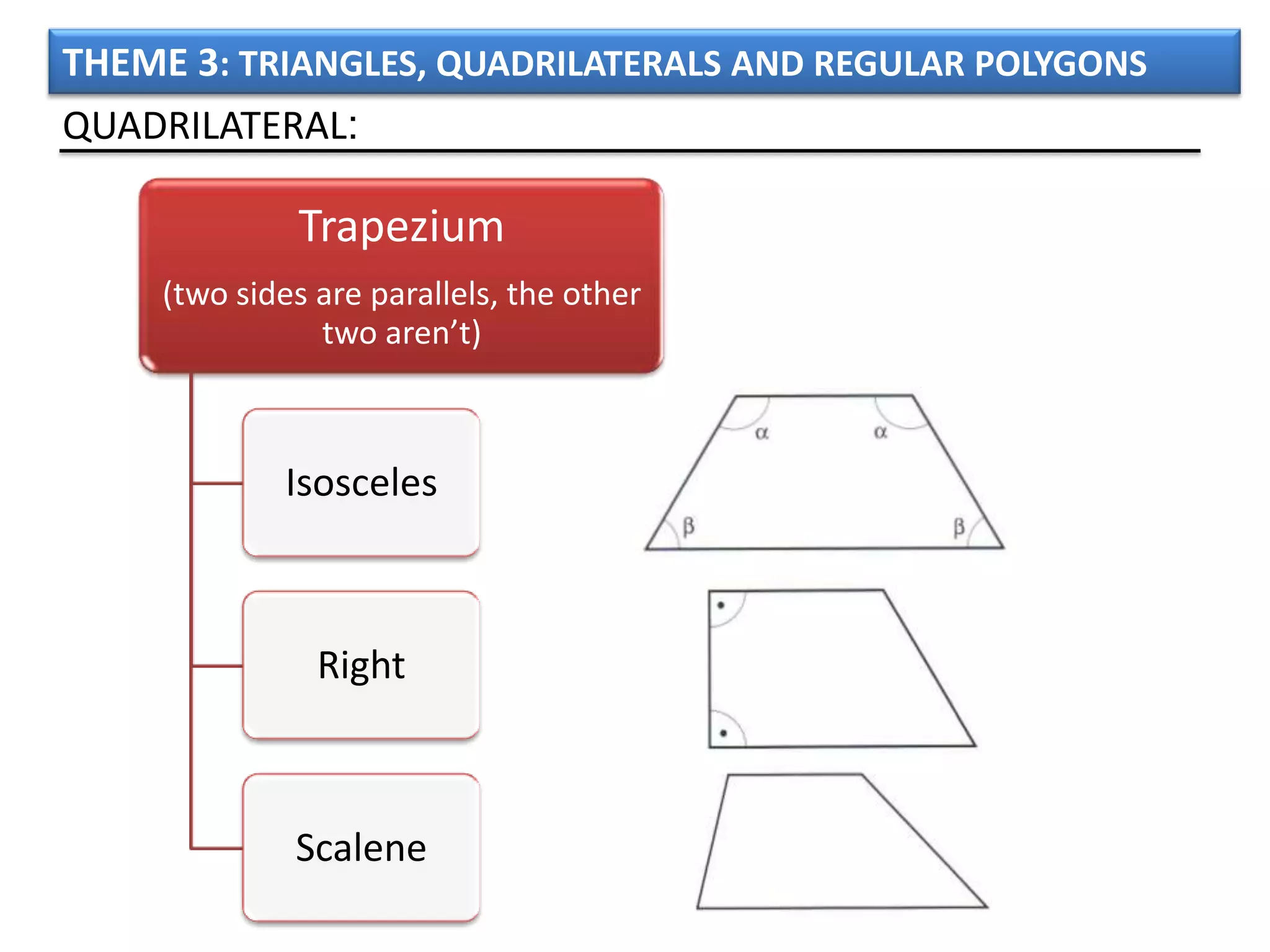
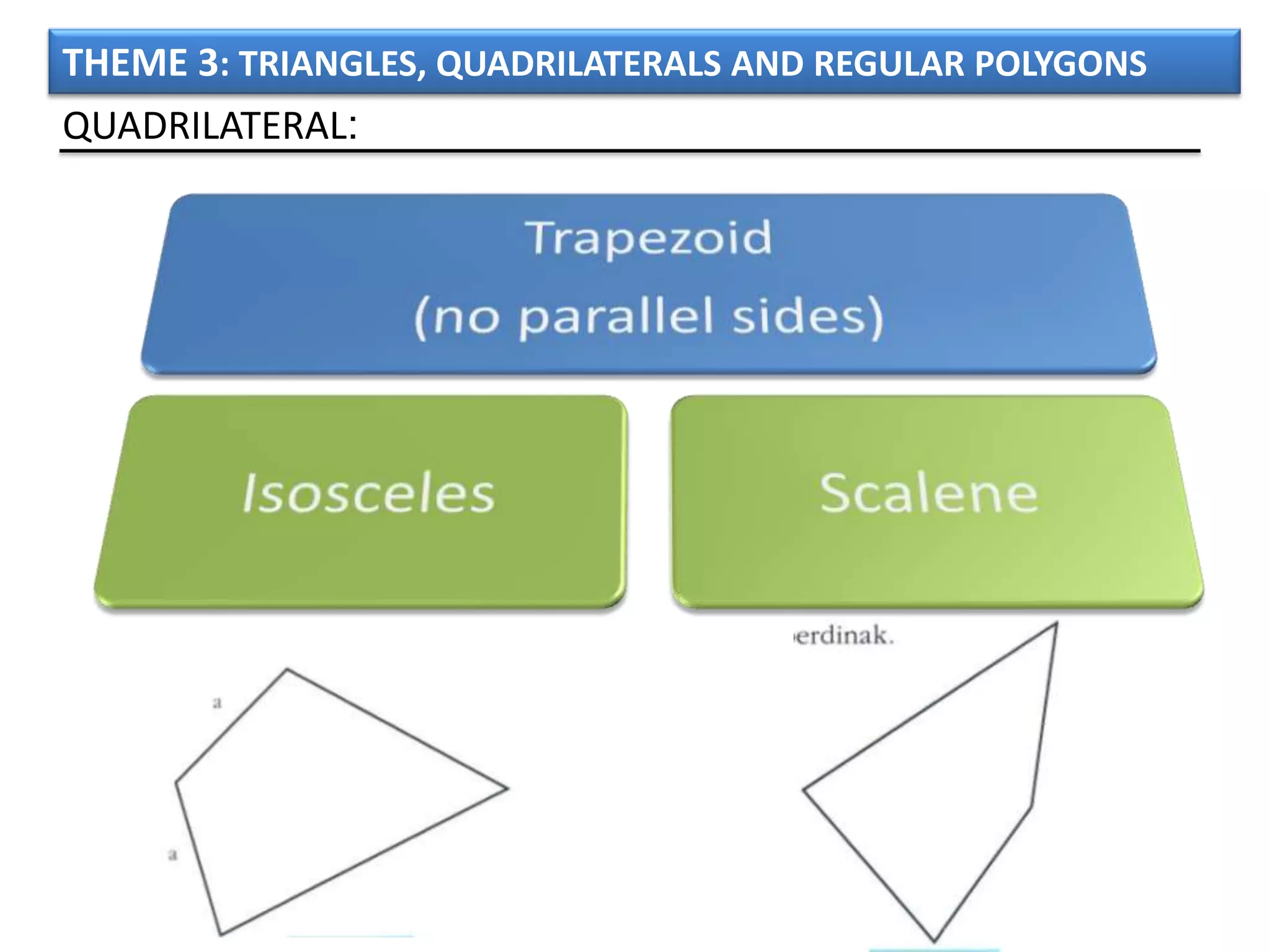
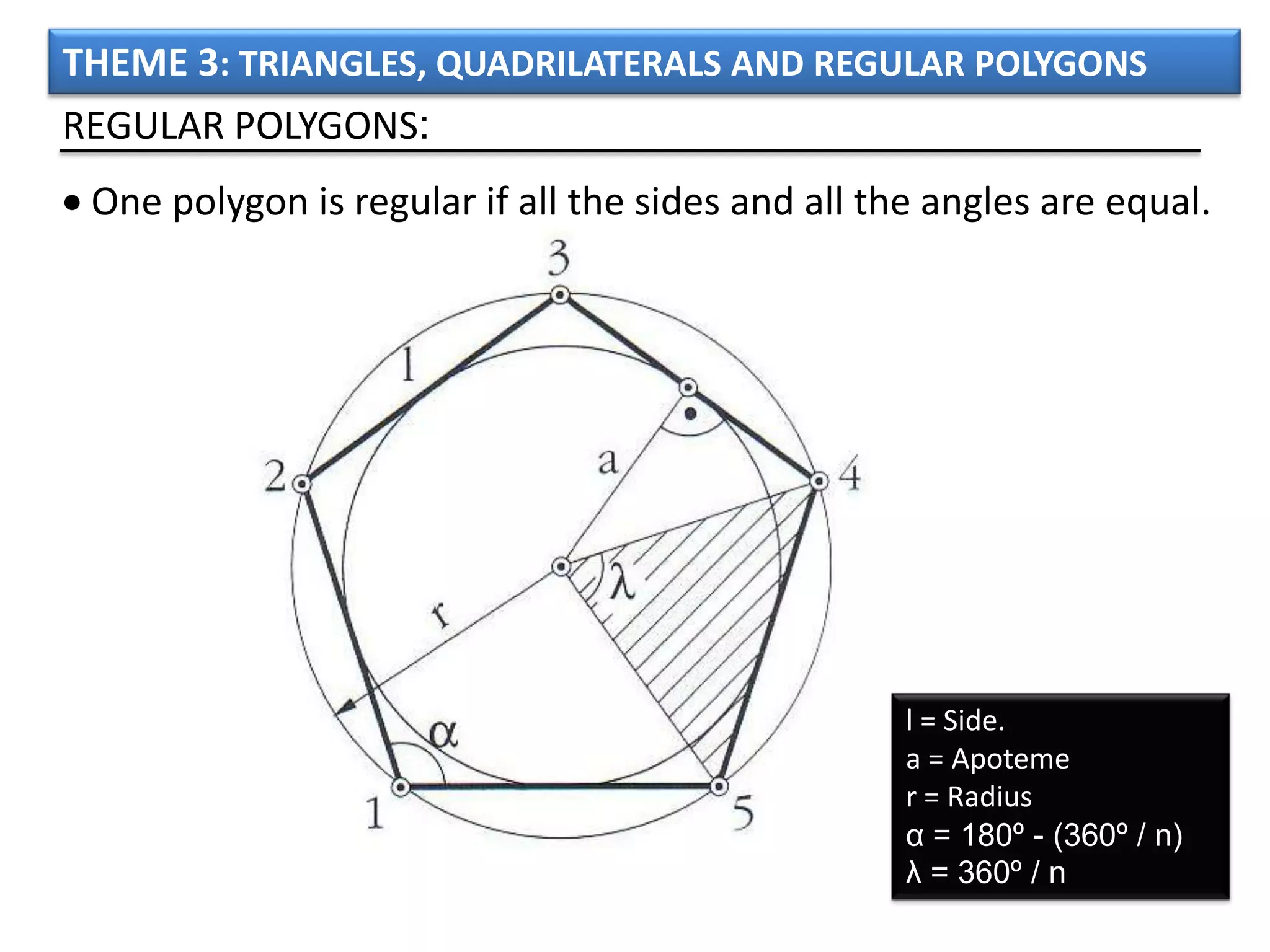
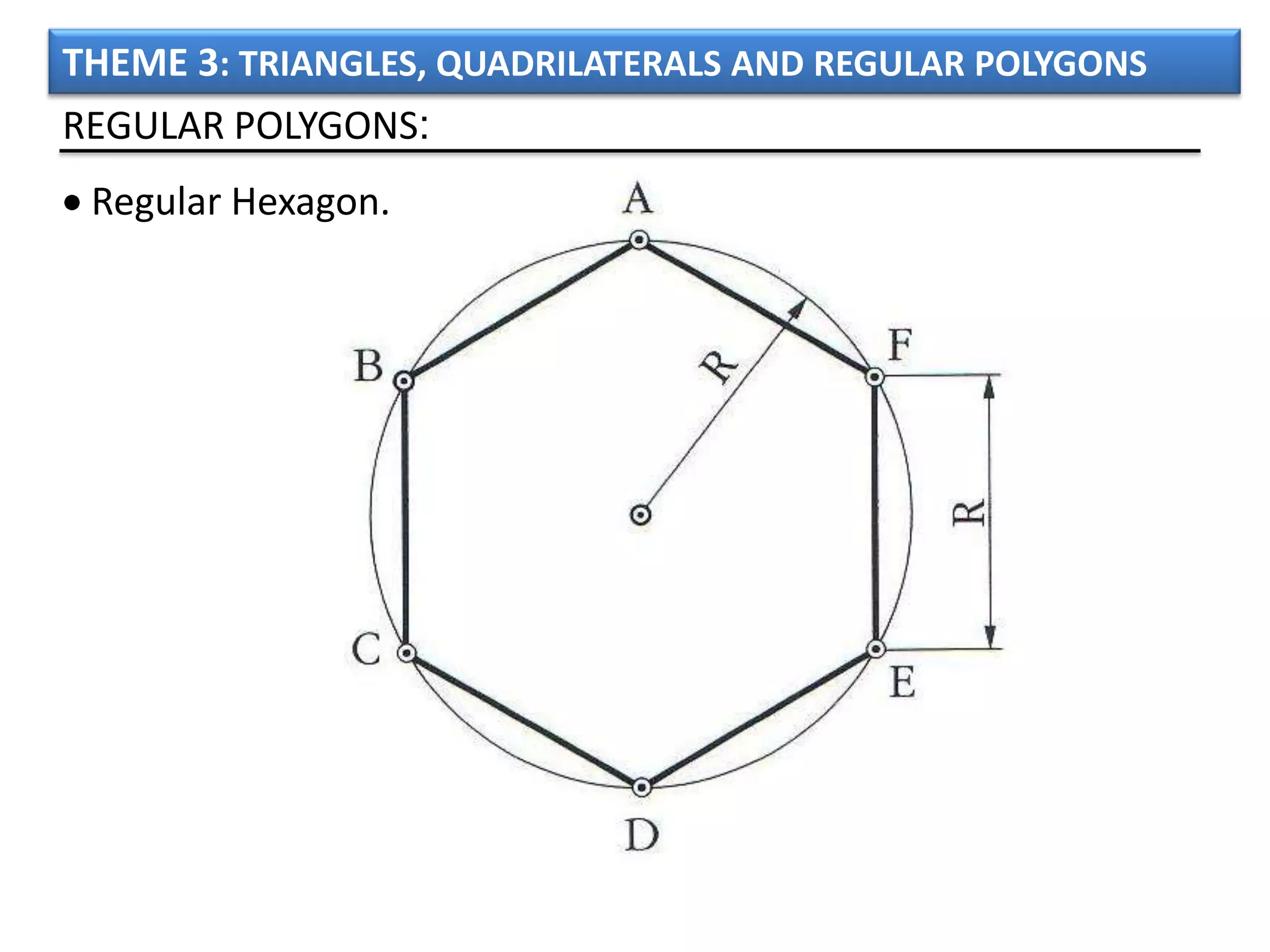
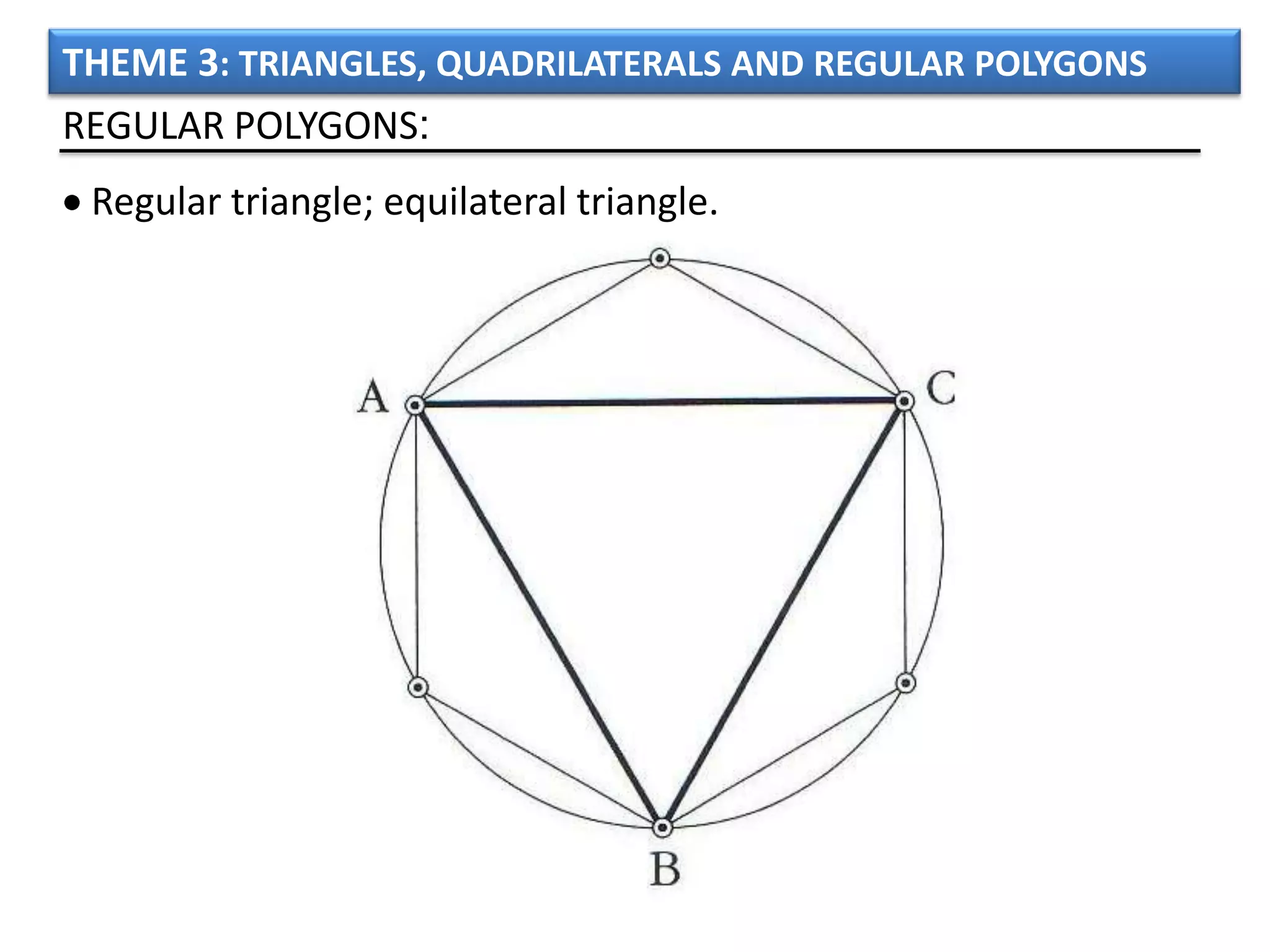
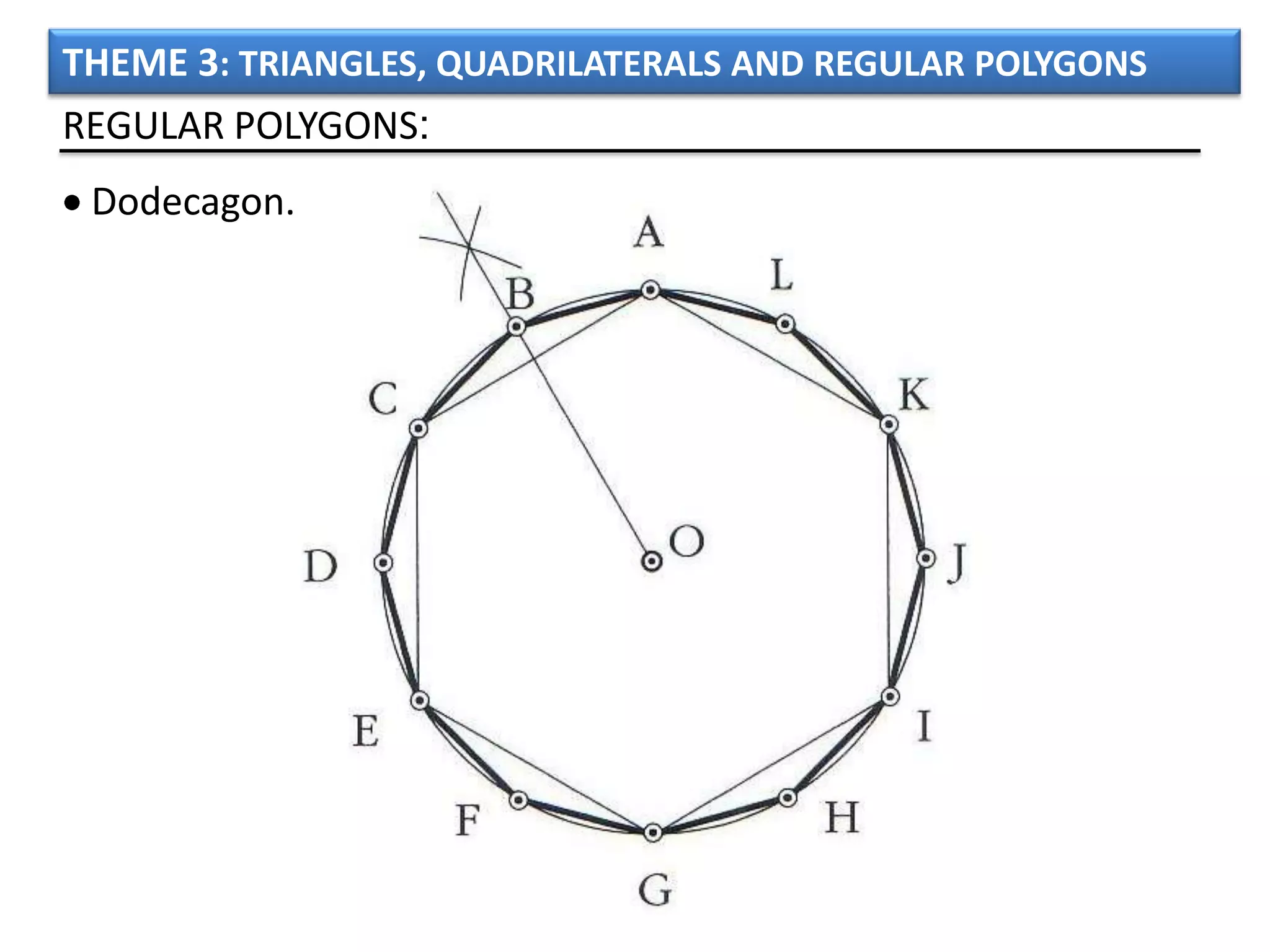
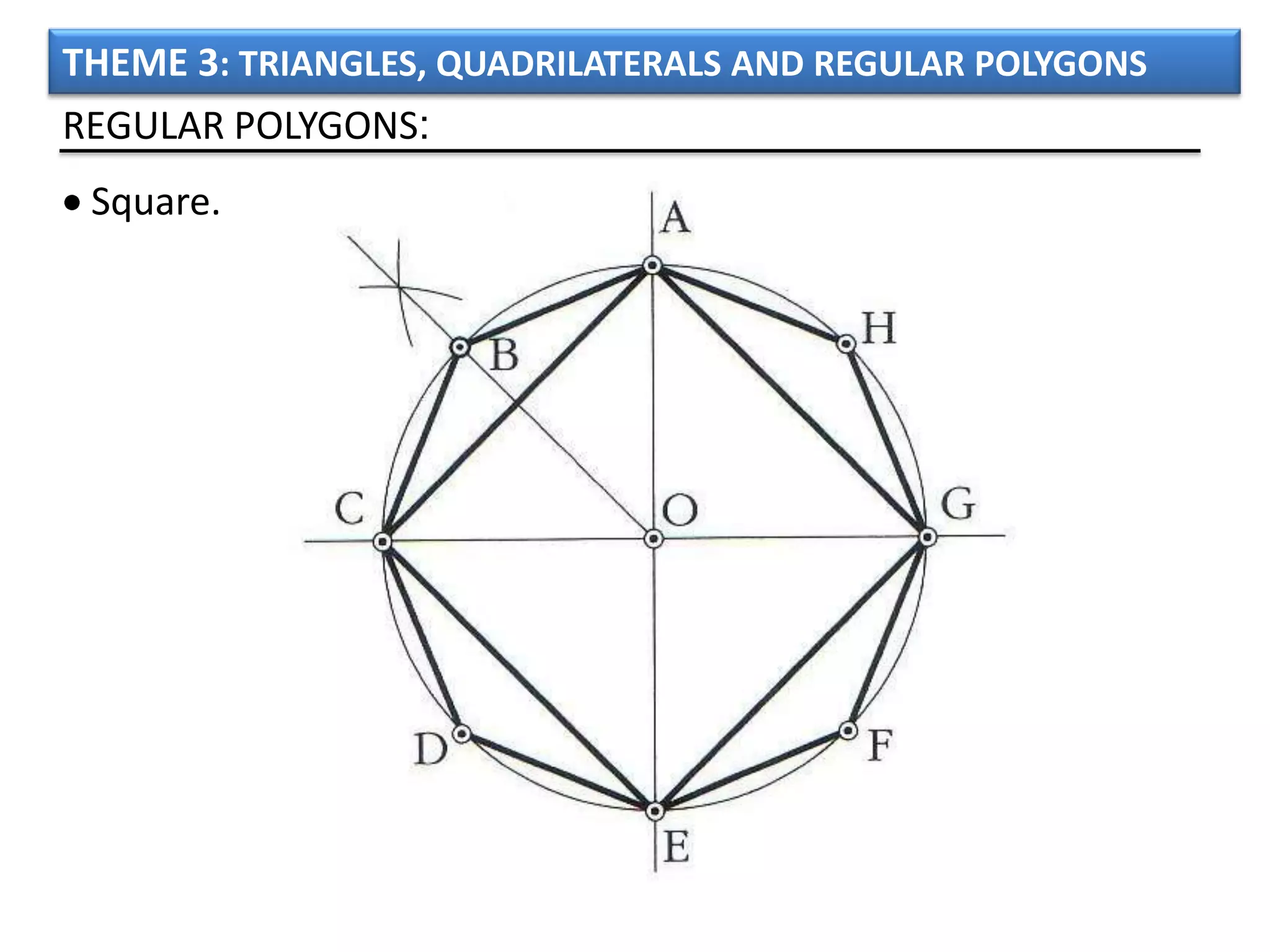
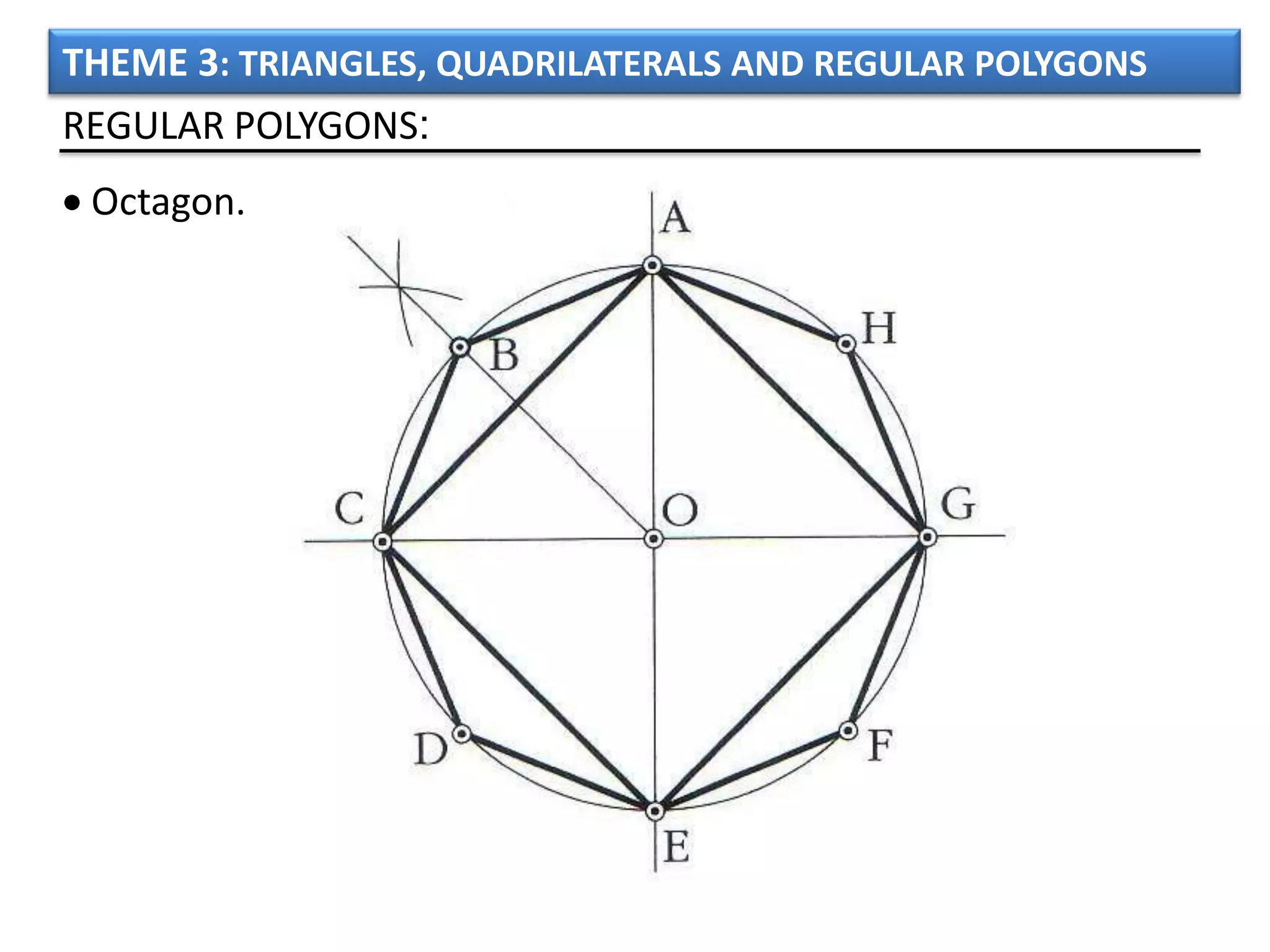
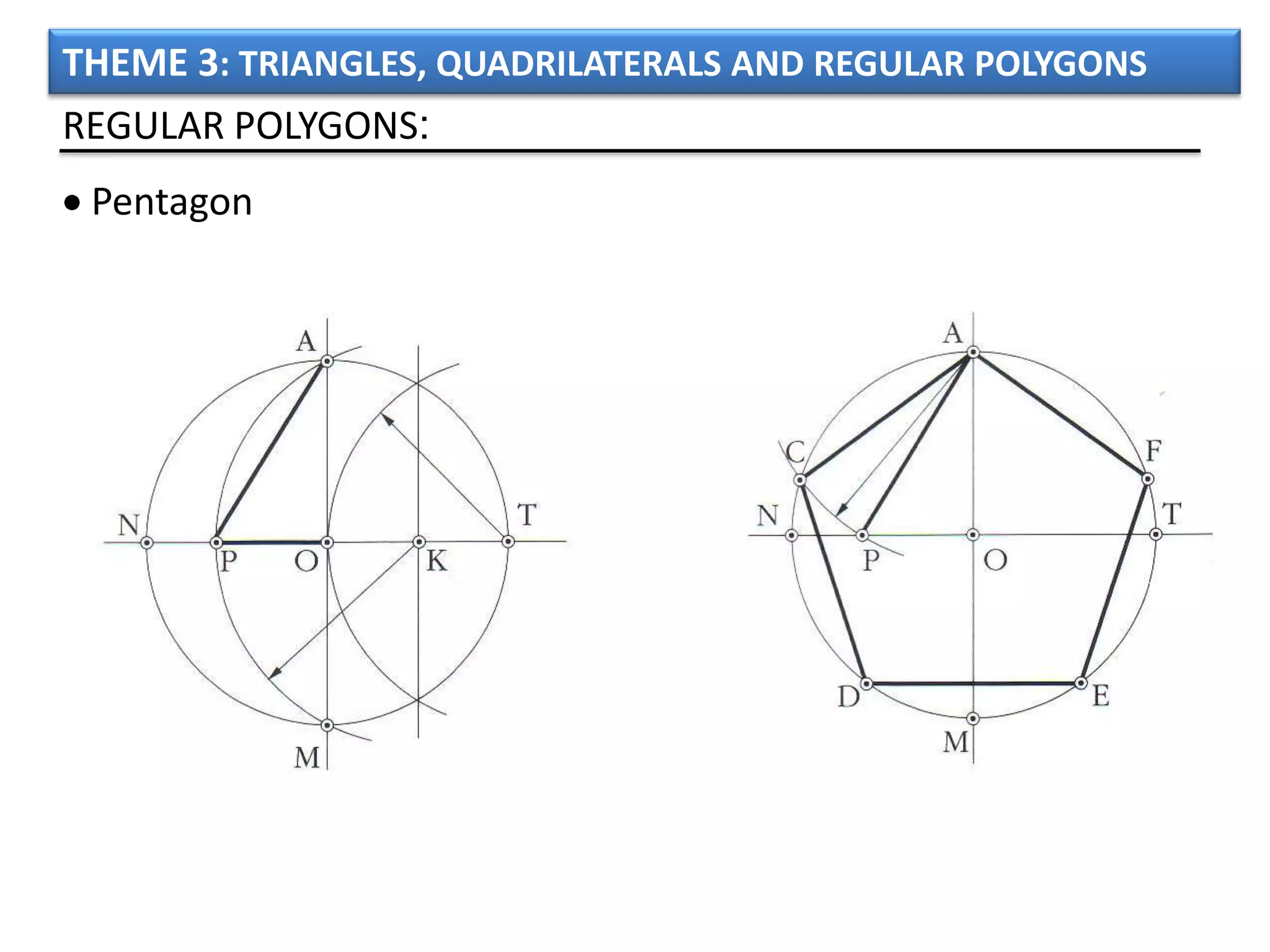
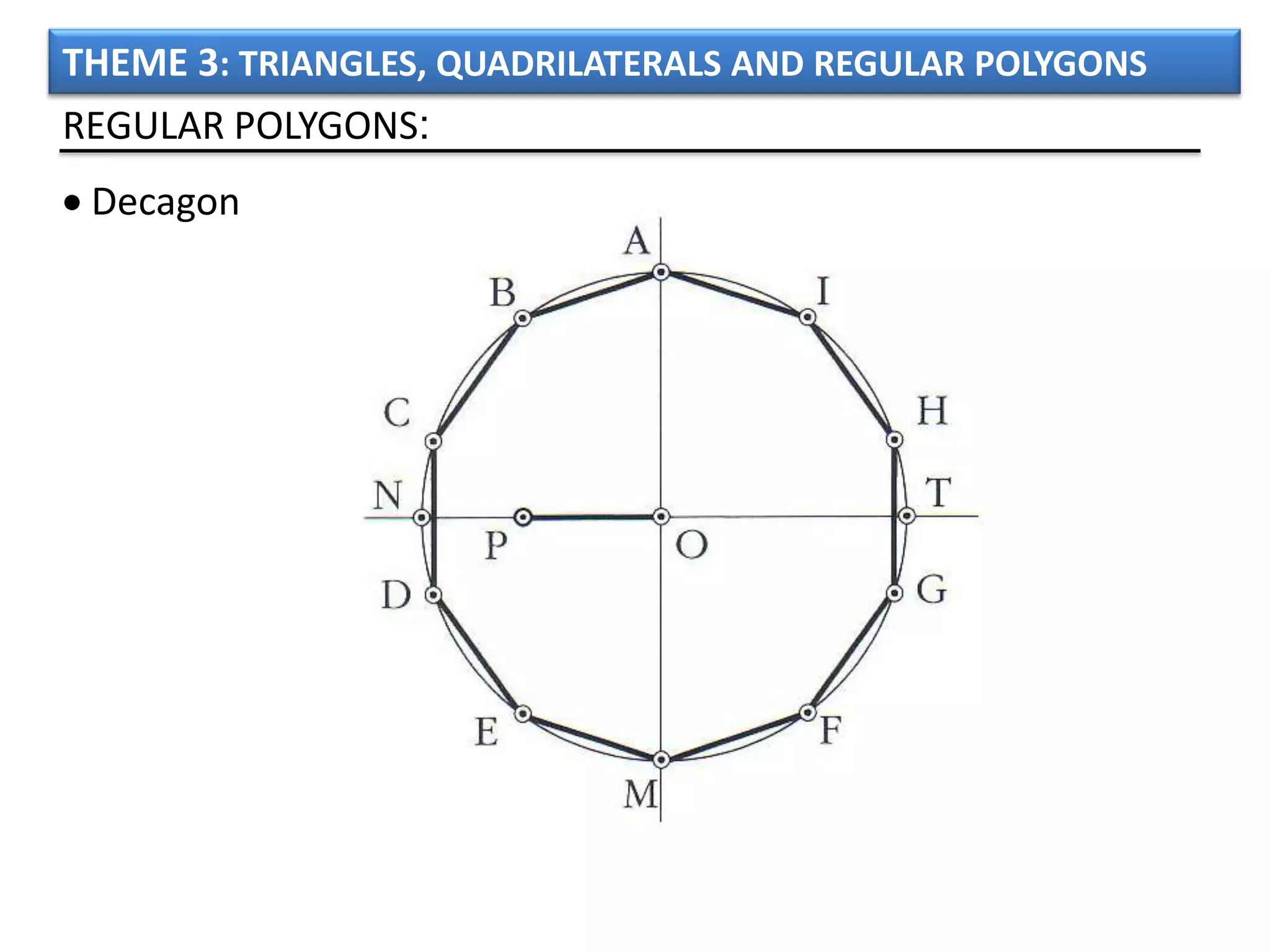
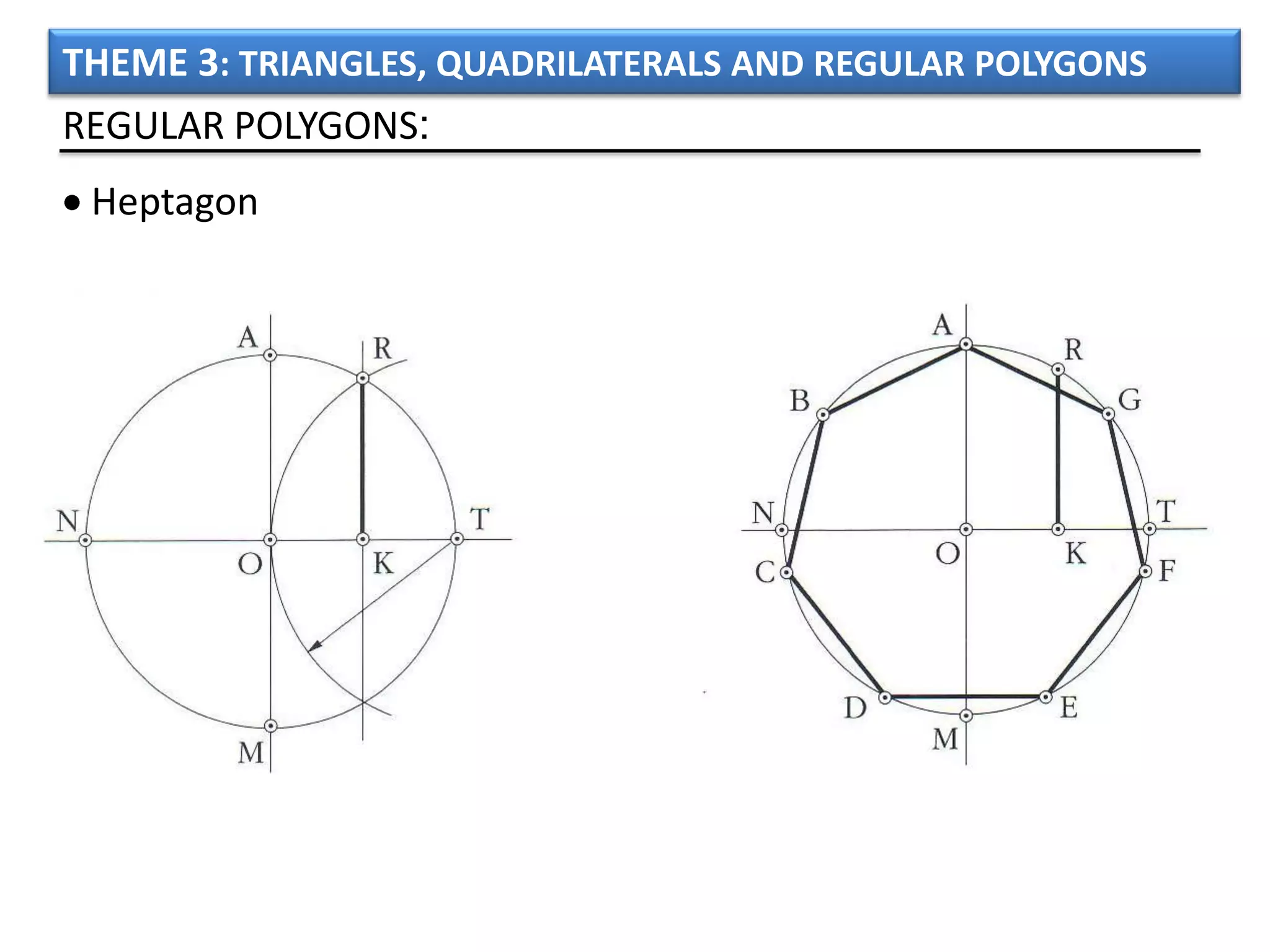
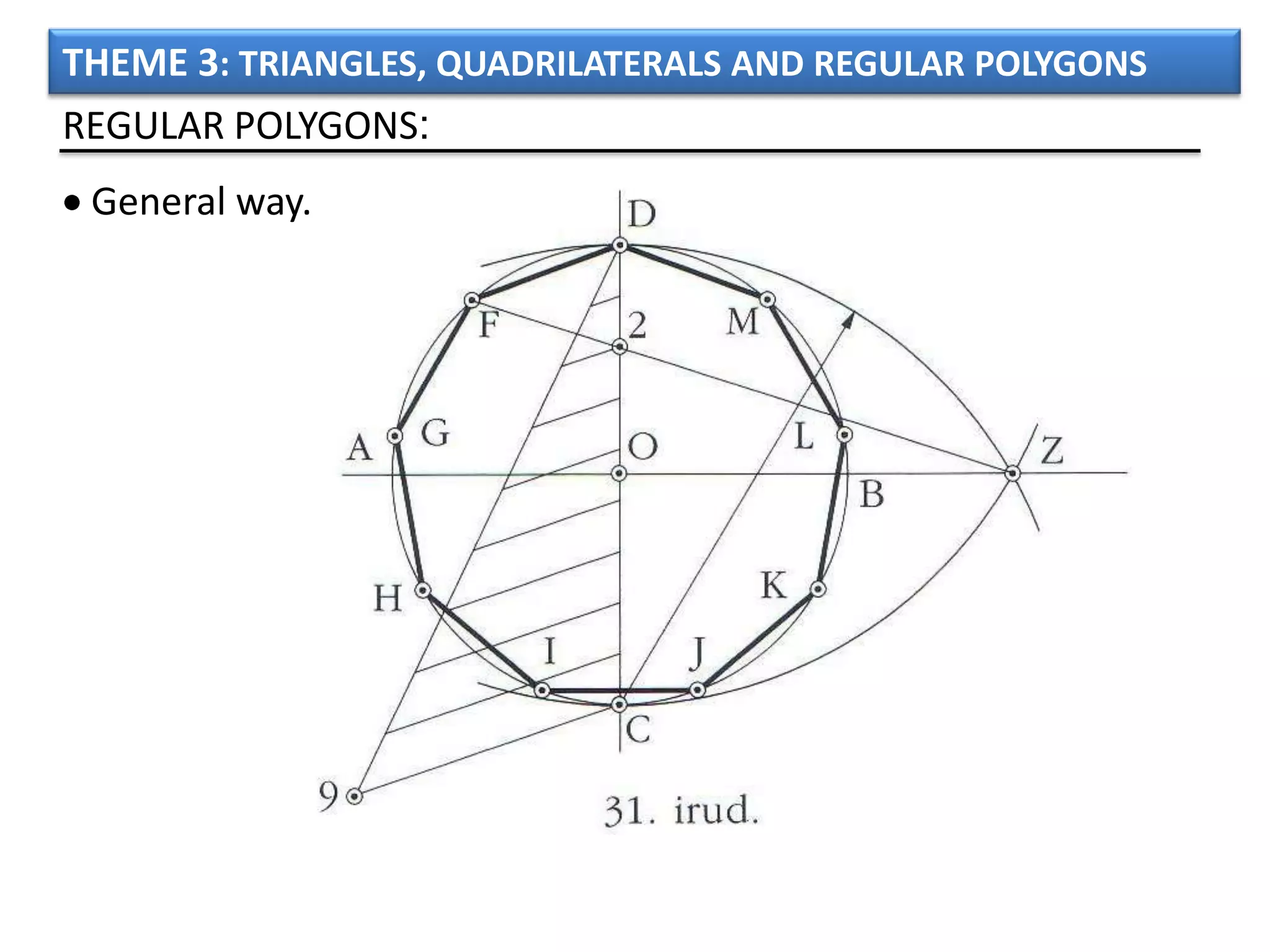
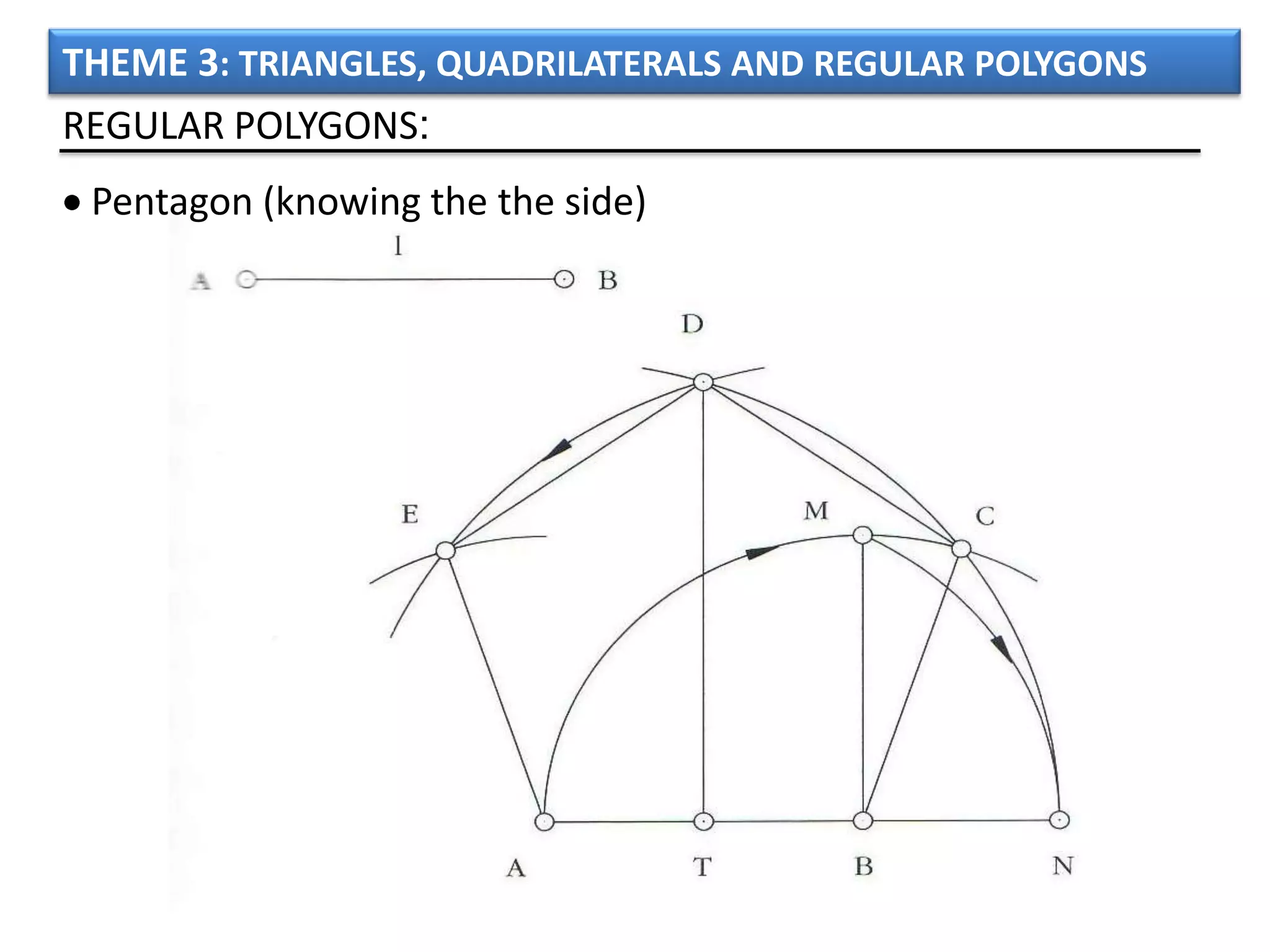
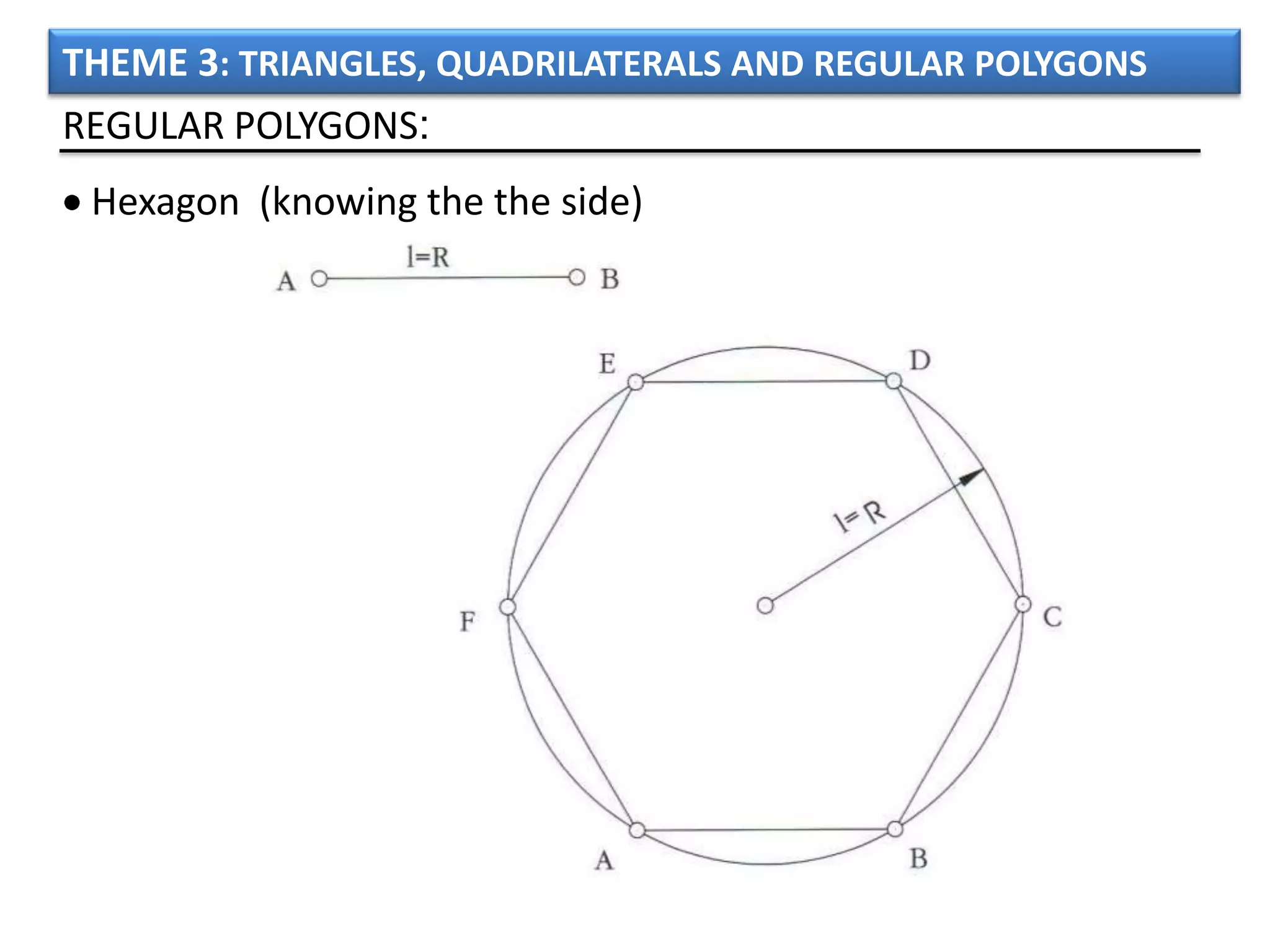
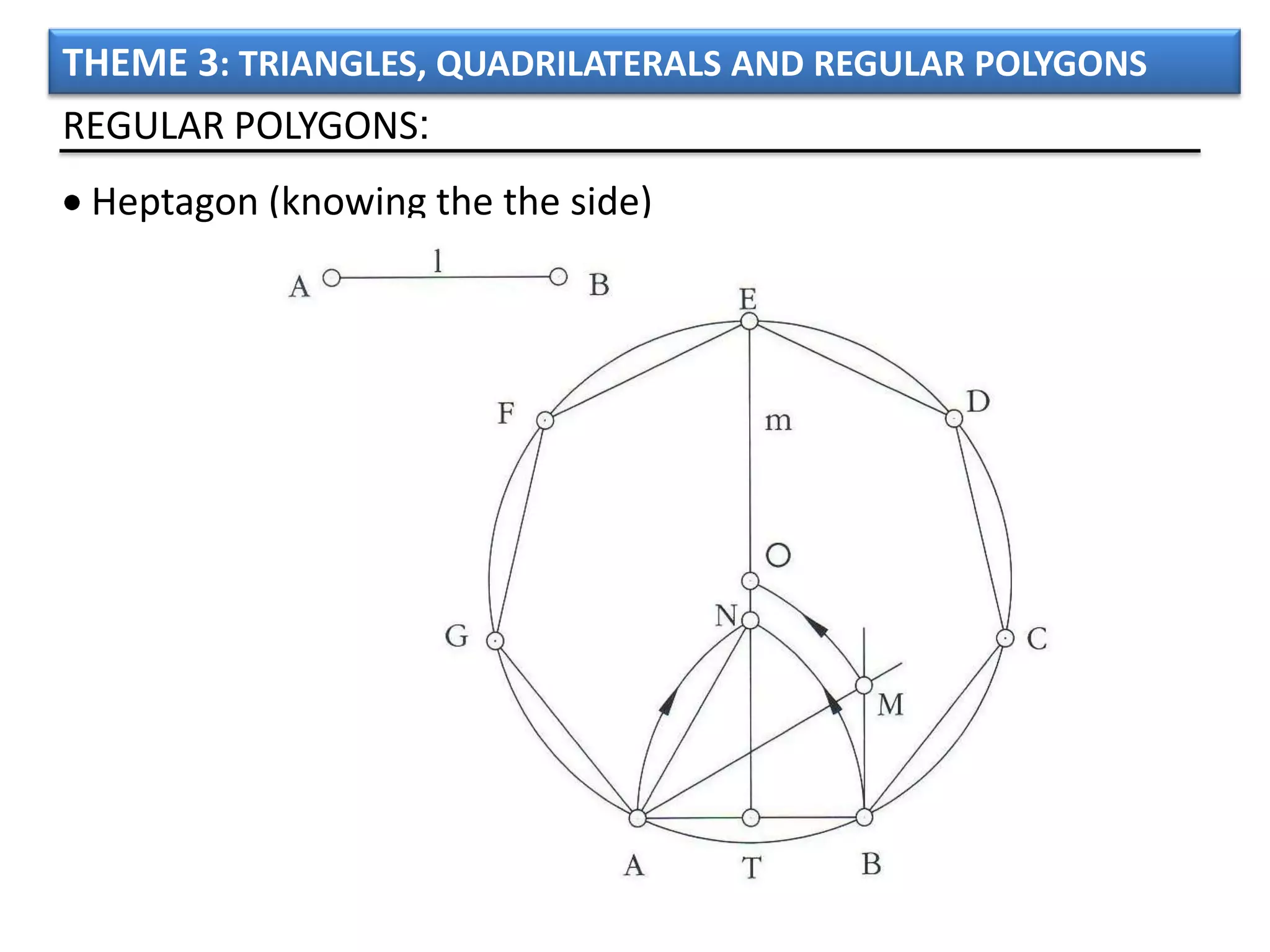
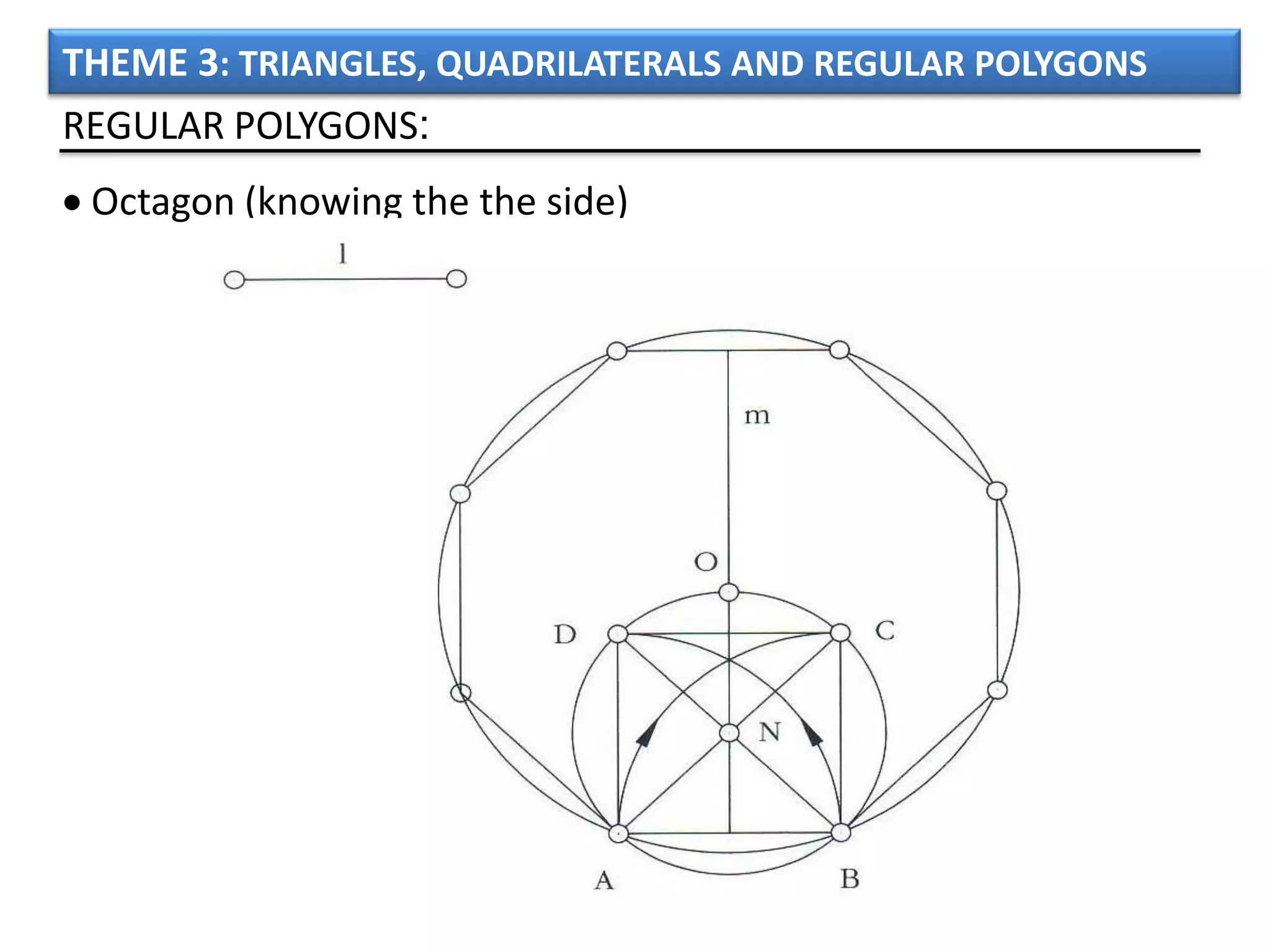
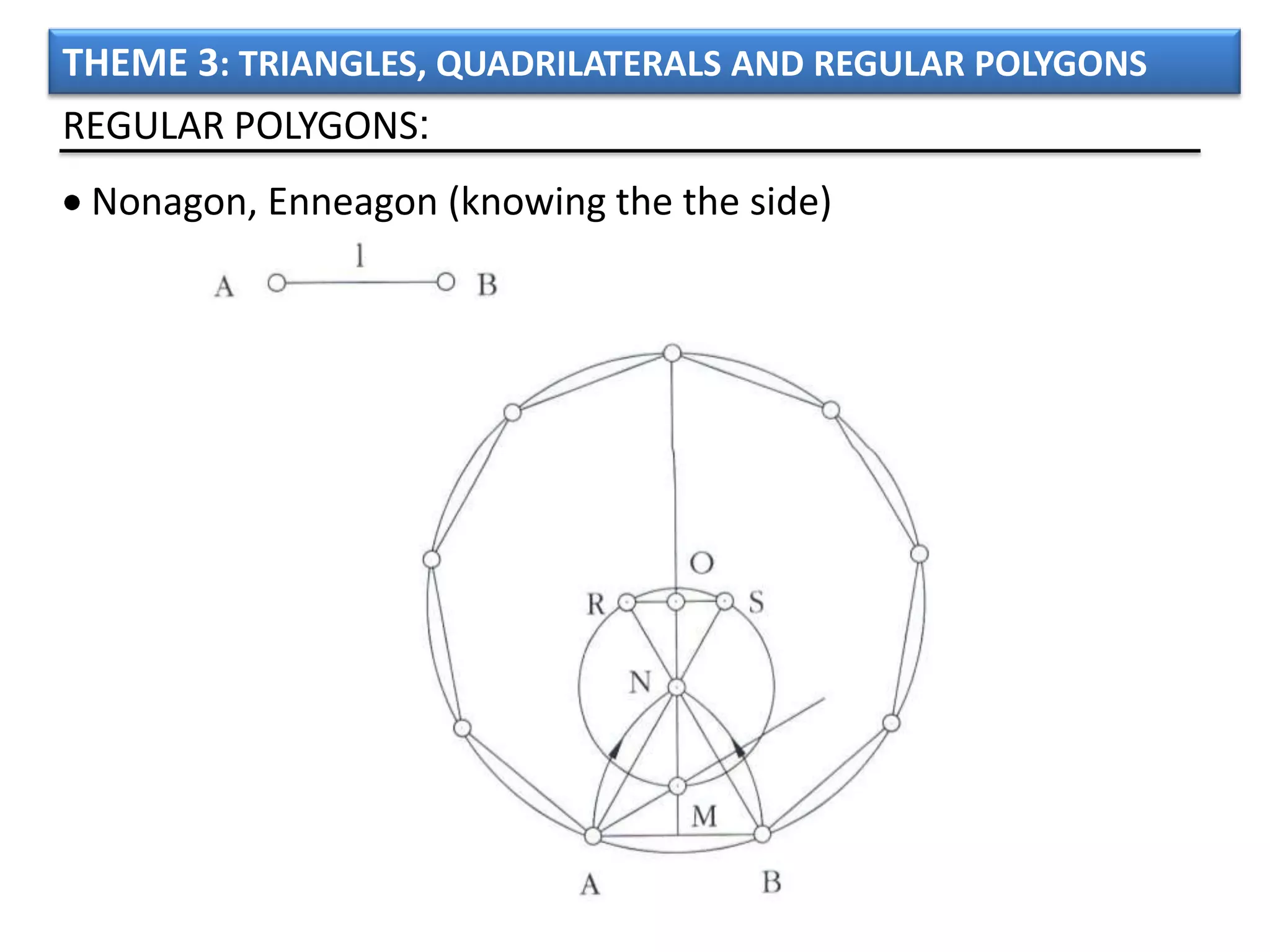
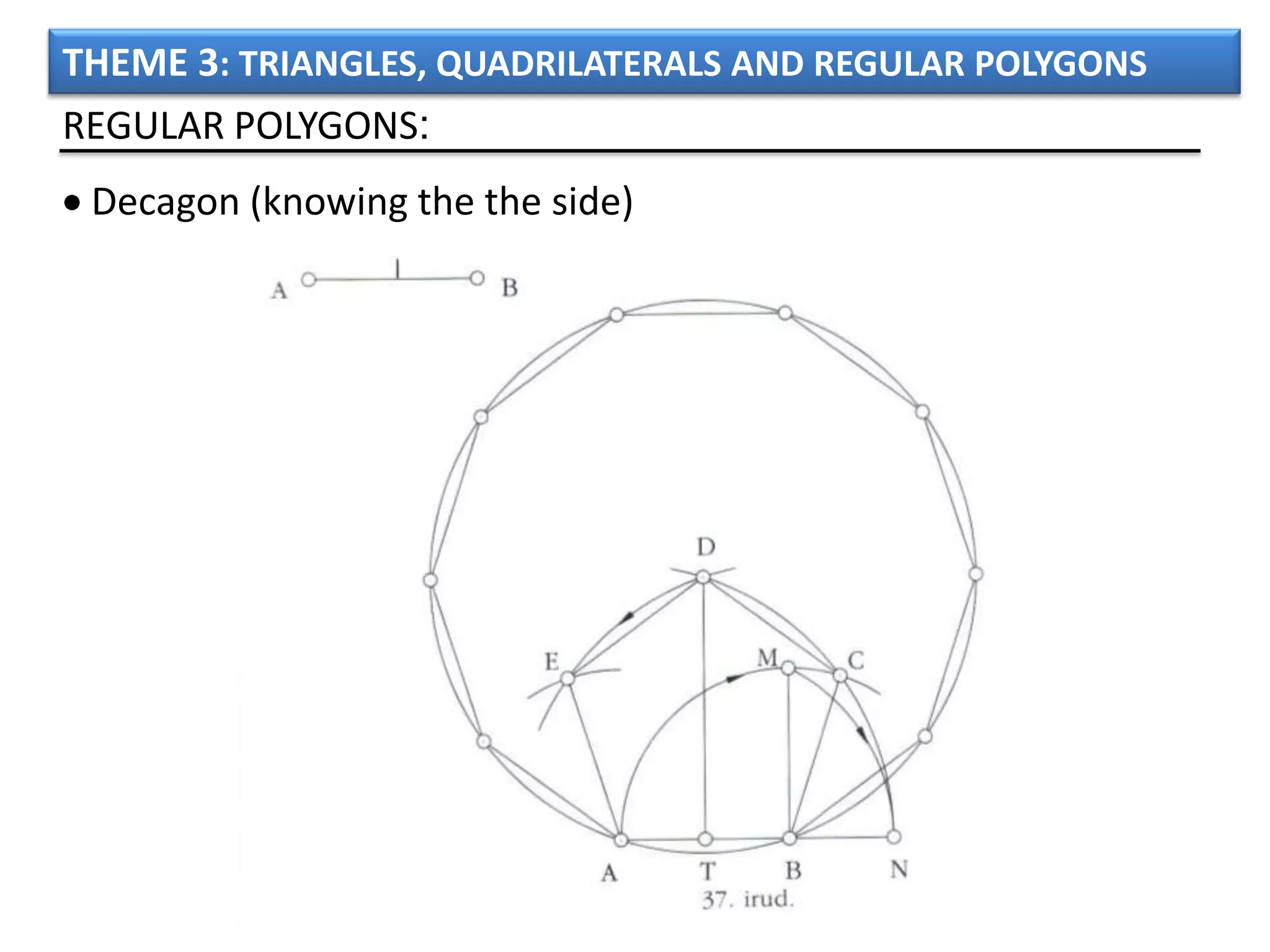
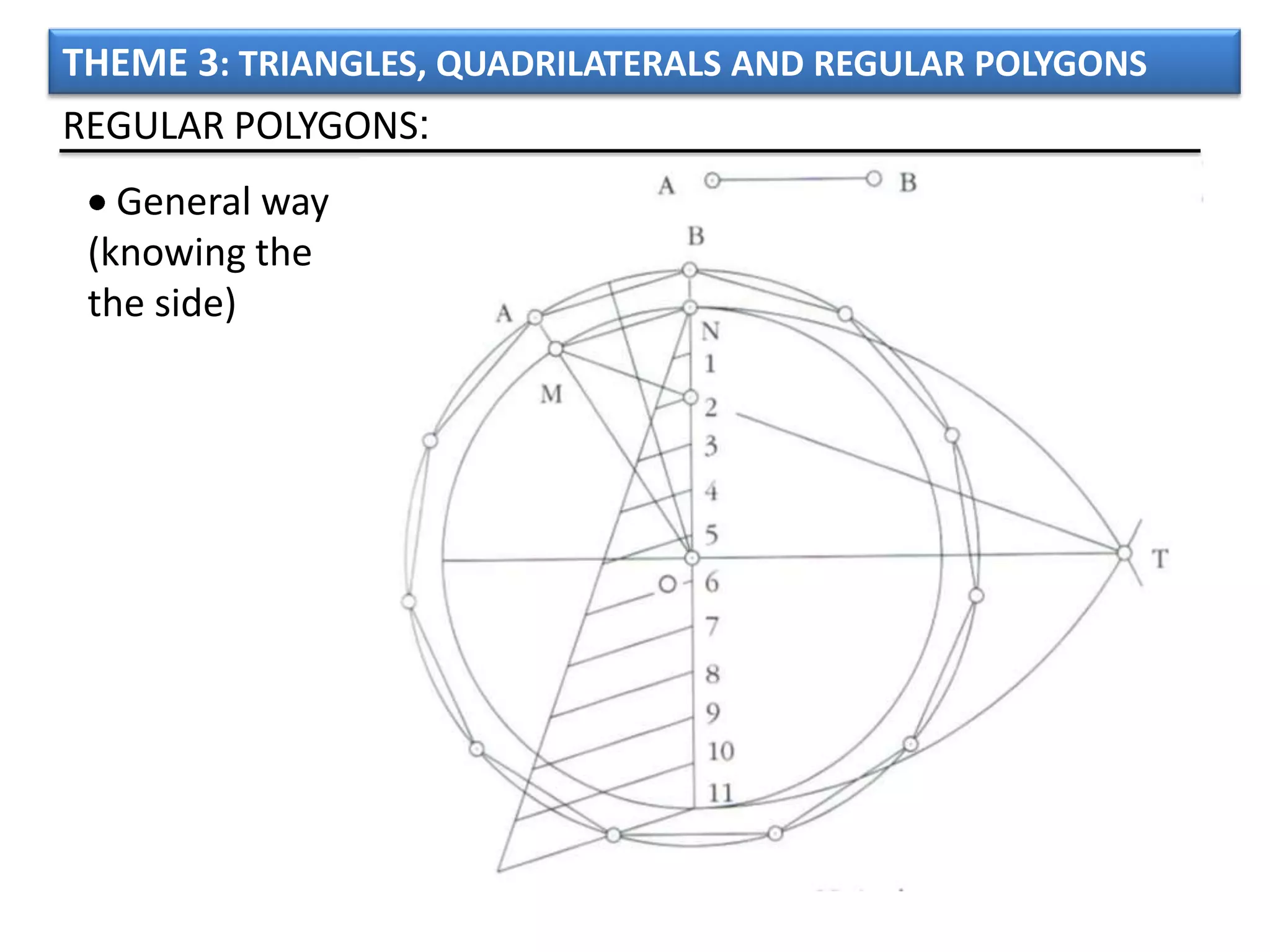
The document discusses basic geometric elements like points, lines, planes, and angles. It defines different types of lines and angles, and how to construct them. It also covers triangles, quadrilaterals, and regular polygons. For triangles, it defines different types and their important points and lines. For quadrilaterals, it categorizes different types like parallelograms, rectangles, and trapezoids. Finally, it discusses regular polygons and how to define them based on equal sides and angles.