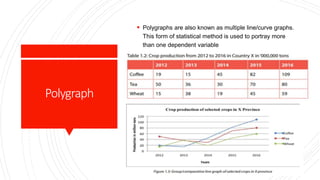
The document outlines the syllabus for a cartography course in BSc Geography, emphasizing the importance and techniques of thematic cartography, including various types of thematic maps and data presentation methods. It covers the definition and significance of thematic maps, diagrammatic data representation using line graphs and climographs, as well as data representation techniques like choropleth, isopleth, and dot maps. Practical assignments include preparing a thematic atlas based on specific themes from any Indian state.