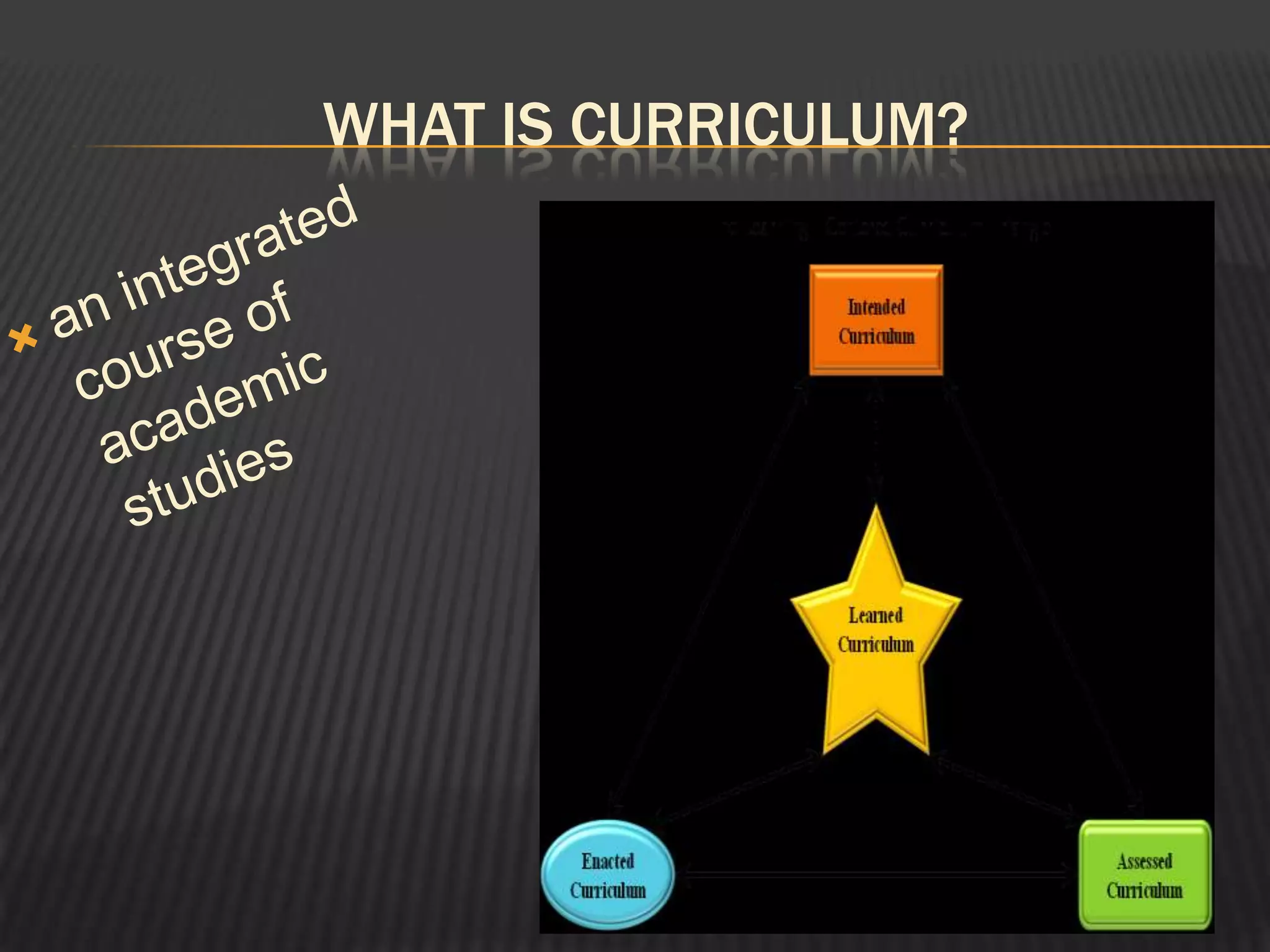
This document discusses the use of technology in K-8 science curriculums. It defines technology and curriculum, and explains that technology should be integrated in a way that supports curricular goals through active engagement, participation, interaction, and real-world connections. It provides guidelines for introducing technology in science teacher preparation and discusses how technology can enhance science learning. Specific examples are given of how technology can significantly change student and teacher roles and increase motivation, collaboration, and use of resources. The document concludes by discussing how to integrate technology into a science classroom.