Embed presentation
Downloaded 39 times



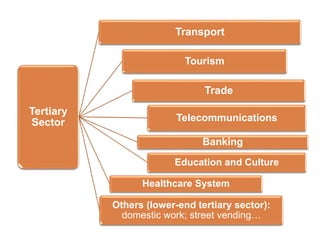


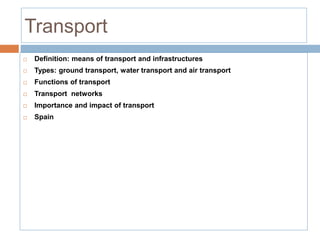



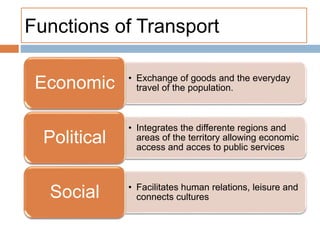
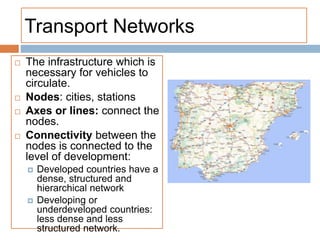
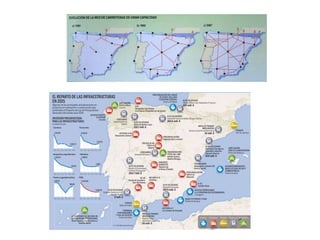
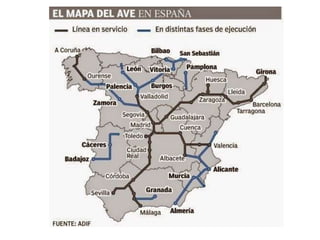
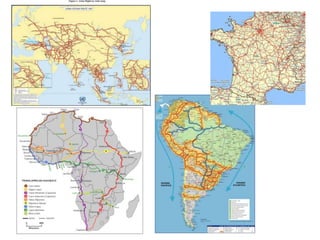
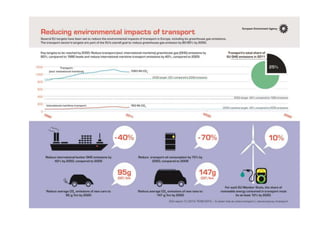

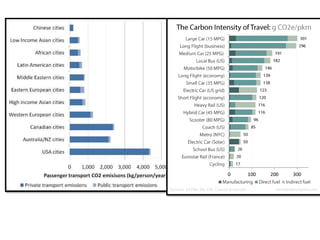


The document provides an overview of the tertiary sector, focusing on services such as transport, tourism, trade, telecommunications, banking, education, and healthcare. It discusses the characteristics, classification, and types of transport, including ground, water, and air transport, as well as its functions and the impact on economic and social connectivity. The text also highlights the varying levels of transport network development between developed and developing countries.




















