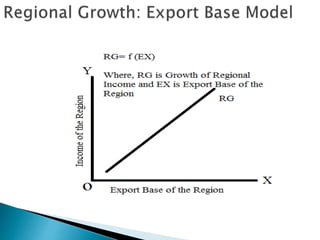
This document discusses Douglas North's export-base theory of regional economic growth. It states that North believed regions are open and interconnected, with goods and services flowing between them, and that a region's growth depends on the expansion and success of its export sector. Increased exports lead to increased regional income, production capacity, and overall economic activity. The pillars of the export-base model are that a region shares a common export base and its growth is determined by its export sector's performance. Criticisms include that the model gives undue importance to exports over domestic growth potential and ignores issues like tariffs and government policies.