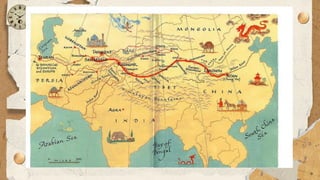
La globalización es un proceso que conecta el mundo a través del comercio, la tecnología y la cultura, promoviendo interacciones y dependencia económica entre regiones. Incluye aspectos como la globalización social, económica, cultural, ecológica y política, impulsada por avances tecnológicos y liberalización del comercio. Sin embargo, también conlleva desventajas como desempleo, degradación ambiental y la pérdida de identidades culturales locales.