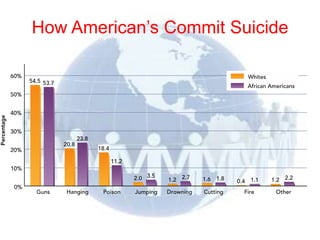
The document provides an overview of key concepts in sociology. It discusses (1) the sociological perspective which looks at how social factors influence individual behavior, (2) key founders of sociology including Auguste Comte, Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, and Max Weber, and (3) goals and methods of sociology as a social science.