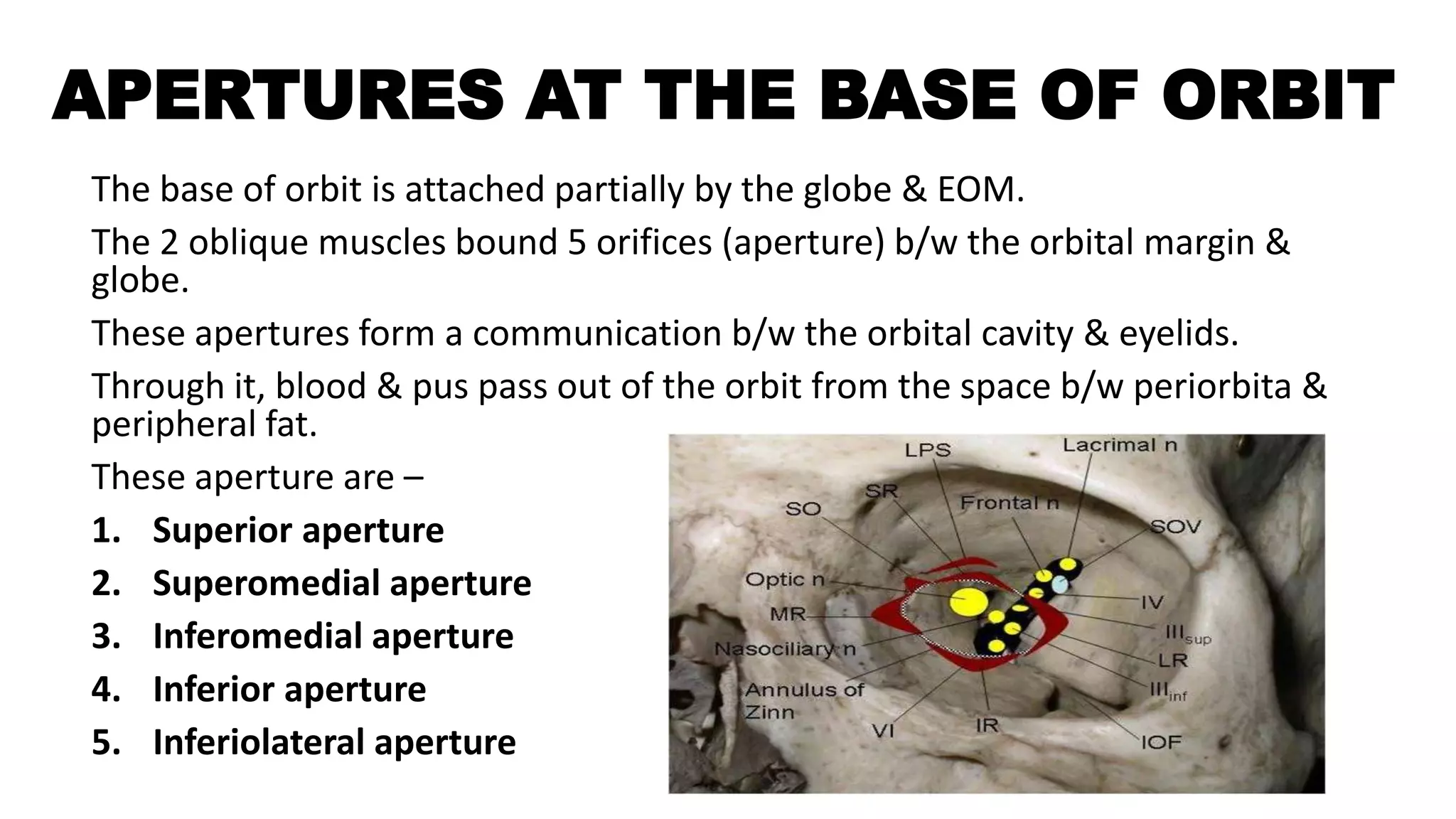
The orbit is a pyramid-shaped cavity in the skull that houses the eyeball and surrounding structures. It is formed by 7 bones and has 4 walls - medial, lateral, roof and floor. The orbit contains the eyeball, extraocular muscles, nerves, vessels, fat and fascia. At the back of the orbit are the optic canal and superior orbital fissure, which transmit nerves and vessels to and from the orbit. The base of the orbit has openings that allow communication between the orbital and eyelid spaces.
![CONTENTS
• Introduction [size, shape, relations]
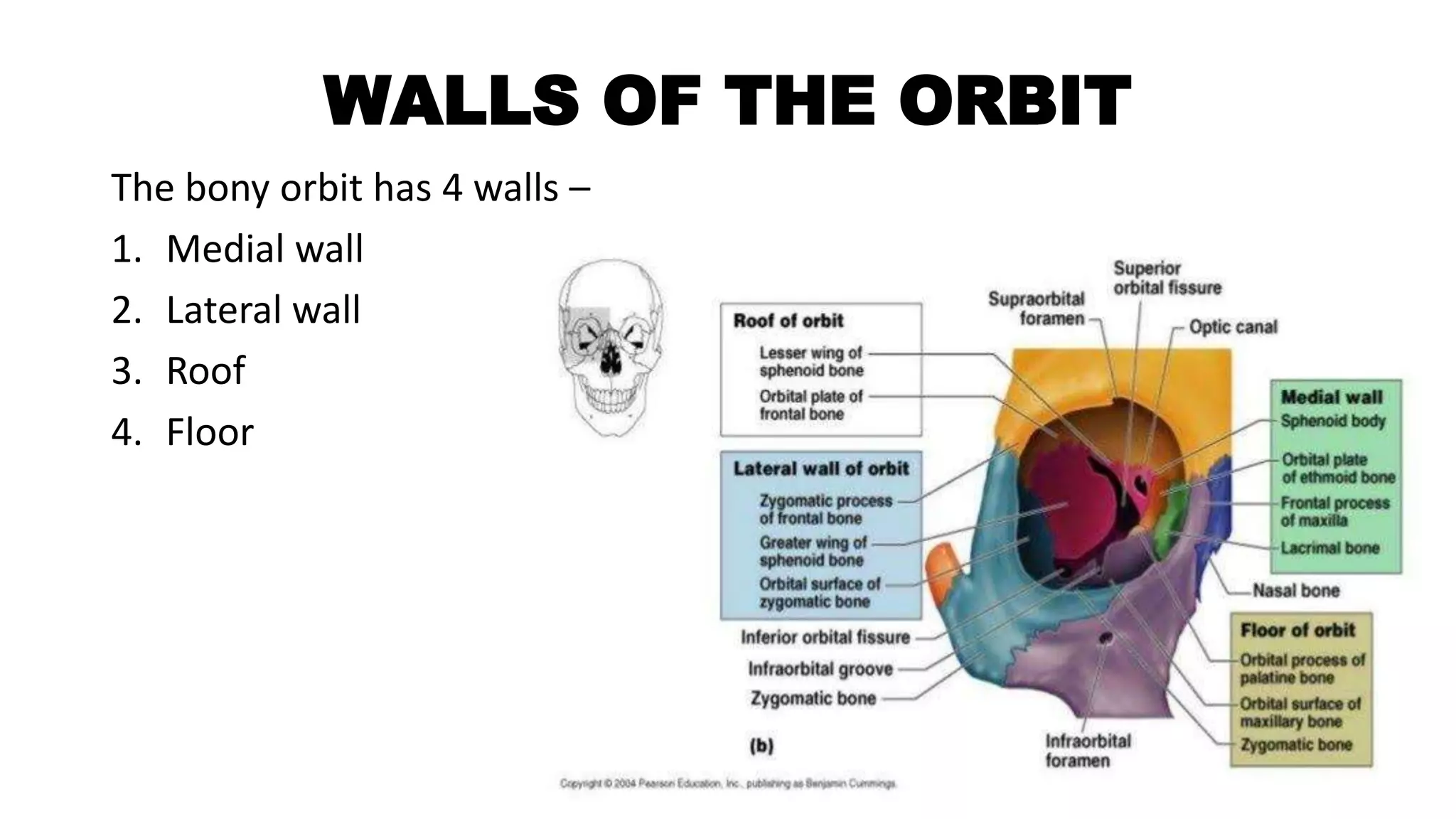
• Walls of orbit
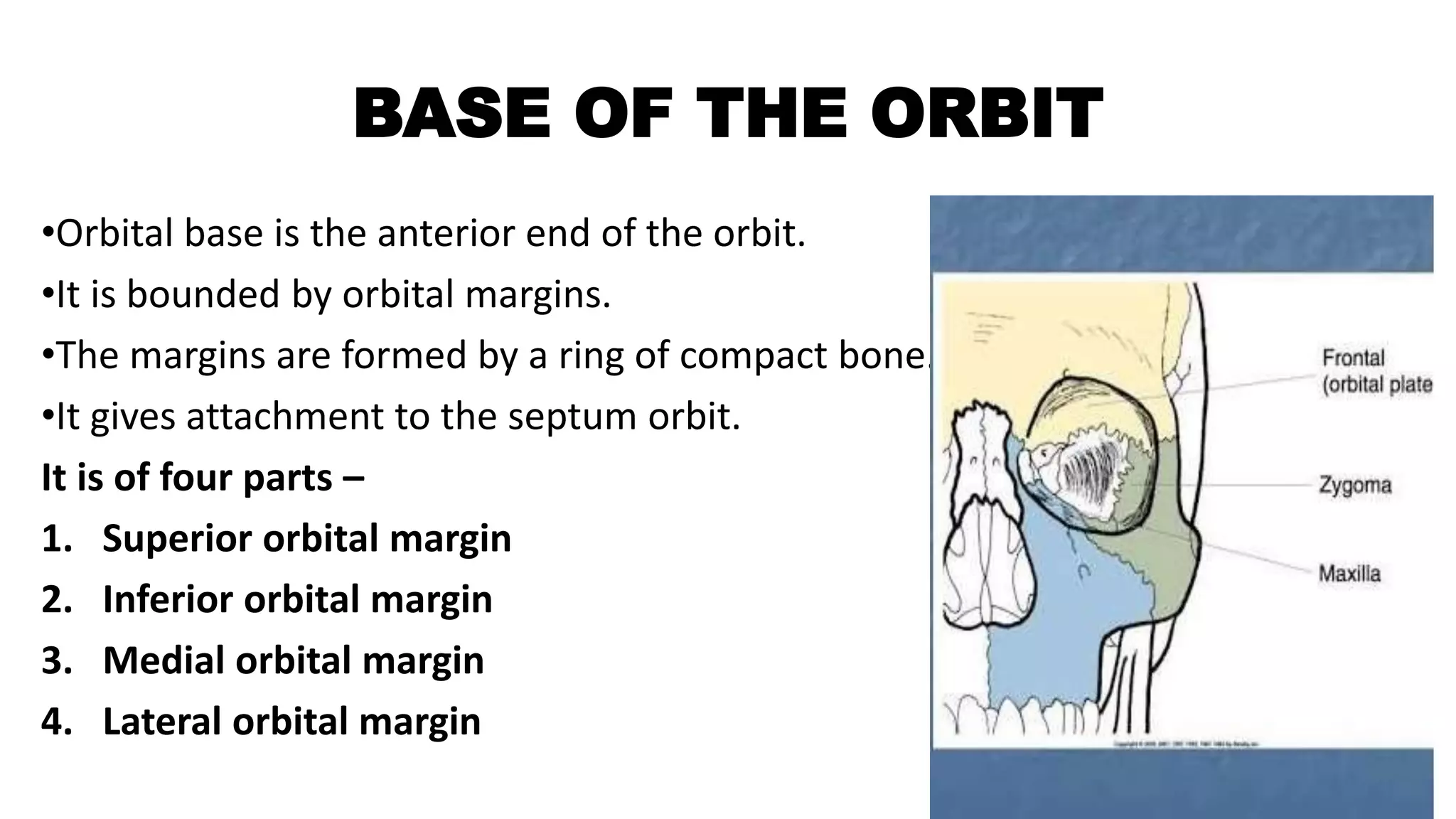
• Base or orbit
• Apex of orbit
• Periorbita
• Orbital fascia
• Fascia bulbi
• Orbital fat and reticular tissue
• Aperture at the base of the orbit
• Surgical space in the orbit
• Contents of the orbit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-2-2048.jpg)
![INTRODUCTION
The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into
the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a
base, an apex and four walls.[4]
Each orbit is formed by seven bones –
1) Frontal bone
2) Ethmoidal bone
3) Lacrimal bone
4) Palatine bone
5) Maxilla bone
6) Zygomatic bone
7) Sphenoid bone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-3-2048.jpg)

![• The medial walls of two orbit are parallel to each other.
• They are in contact with the sphenoid bone & ethmoid bone.
• The depth of the orbits is 42mm along to medial wall & 50mm
along the lateral wall.
• Base of orbit is 40 mm in width & 35 mm in height.
• The intra orbital width [b/w the medial margin of two orbit] is
25mm.
• The extra orbital width [b/w the lateral margin of two orbit] is
100mm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-5-2048.jpg)
![MEDIAL WALL
The medial wall is formed primarily by the orbital plate of ethmoid, as well as
contributions from the frontal process of maxilla, the lacrimal bone, and a small part of the
body of the sphenoid. It is the thinnest wall of the orbit, evidenced by pneumatized
ethmoidal cells.[7]
The anterior part of medial wall – lacrimal sac fossa
Lacrimal fossa attached, inferiorly - naso-lacrimal canal.
anteriorly - anterior lacrimal crest
posteriorly – posterior lacrimal crest.
Behind the posterior lacrimal crest – fibres of orbicularis muscle, orbital septum
and medial rectus muscle ligaments.
Medial part of medial wall – anterior ethmoidal sinus, middle ethmoidal sinus and
posterior ethmoidal sinus and sphenoid sinus.
In it, SO & MR muscle, b/w two muscles situated anterior and posterior ethmoidal
nerve, ophthalmic artery and infratrochlear nerve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-7-2048.jpg)

![SUPERIOR WALL [ROOF]
It is triangular in shape.
The roof (superior wall) is formed primarily by the orbital plate frontal
bone, and also the lesser wing of sphenoid near the apex of the orbit.
The orbital surface presents medially by trochlear fovea and laterally by
lacrimal fossa.[7]
Above the roof – cerebrum and meninges.
Below the roof – periorbita, frontal nerves, LPS muscle, superior rectus,
lacrimal gland, trochlear nerve.
Antero-lateral part of the roof has a fossa, called lacrimal gland fossa.
b/w medial wall and roof has a superior oblique fossa, ethmoidal sinus.
b/w lateral wall and roof has a superior orbital fissure [space].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![INFERIOR WALL [FLOOR]
It is triangular in shape.
It is formed by 3 bones – medially maxilla bone, laterally zygomatic bone
and posteriorly palatine bone.
Above the floor – inferior rectus muscle, inferior oblique muscle.
Below the floor – maxillary sinus and palatine sinus.
Posterior part – infra orbital foramen [hole] – transmits, infra orbital
artery, infra orbital vein [connects to facial vein].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-10-2048.jpg)


![APEX OF THE ORBIT
Orbital apex is the posterior end of the orbit.
The apex has two orifices (opening)– optical canal & superior orbital
fissure [in sphenoid bone].
OPTICAL CANAL –
• It connects the orbit to the middle cranial fossa.
• It transmits the optic nerve & ophthalmic artery.
• Its normal dimensions, attained by the age of 4-5 years.
• Its average length is 6-11 mm.
• Tumours may lead to unilateral enlargement of optic canal, detected by X
ray.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-14-2048.jpg)




![ORBITAL FASCIA
•This part has head of fascia bulbi, muscular sheaths, inter-muscular
septum and extra ocular muscles ligaments.
• It is a thin connective tissue membrane lining the various intra orbital
structure.
•In the orbit, the surrounding fascia allows for smooth rotation and
protects the orbital contents. If excessive tissue accumulates behind
the ocular globe, the eye can protrude, or become exophthalmic.[4]
•Graves disease may also cause axial protrusion of the eye, known
as Graves' ophthalmopathy, due to build up of extracellular
matrix proteins and fibrosis in the rectus muscles. Development of
Graves' ophthalmopathy may be independent of thyroid function.[10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorbit-230614045557-5ba5f7fd/75/THE-ORBIT-pptx-19-2048.jpg)